Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
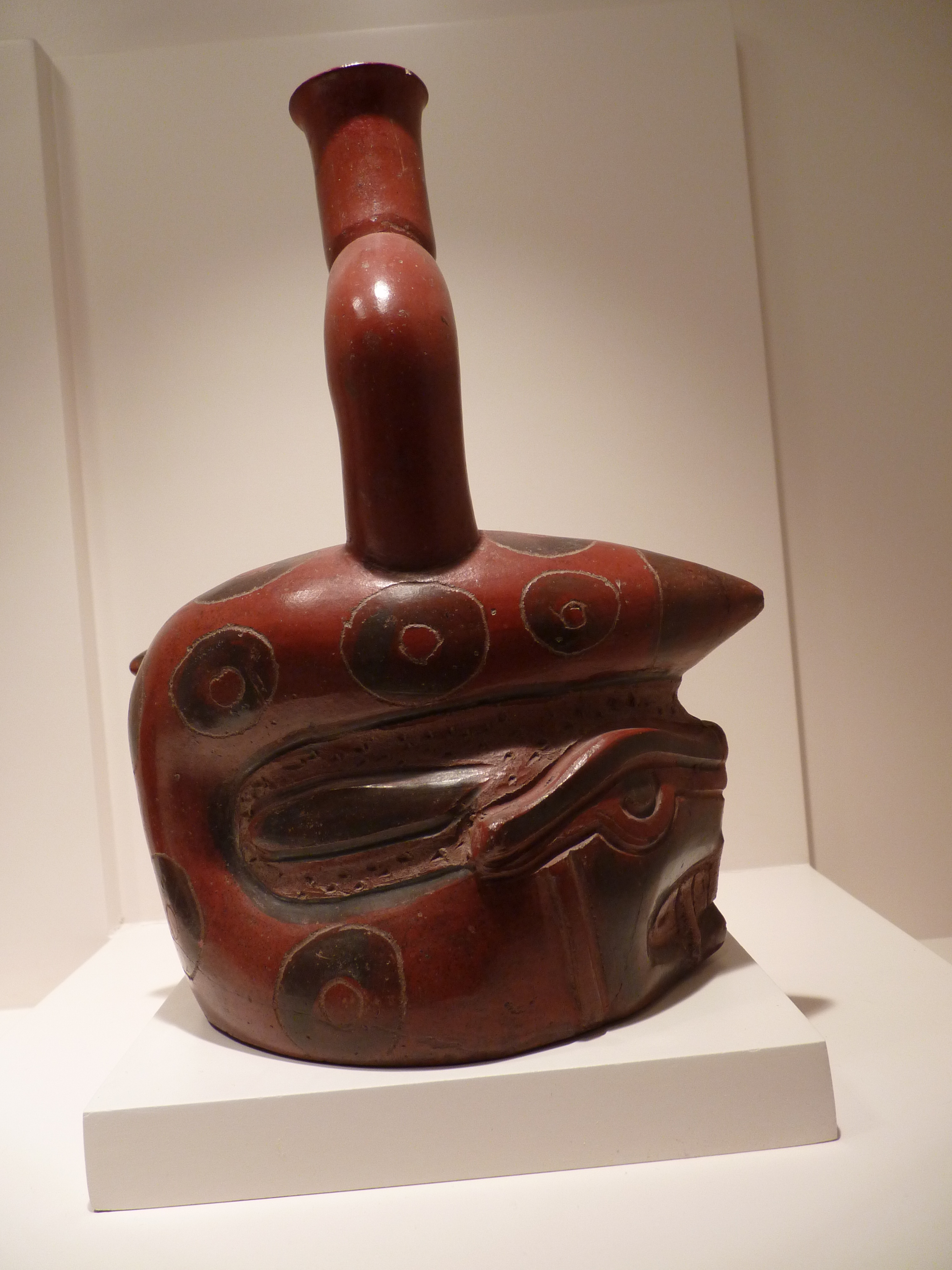
The El Brujo Archaeological Complex, located in the Chicama Valley of Peru, is a significant site showcasing the evolution of ancient cultures from preceramic times through the Moche period and beyond. The complex features monumental stepped pyramids, known as huacas, including Huaca Prieta, Huaca Cao Viejo, and Huaca Cortada, which