Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
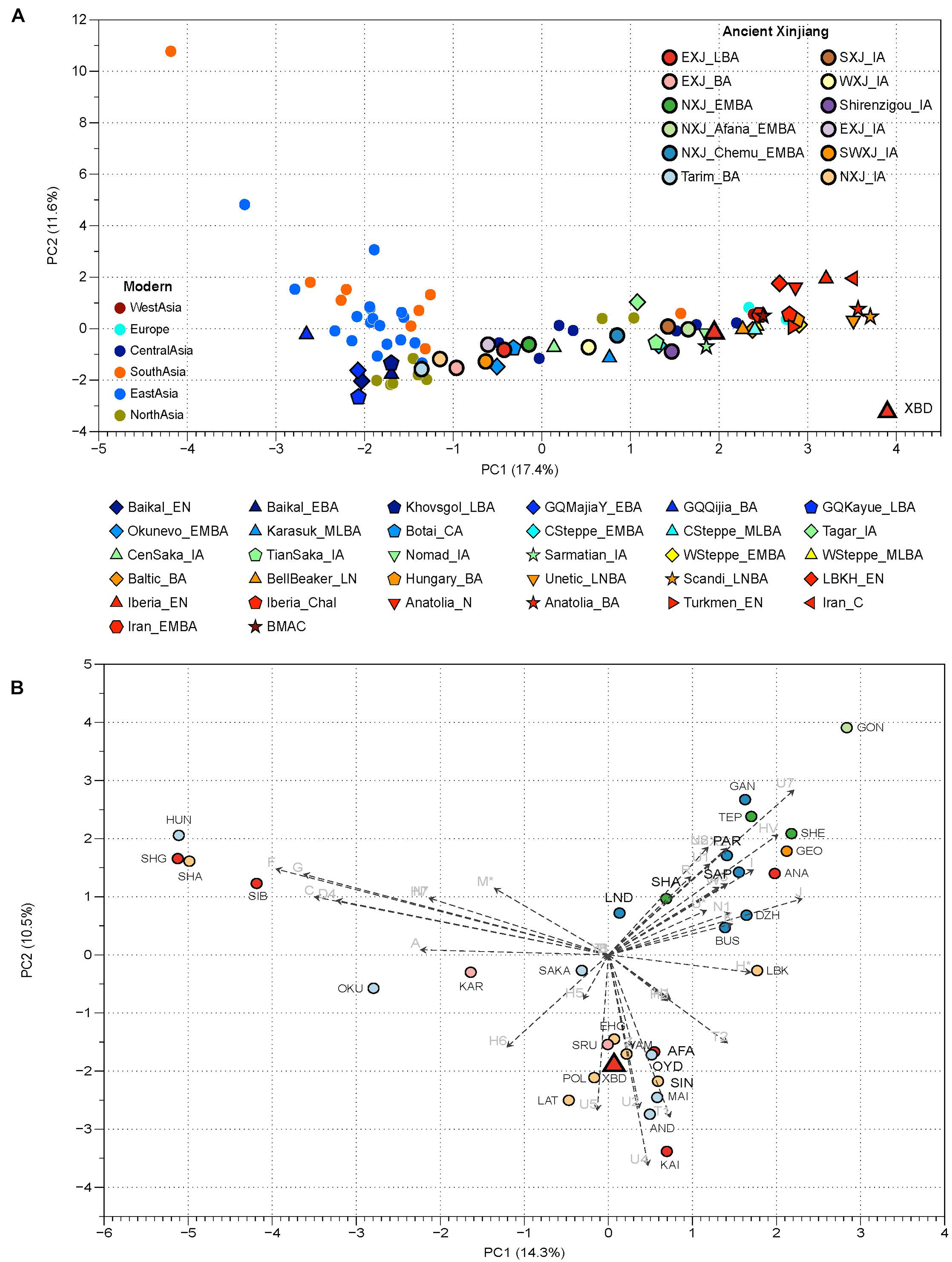
The Shirenzigou culture, dating from approximately 410 BCE to 190 BCE, is an archaeological culture located in Barkol County, east of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang, China. This site is significant for its evidence of horseback riding and mounted archery by the fourth century BCE. Genetic studies of individuals from the Iron Age at this site have revealed a balanced admixture of West and East Eurasian genetic components, linking the population to the Yamnaya and Northeast Asian lineages. This genetic data suggests ties to the Afanasievo culture, which may have been Indo-European-speaking and potentially connected to the origins of the Tocharians. The Shirenzigou culture also exhibits cultural