Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Tamarindito is a significant archaeological site located in the Petexbatún region of the Petén department in Guatemala. As a city of the ancient Maya civilization, Tamarindito was strategically situated on a high hill escarpment, featuring a rich array of structures including palaces, temples, and agricultural terraces. Initially flourishing as the capital of the region during the Early Classic period, it later succumbed to the dominance of Dos Pilas, a rival city. Tamarindito regained prominence in the 8th century by defeating Dos Pilas, though this victory was followed by a period of chaos and eventual abandonment by the 9th century. The site offers insights into the socio-political dynamics and agricultural practices of the Maya, with extensive remains of residential areas, ceremonial platforms, and a notable royal tomb.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Tamarindito
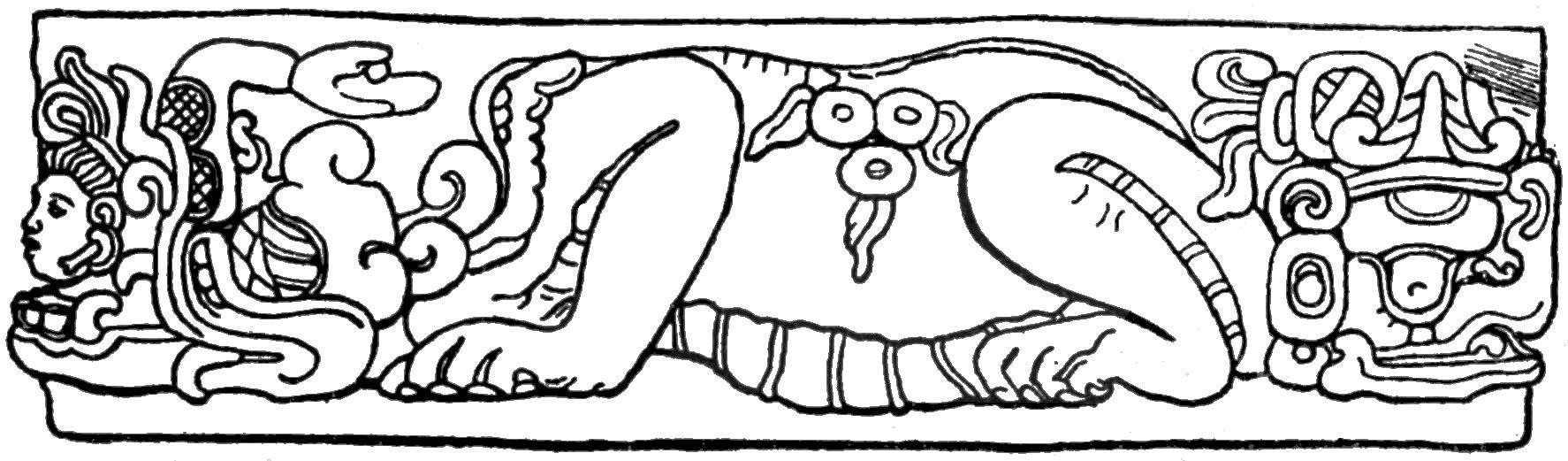
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Water Management Features
Public and Civic Structures
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Agricultural and Land Use Features
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Transportation and Communication Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Guatemala
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Guatemala

La Corona
Ancient Maya court residence with artistic reliefs
Naachtun
Maya city with pyramids and stelae
Motul de San José
Significant Maya civic-ceremonial center.

