Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
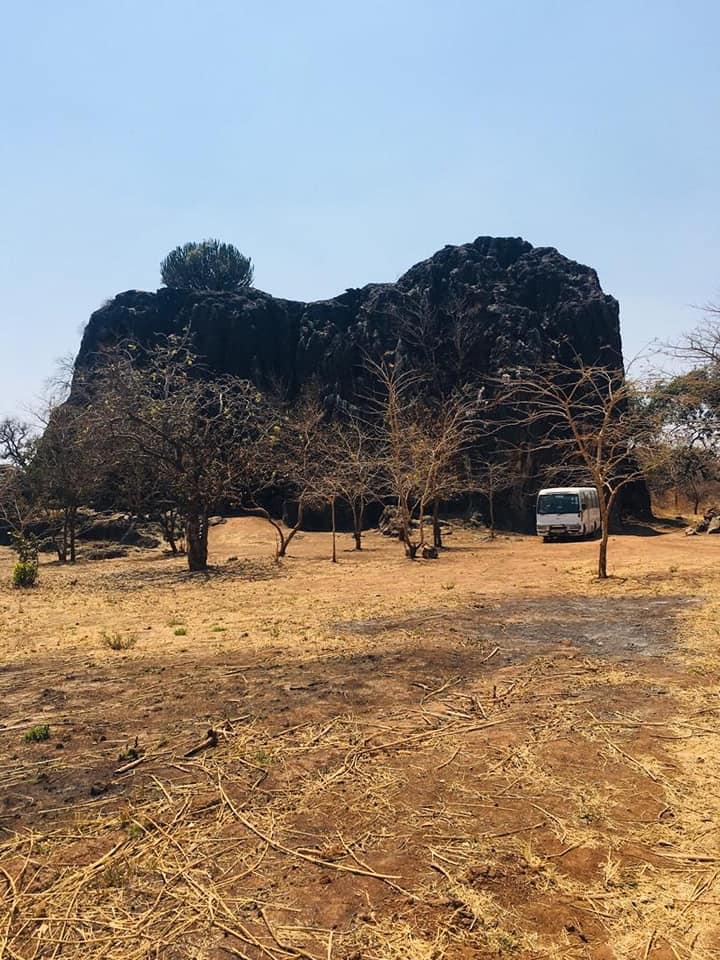
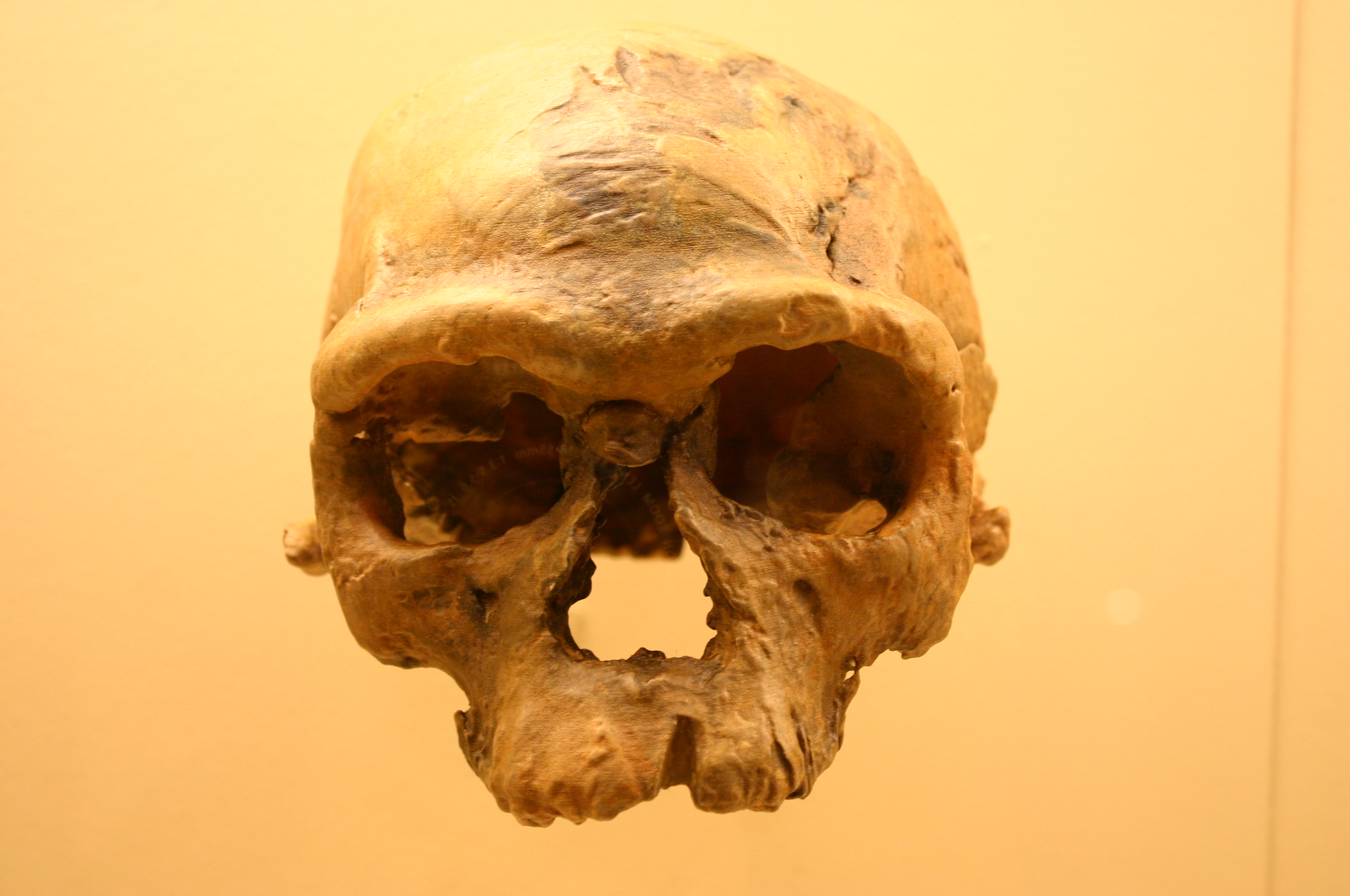
The Gwisho hot-springs in Lochinvar National Park, Zambia, is a significant archaeological site, renowned for its well-preserved animal and plant remains. Excavations have revealed a rich array of faunal remains and quartz tools, offering insights into the region's prehistoric economic and technological practices. Radiocarbon dating places human activity at the site between 2750 and 2340 BCE, indicating settlements dating back to the Neolithic and Chalcolithic periods. The presence of organic remains, wooden artifacts, and animal bones suggests a subsistence strategy reliant on hunting, trapping, and possibly fishing. The site's stratigraphy includes layers of sterile soil and rich organic deposits, providing invaluable data on environmental conditions and human adaptation strategies. The Gwisho hot-springs offer a unique window into the lives of early human inhabitants of the Kafue Flats, contributing significantly to our understanding of African prehistory.
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Environmental and Natural Features
Food Production and Processing Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Zambia
- Source
- Wikipedia