served religious and ceremonial purposes. Notably, the site is renowned for the discovery of the Señora de Cao, providing evidence of a female ruler during the Moche era. The site's rich polychrome reliefs and murals depict the artistic achievements of the Moche culture. Although the site experienced decline post-Moche, it remained a ceremonial and funerary area through subsequent cultural phases. The discovery of a 17th-century letter reveals linguistic connections to the Quingnam language, offering insights into historical communication practices.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at El Brujo
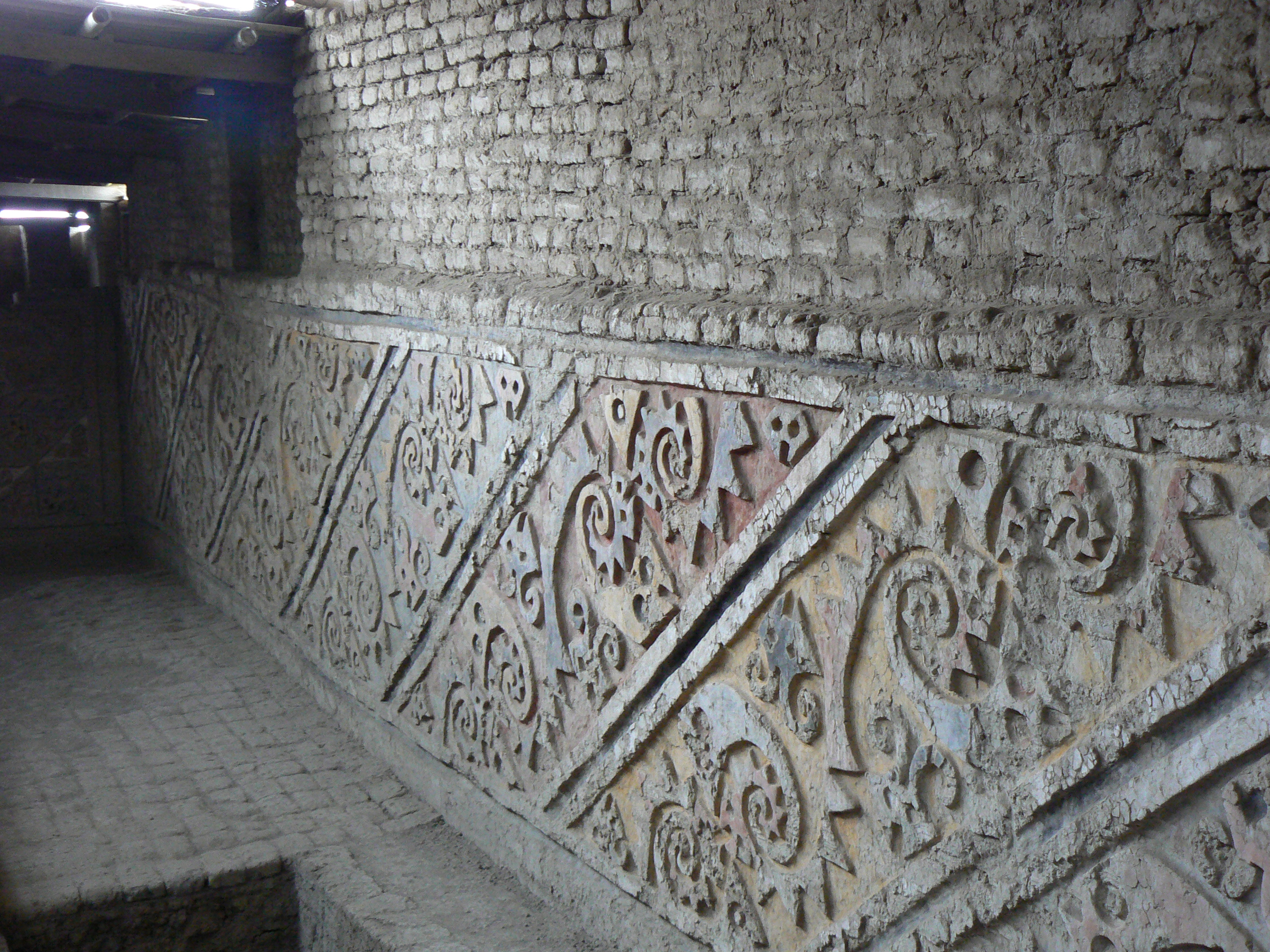
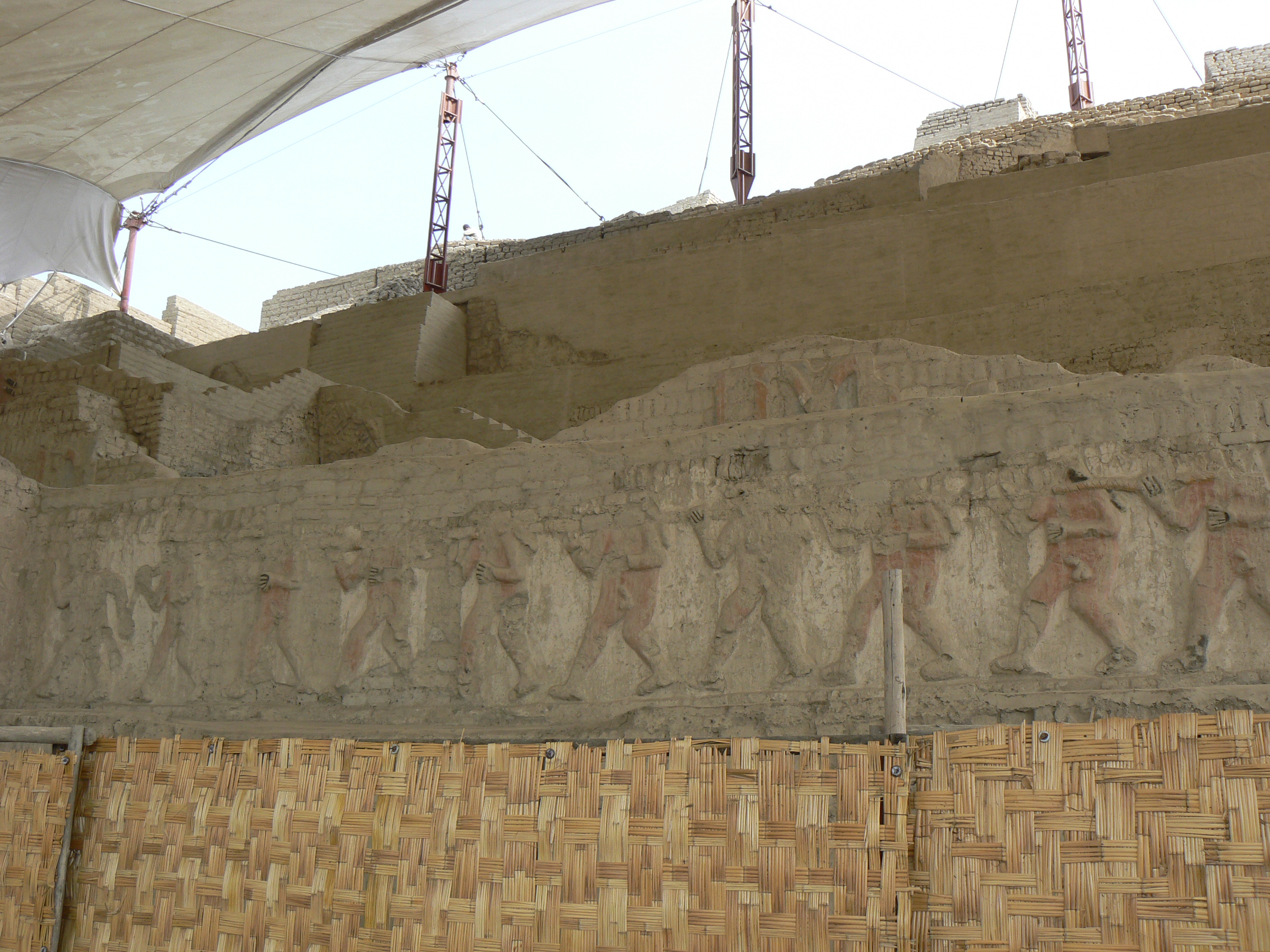



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- La Libertad Region
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in La Libertad Region