El Chal
Pre-Columbian Maya site with ceremonial plazas
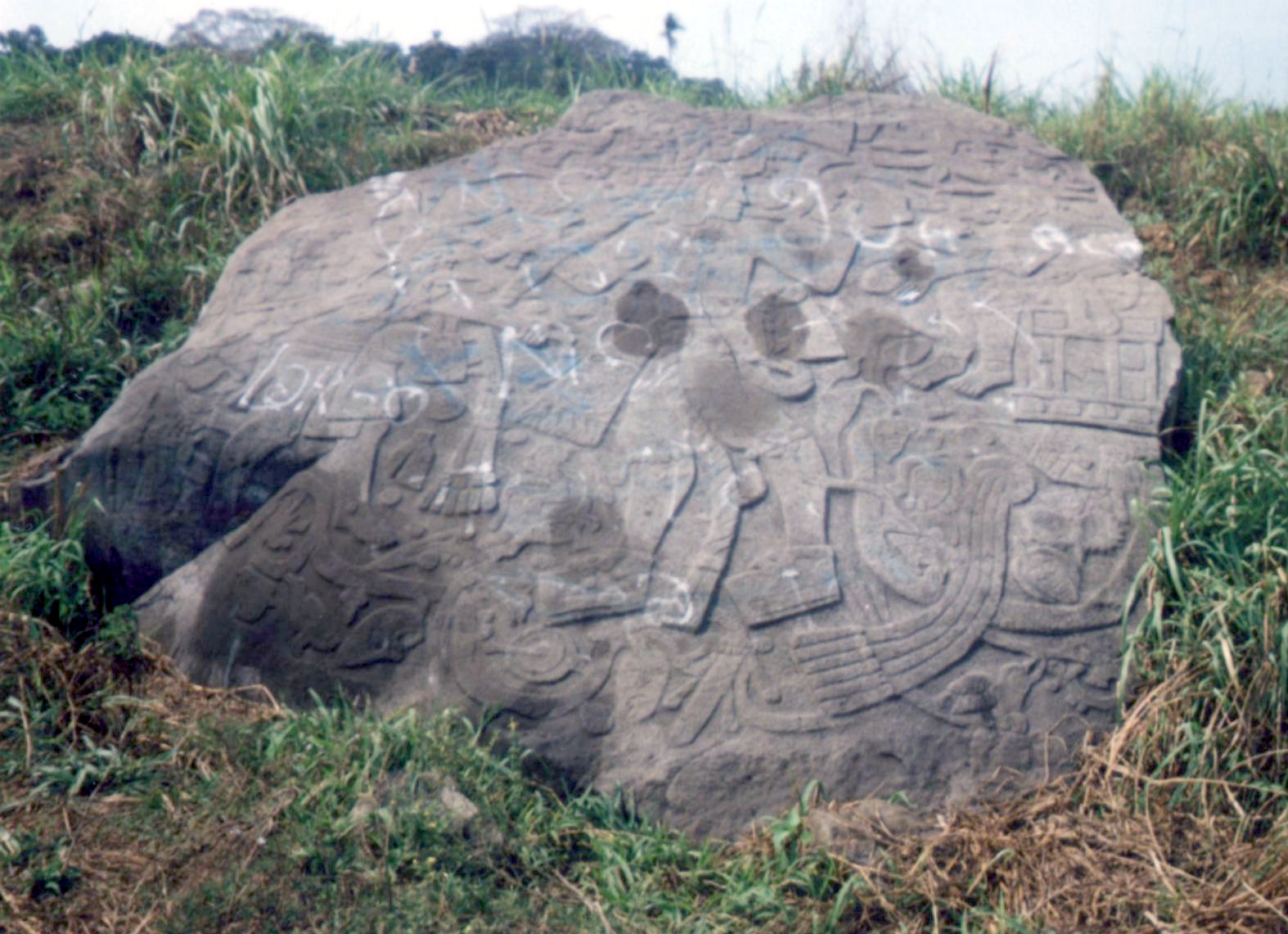

Bilbao (Mesoamerican site)
Mesoamerican site with Classic Period sculptures
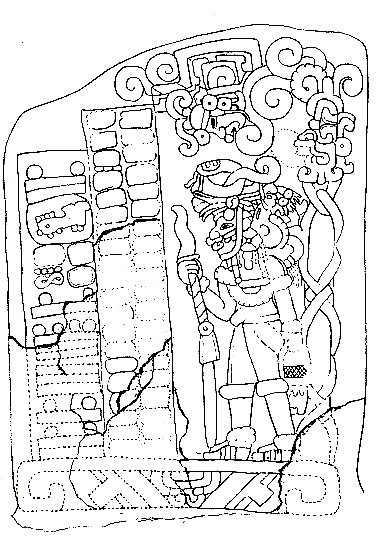
Cotzumalhuapa
Extensive Late Classic Maya city zone