affinities with neighboring Yanbulake and Pazyryk cultures, with evidence of trade, such as imported beads from China. These findings highlight the site's importance in understanding the movement of peoples and cultural exchanges along China's northwest frontier during the Iron Age.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Shirenzigou culture
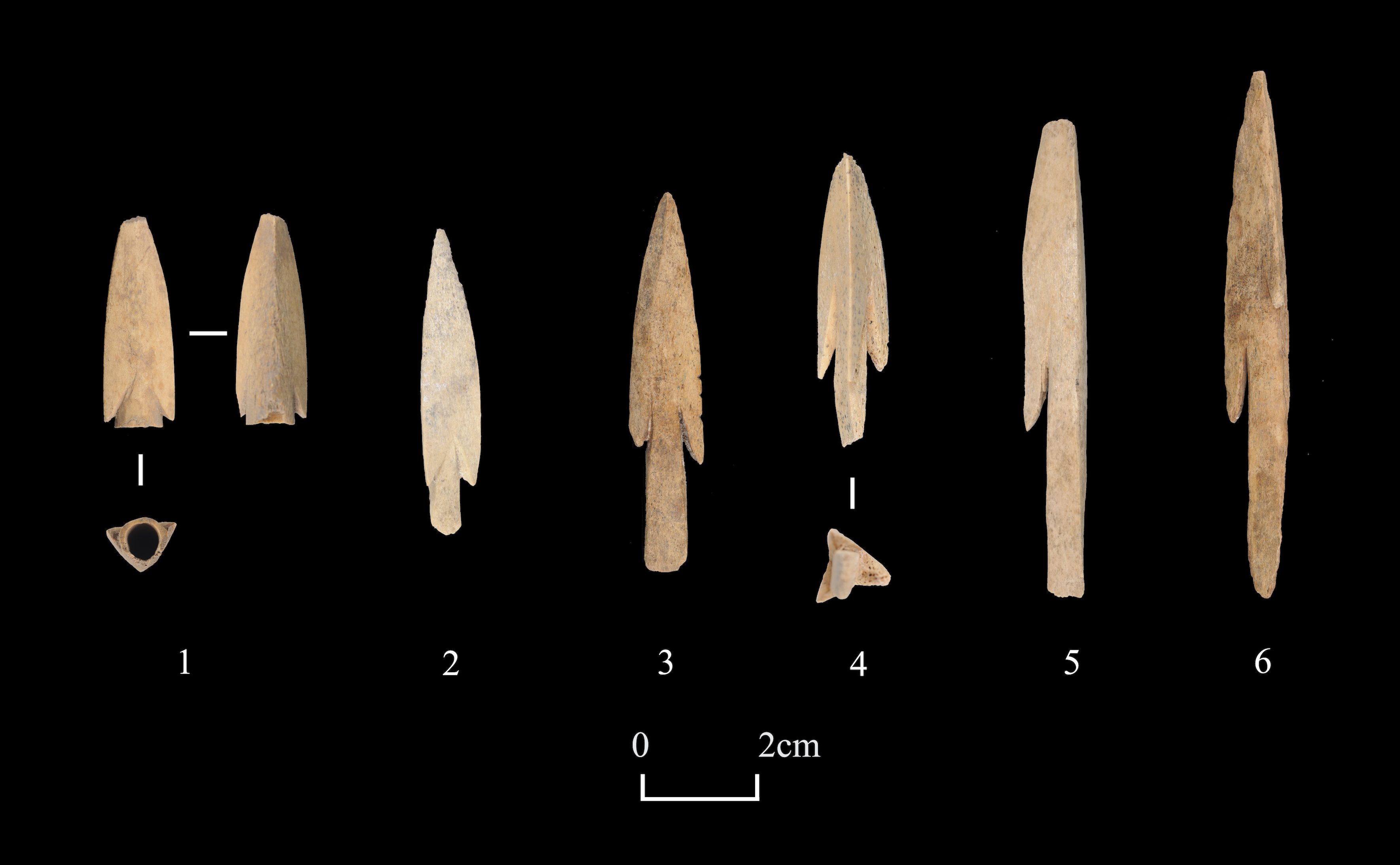

Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- China
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in China

Ancient Linzi
Ancient city with defensive walls and tombs.
Shengle
Ruins of Shengle, ancient capital city
Liye Ancient City
Ancient city with Qin dynasty artifacts
Liye
Ancient town with Qin dynasty relics
Tanheli
Bronze Age cultural center in Hunan

Daxinzhuang
Shang urban center with oracle bones