Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
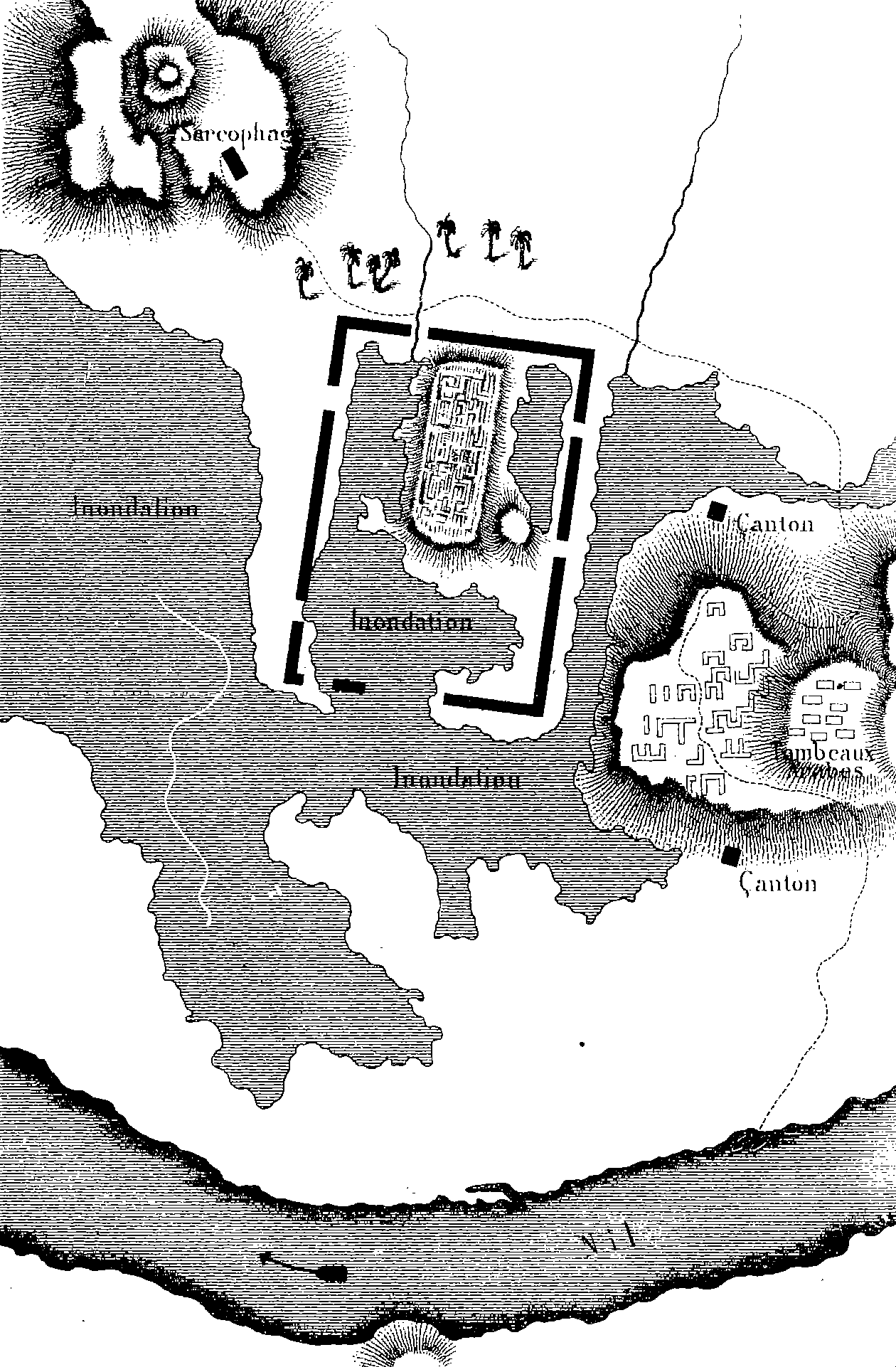
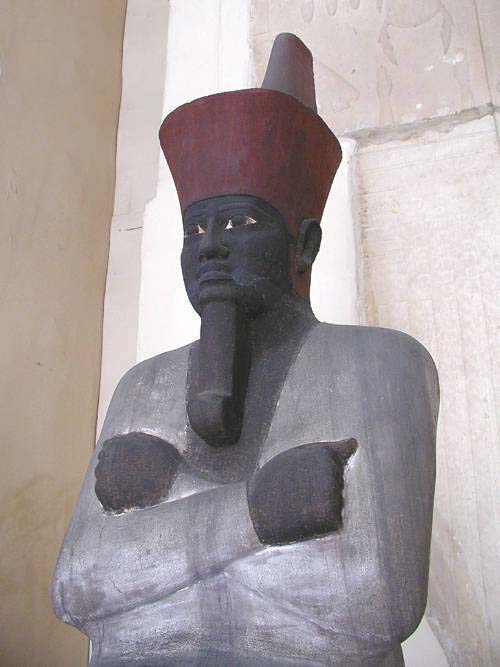
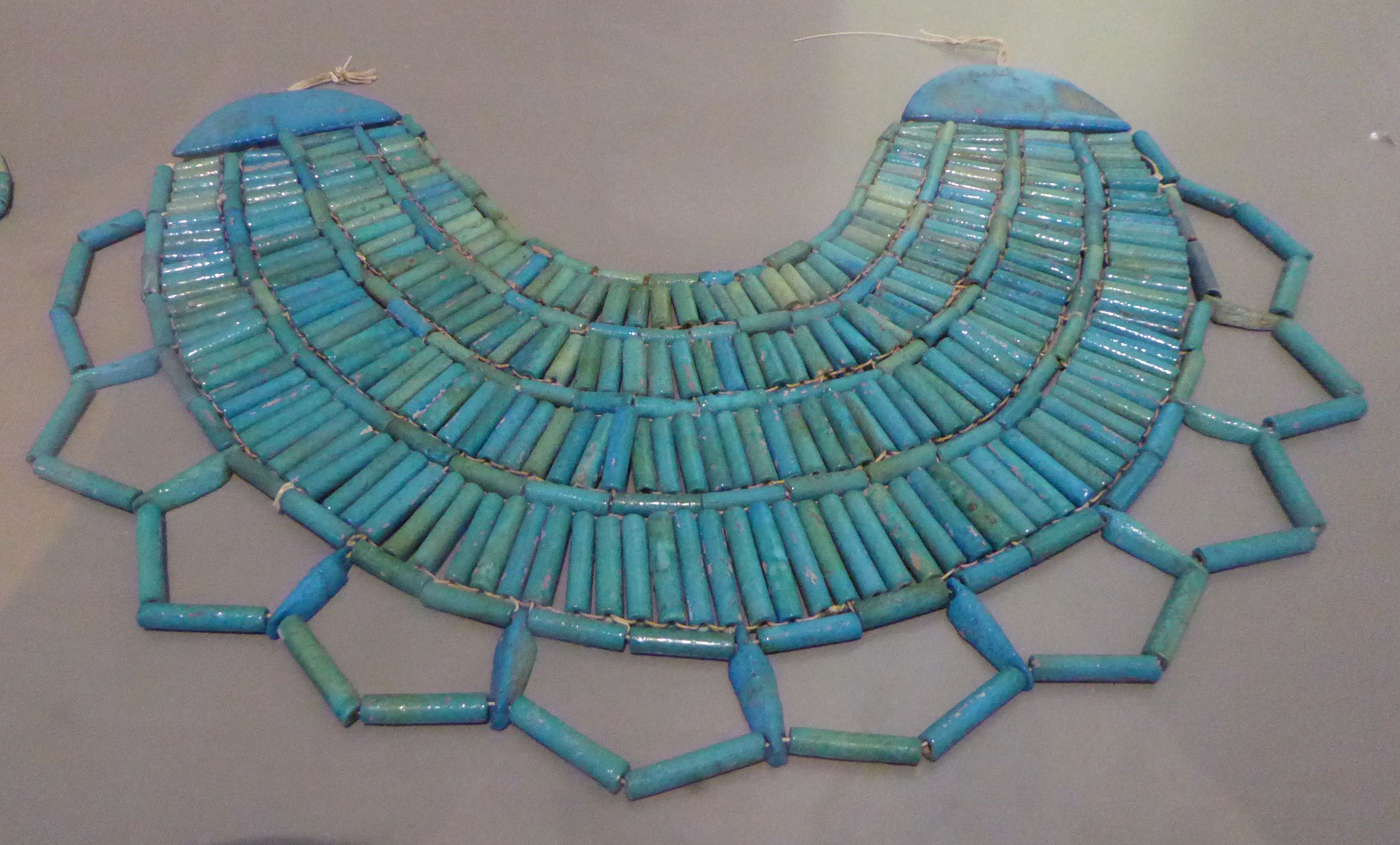
Mendes, known in ancient Egypt as Djedet or Per-Banebdjedet, is an archaeological site located in the eastern Nile Delta, now identified as Tell El-Ruba. It was a prominent city and the capital of the 16th Lower Egyptian nome, and later the capital of Egypt during the 29th Dynasty. Archaeological evidence indicates that Mendes was established as early as the Naqada II period, around 