Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Tabgha is a historically and archaeologically significant site located on the north-western shore of the Sea of Galilee in Israel. Noted for its religious importance, it is traditionally associated with the miracle of the multiplication of the loaves and fishes and the fourth resurrection appearance of Jesus. The site has undergone various historical phases, with significant structures dating back to the 4th and 5th centuries CE, including the Church of the Multiplication, famous for its Byzantine mosaics. The site was a part of the Byzantine period's water management system and later became a village during the Ottoman period. In the 20th century, the village was depopulated during Operation Broom. Recent events include a significant arson attack in 2015. Tabgha's archaeological and historical depth offers a vivid glimpse into religious, cultural, and social transformations over centuries.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Tabgha
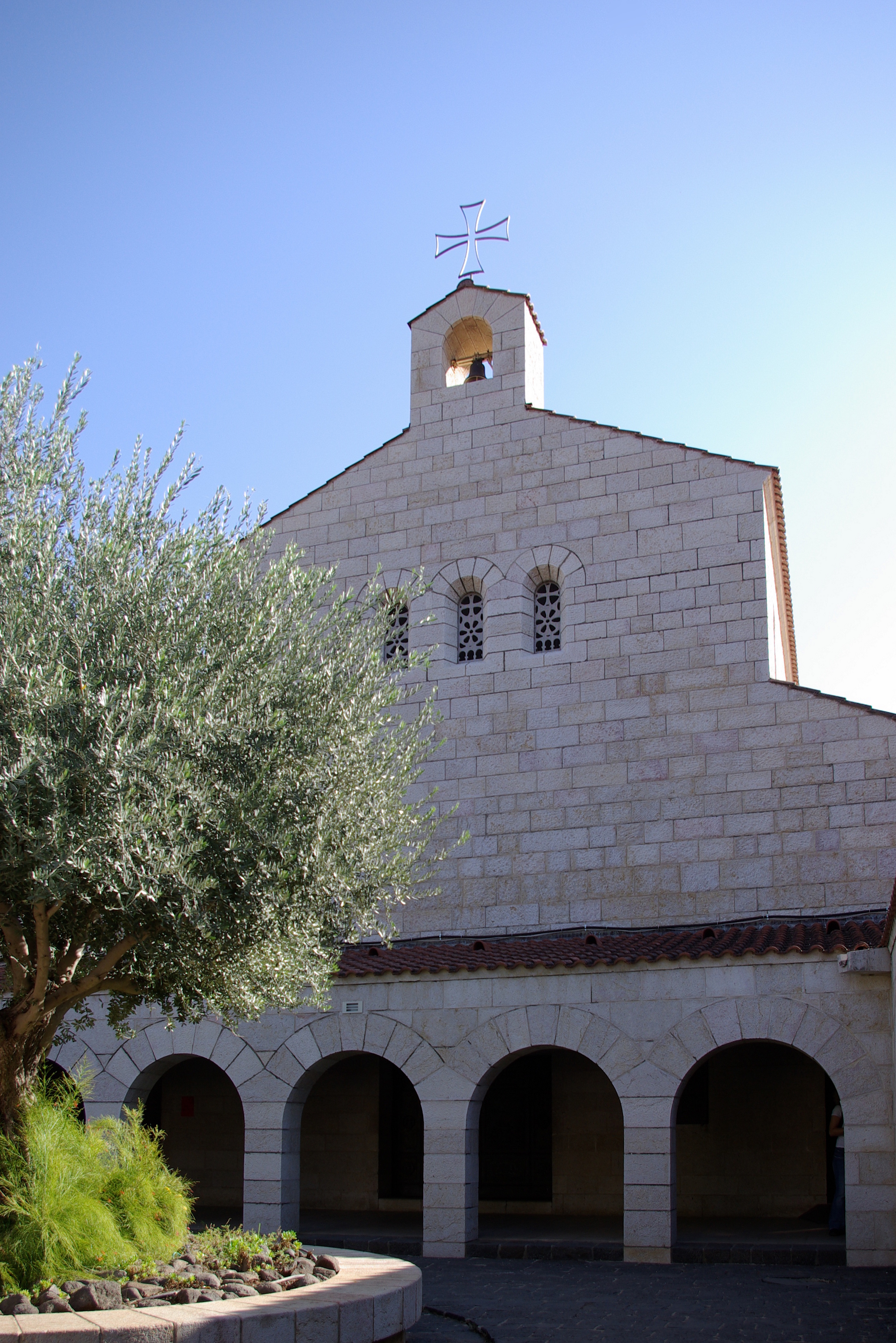
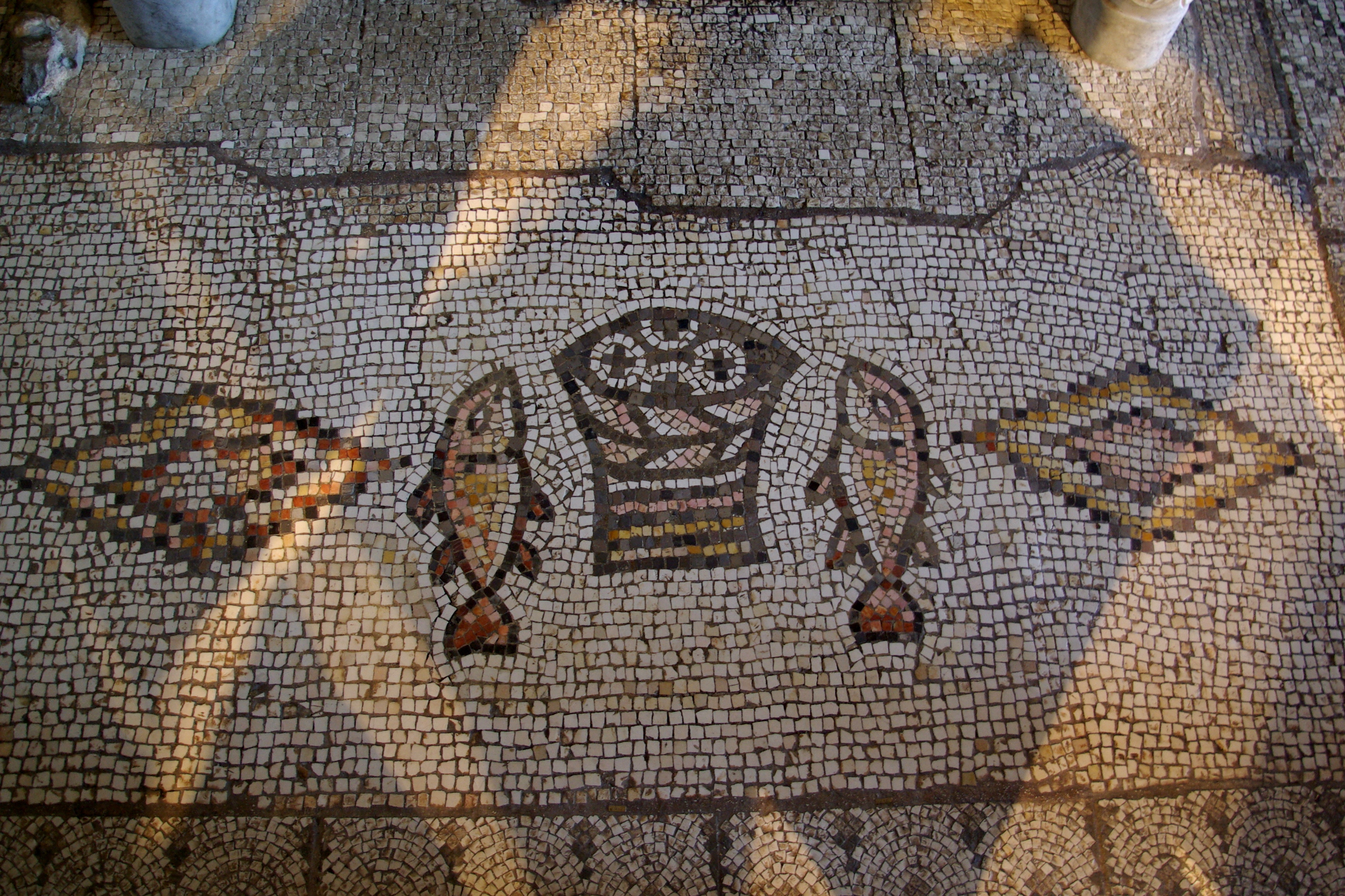



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Water Management Features
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Israel
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Israel
Tel Shem
Flattened tell with scattered artifacts.
Suba, Jerusalem
Crusader castle ruins on a conical hill

Bayt Jibrin
Ancient city with diverse cultural influences

Sataf
Ancient village with terraced agriculture.

Gezer
Ancient Canaanite city with biblical significance.
Beit Qufa
Ancient multi-period settlement and industrial site