Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Magdala is an ancient site on the shore of the Sea of Galilee, known for its significant archaeological remains from multiple periods. Originally settled during the Hellenistic period, it flourished in the early Roman period, with structures like synagogues from the Second Temple period showcasing its religious importance. The site features a notable carved stone with a menorah, indicating its Jewish heritage. Magdala was destroyed by Romans during the First Jewish-Roman War, but continued to hold significance into the Byzantine era with the establishment of a church attributed to Empress Helena. The discovery of two synagogues from the same period is particularly noteworthy, as such finds are rare in a single site. Today, it is recognized for its historical and religious significance, particularly in connection to Mary Magdalene.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Magdala
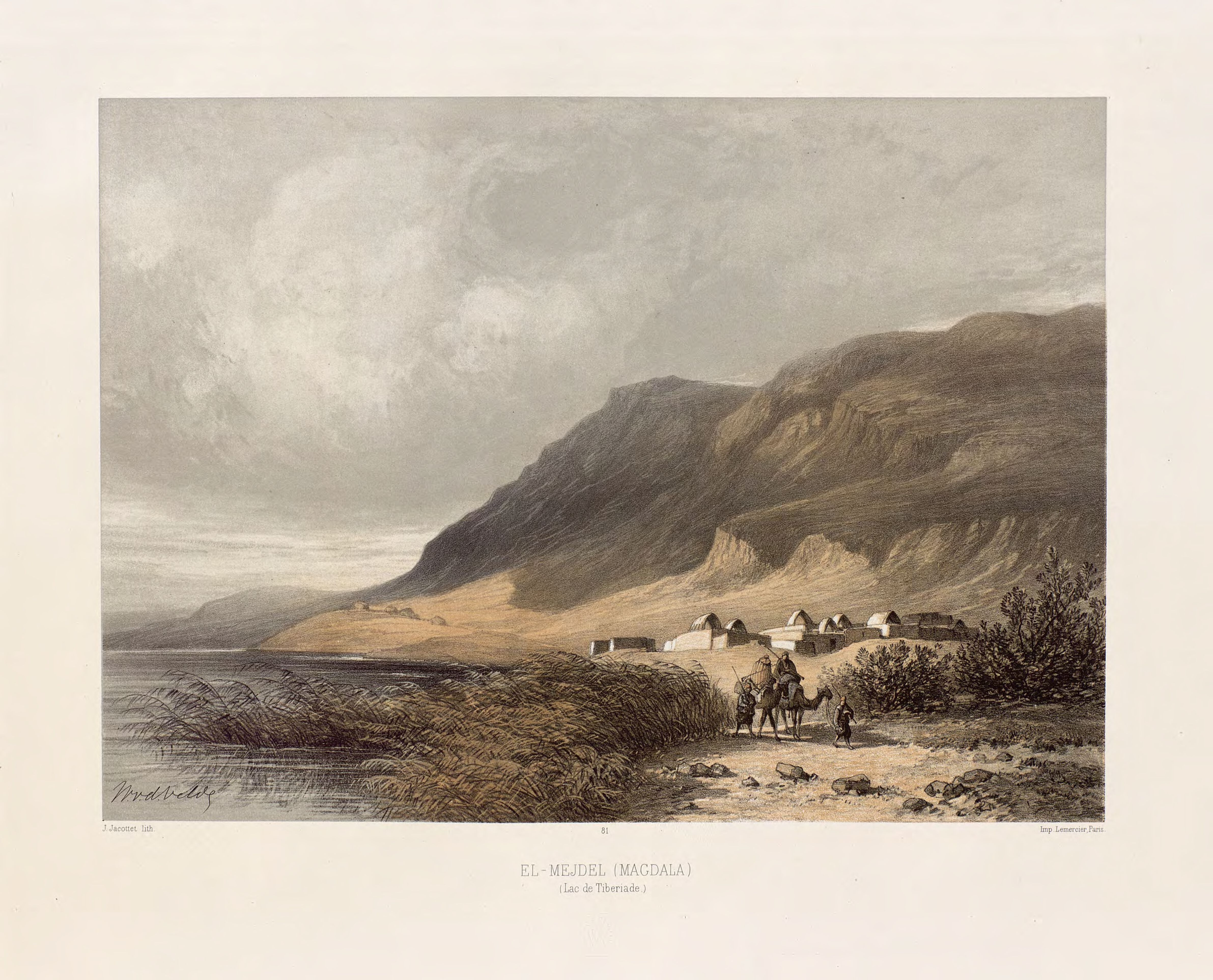
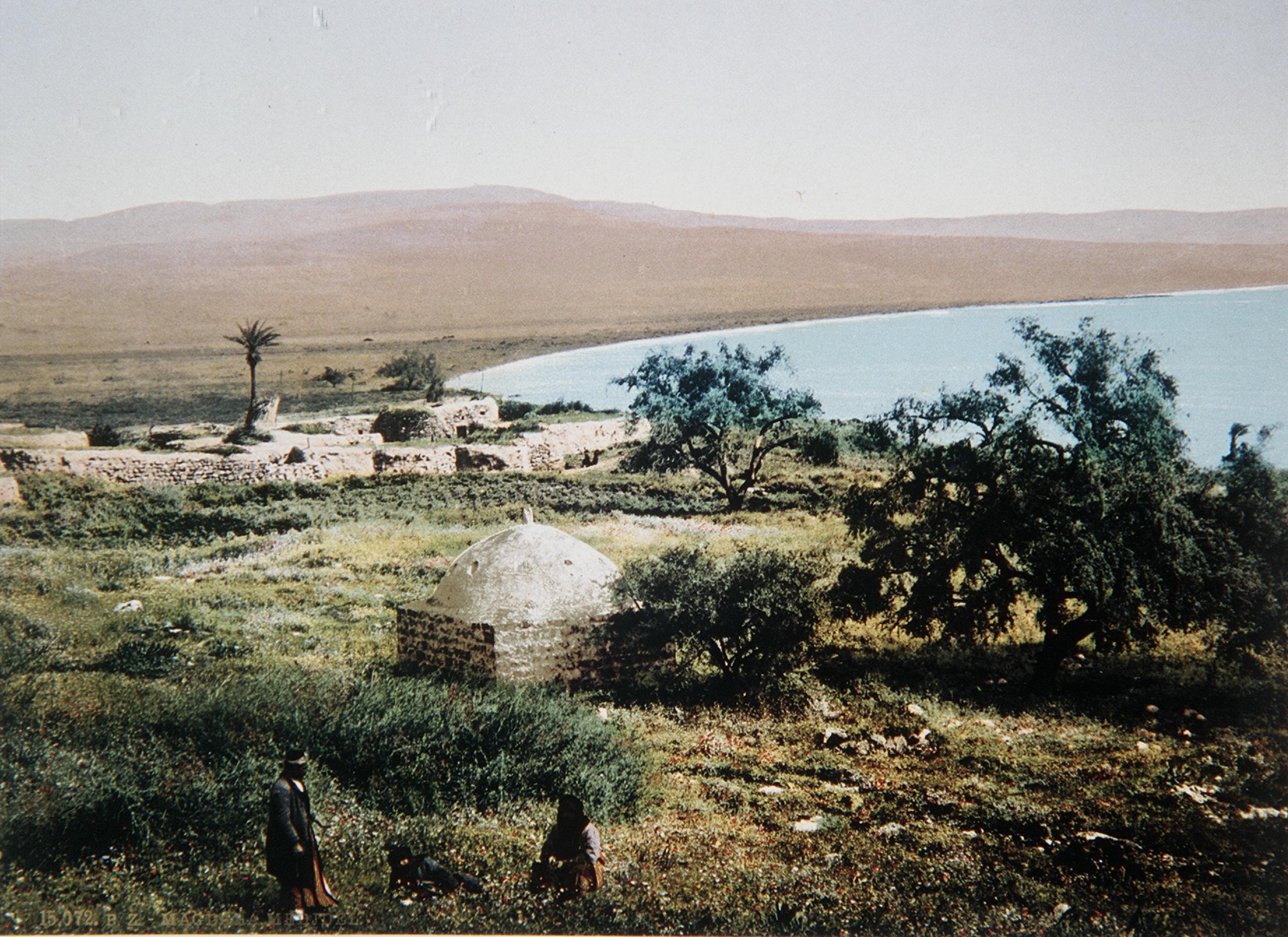


Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Water Management Features
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Transportation and Communication Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Israel
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Israel
Tel Barom
Basalt hill with strategic location.
Rehovot-in-the-Negev
Ancient Nabatean and Byzantine town remains

Tell Qudadi
Iron Age fortress near Yarkon River

Tel Dor
Ancient coastal city with diverse rulers

Beit Guvrin, Israel
Roman city ruins with Hellenistic caves.
Tel Shem
Flattened tell with scattered artifacts.