4000 BCE. The city was renowned for its major religious structures, including temples dedicated to the ram deity Banebdjedet and his consort Hatmehit. The site also contains burial structures, such as an Old Kingdom necropolis with over 9,000 interments and a cemetery of sacred rams. The city experienced decline by the first century CE, likely due to changing trade routes and environmental factors. Mendes remains significant for its religious and historical contributions to ancient Egyptian civilization.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Mendes
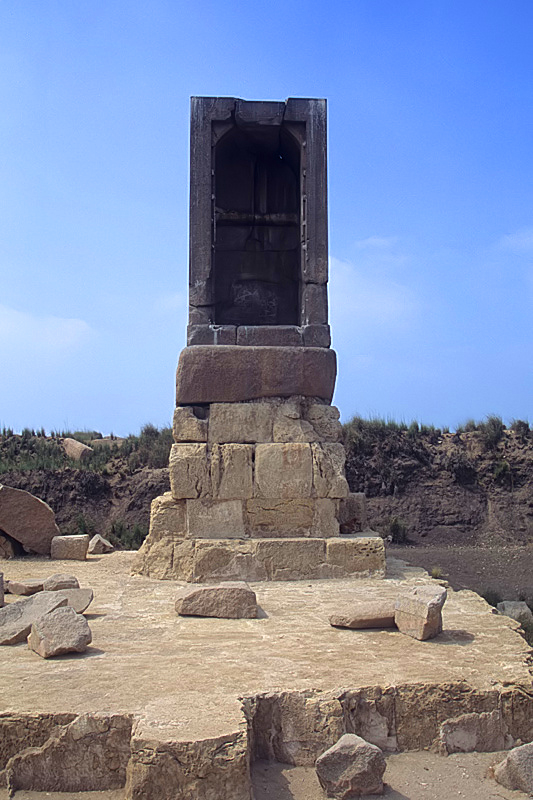
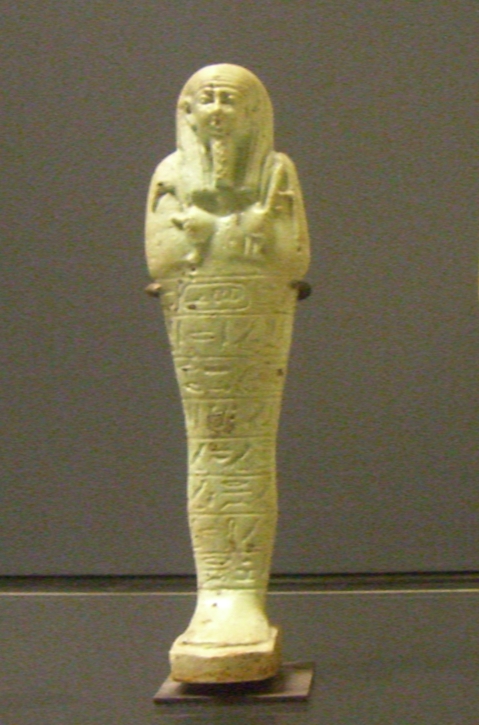


Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Egypt
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Egypt

Edfu
Ancient Egyptian city with temple and settlement.
Sais, Egypt
Ancient Egyptian city with Neolithic origins

Thinis
Ancient Upper Egypt's undiscovered capital city.

Sedment
Ancient village with cemeteries and Christian history.
Elkab
Ancient Egyptian city with temples and tombs.
Elephantine
Island with temples and ancient papyri.