Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
The Samosdelka site in southern Russia, excavated by Dmitry Vasilyev and his team, is a significant archaeological location due to its potential identification as Atil, the medieval capital of the Khazar kingdom. Excavations revealed a triangular fortress made of kiln-fired bricks, a distinctive feature as Khazar law reserved such bricks for their capital. The site also contained yurt-like dwellings, suggesting habitation. Despite initial claims, the association with Atil remains controversial due to a lack of definitive evidence like Khazar writings or coins dating to the 10th century. Artifacts from the 11th to 12th centuries indicate subsequent occupation by Oghuz people, linking the site to the medieval city of Saqsin. The site's significance lies in its potential to illuminate Khazar history and Russian historical succession.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Samosdelka
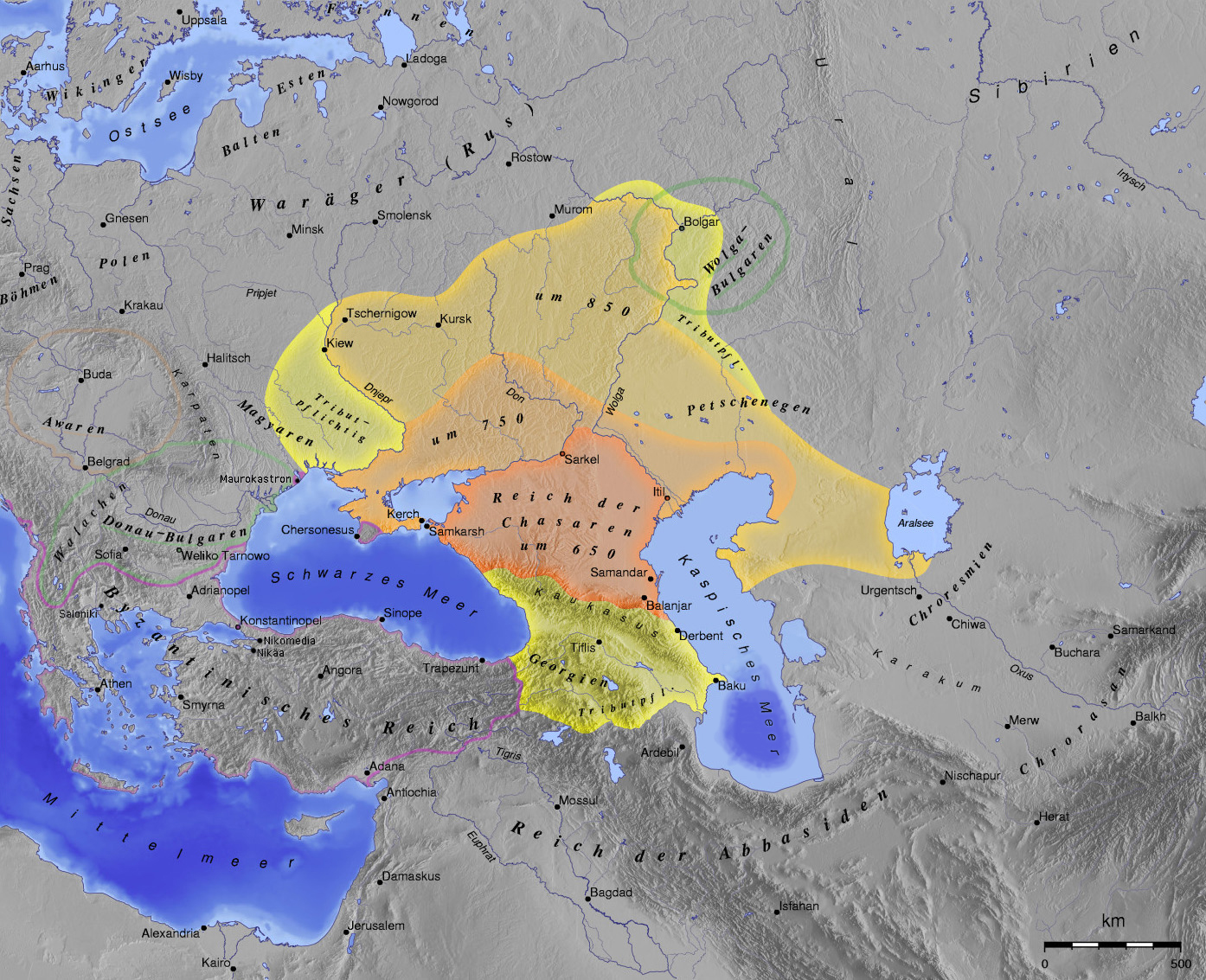
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Industrial and Craft Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Russia
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Russia
Timerevo
Unfortified Scandinavian trade outpost near Volga.
Tmutarakan
Medieval trading town, Kievan Rus principality
Sernya
Medieval city ruins with fortress remains

Por-Bazhyn
Ruined Uyghur palace on mountain lake island

Veliky Novgorod
Historic city with medieval structures and artifacts.
Semikarakorsk Fortress
Early medieval Khazar fortress on island hill.