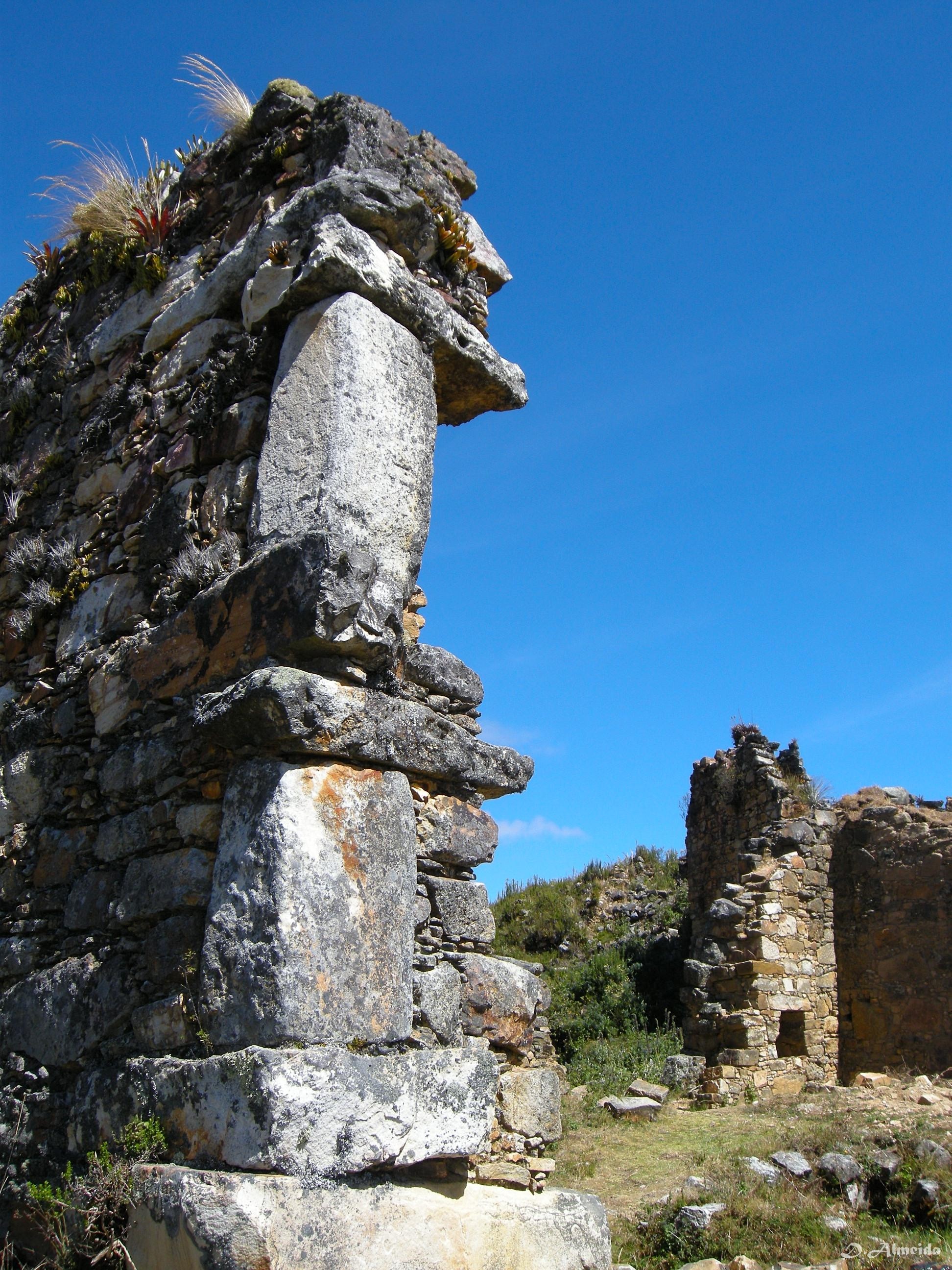

Marcahuamachuco
Pre-Incan ruins with defensive stone walls.

Pacatnamu
Ancient ceremonial center with defensive walls.
Pirca Pirca, La Libertad
Hilltop site with ceremonial and strategic structures

Huaca Prieta
Prehistoric coastal settlement with ceremonial mound
San Jose de Moro
Moche ceremonial funerary complex in Peru

Caballo Muerto
Ancient mound complex with ceremonial platforms