Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
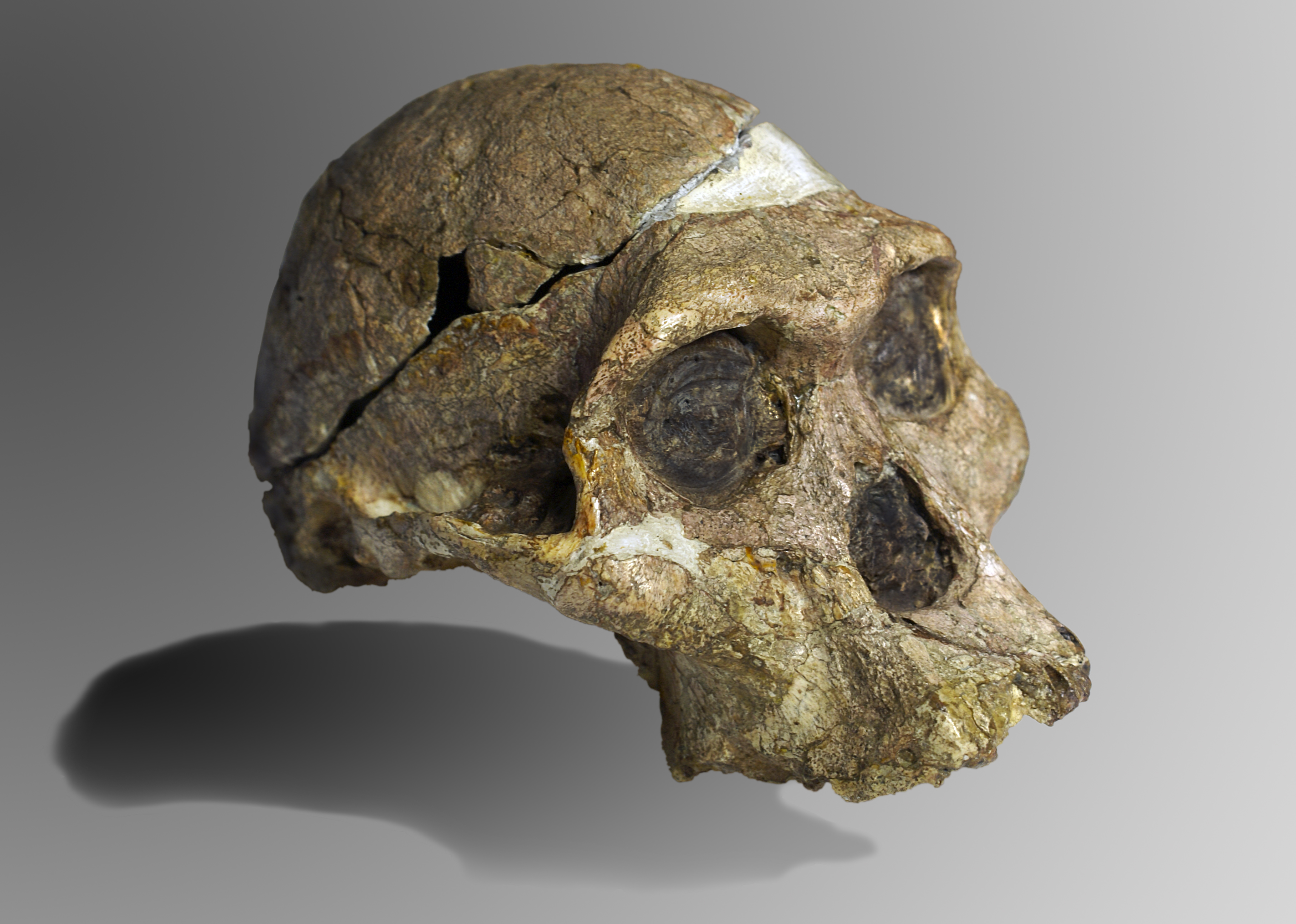
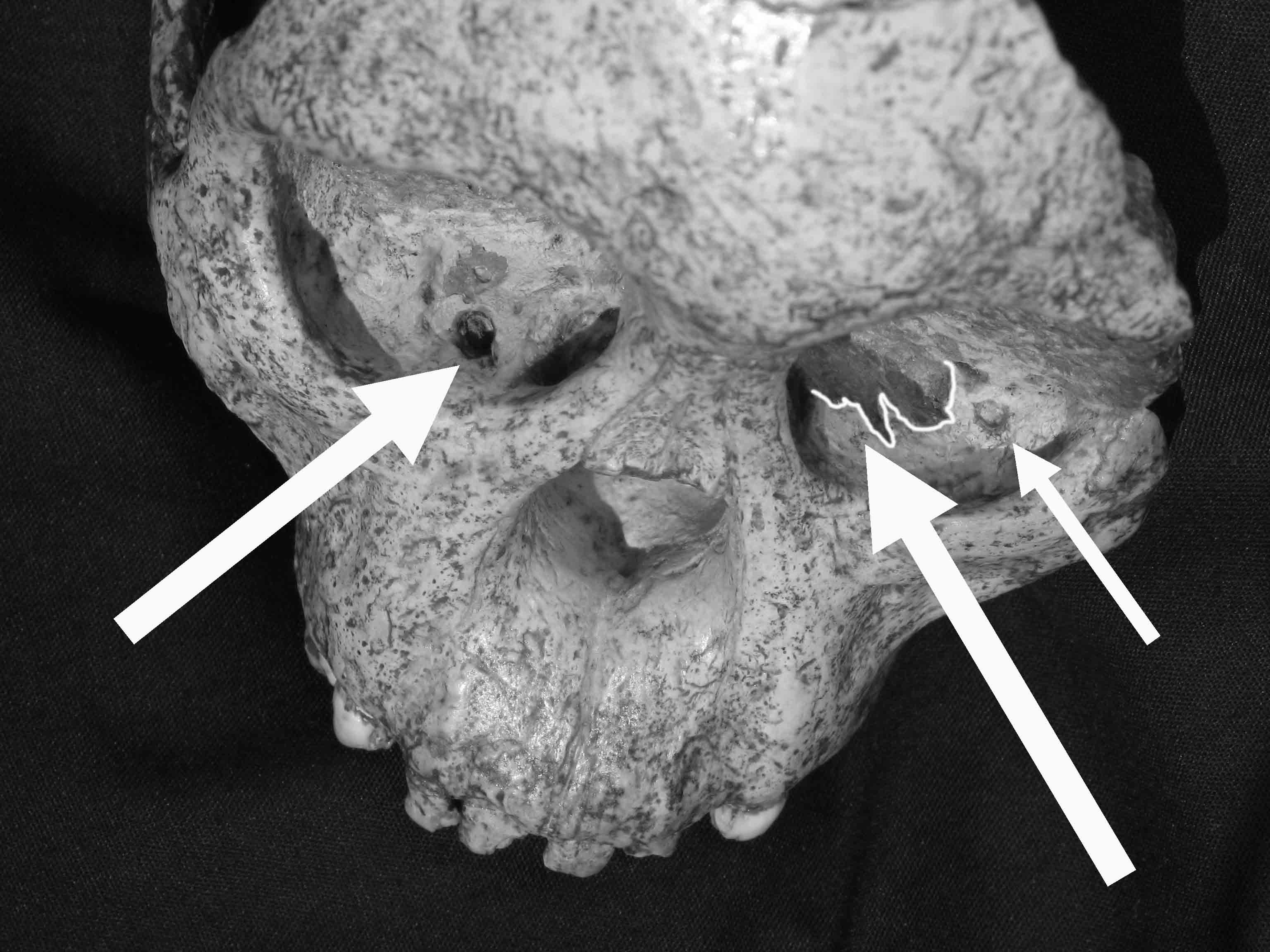
The Malapa fossil site, located in the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site in South Africa, is a significant archaeological discovery providing insight into early human ancestors. The site is home to one of the most complete assemblages of early hominid fossils, dating back approximately 1.977 million years ago. These fossils, preserved in calcified clastic sediments, include partial skeletons of a juvenile and an adult female, which were identified as a new species, Australopithecus sediba. The site also contains remains of extinct animals, such as a sabre-toothed cat and antelopes, indicating a rich biodiversity during that period. The Malapa site contributes crucial data on the transition between Australopithecus africanus and Homo habilis or Homo erectus, offering valuable insights into our evolutionary history.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Malapa Fossil Site, Cradle of Humankind



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Environmental and Natural Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- South Africa
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in South Africa

Cooper's Cave
Fossil-bearing breccia-filled dolomitic caves.

Stadsaal Caves
Sandstone caves with San rock art.

Border Cave
Rock shelter with long prehistoric sequence.
Rose Cottage Cave
Multi-layered Middle and Later Stone Age cave
Wonderwerk Cave
Ancient cave with extensive archaeological deposits
Taung
Early hominid fossil site in limestone quarry
