Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Abu Simbel is an archaeological site of immense significance, featuring two monumental rock-cut temples constructed during the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses II in the 13th century BCE. Located in Upper Egypt near the modern border with Sudan, these temples were intended to showcase Egypt's power and promote the Egyptianization of Nubia. The Great Temple, dedicated to the gods Amun, Ra-Horakhty, and Ptah, as well as to the deified Ramesses II, is renowned for its colossal statues of the pharaoh and intricate reliefs depicting his military triumphs, especially the Battle of Kadesh. The smaller temple honors the goddess Hathor and Ramesses's chief wife, Nefertari. Both temples were relocated in the 1960s to prevent submersion by Lake Nasser, a result of the Aswan High Dam, showcasing one of the greatest feats in archaeological engineering.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Abu Simbel
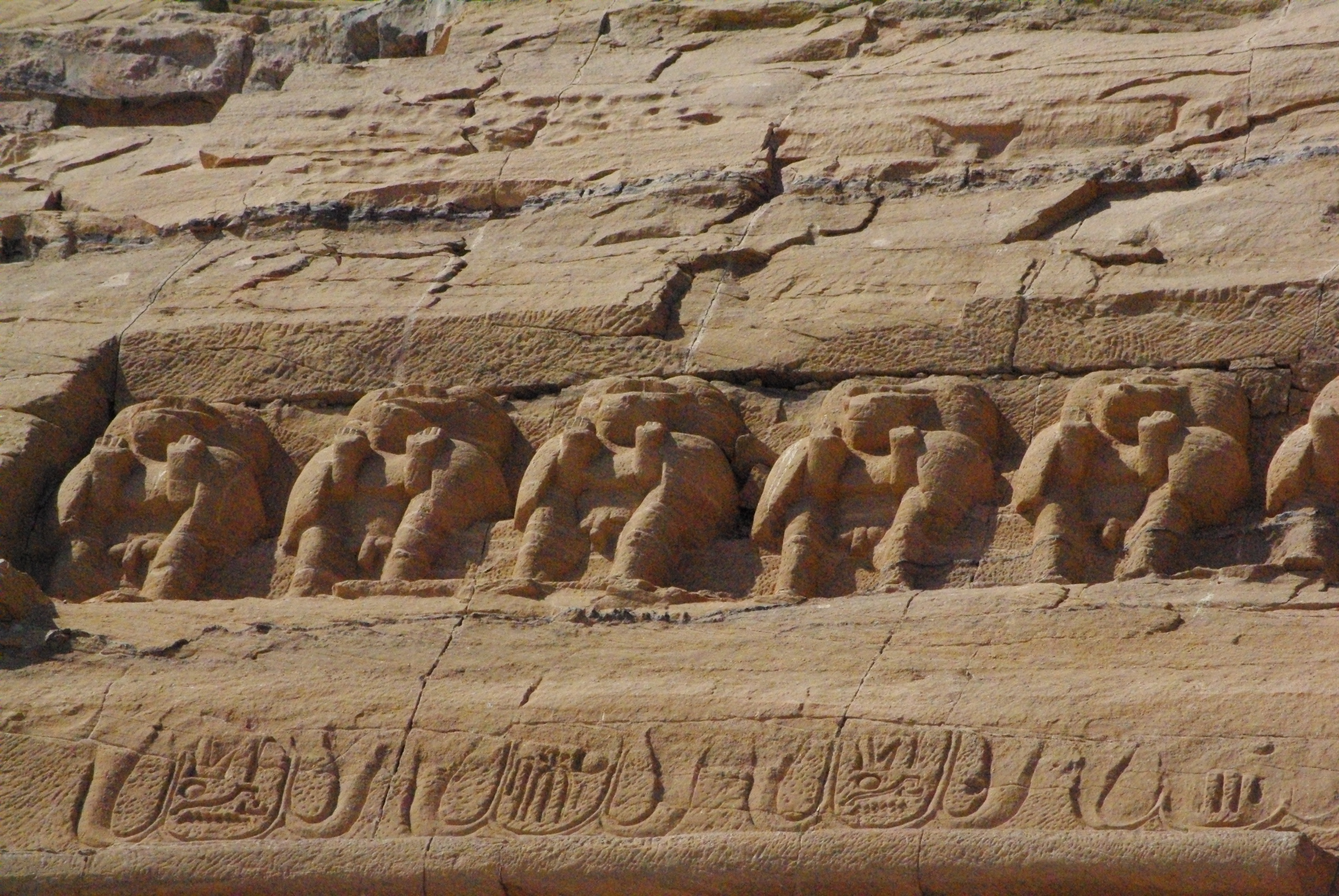
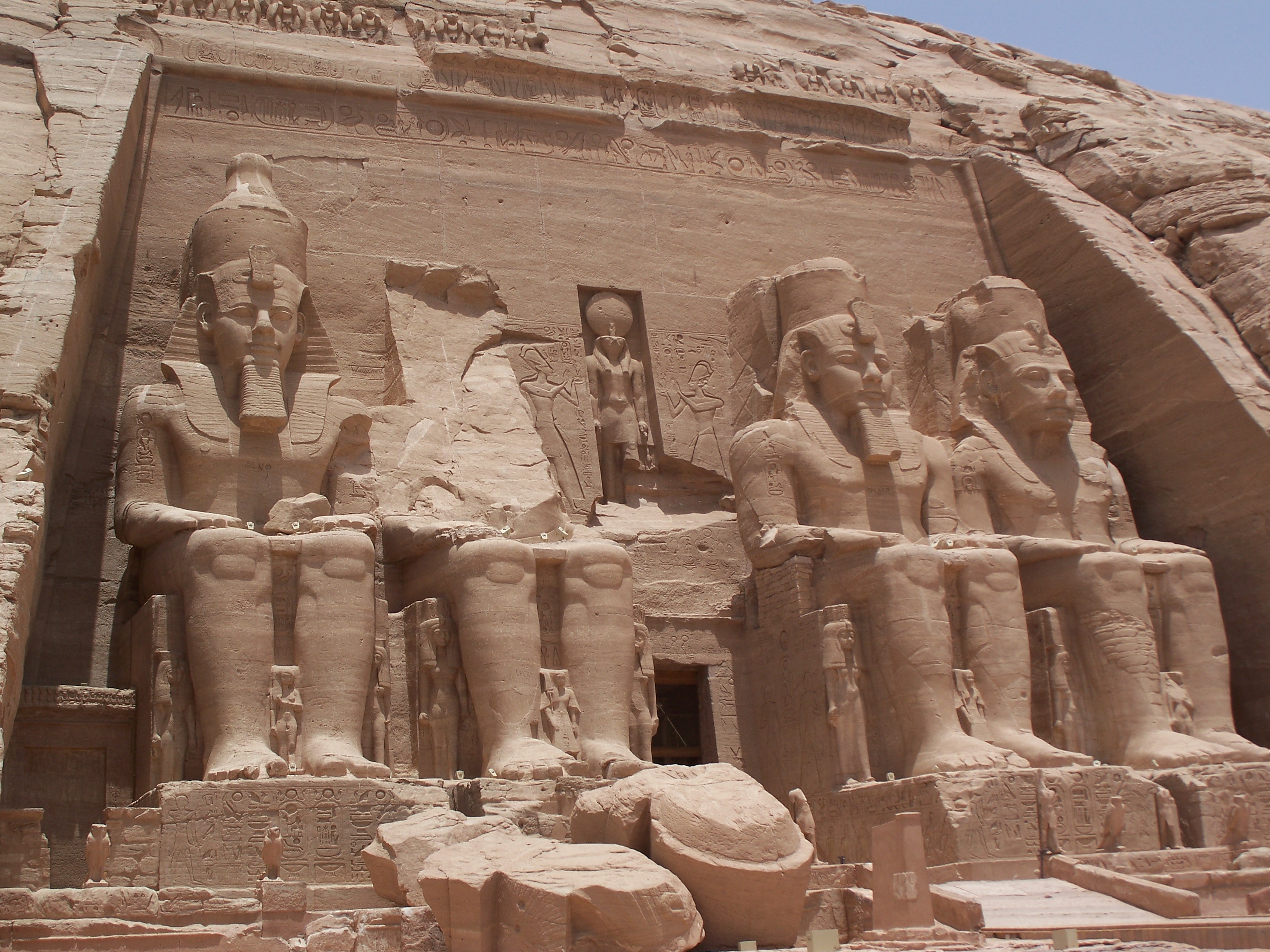



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Egypt
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Egypt
Elephantine
Island with temples and ancient papyri.

Thinis
Ancient Upper Egypt's undiscovered capital city.
Sais, Egypt
Ancient Egyptian city with Neolithic origins
El-Gabal el-Ahmar
Ancient quarry site with quartzite sandstone.
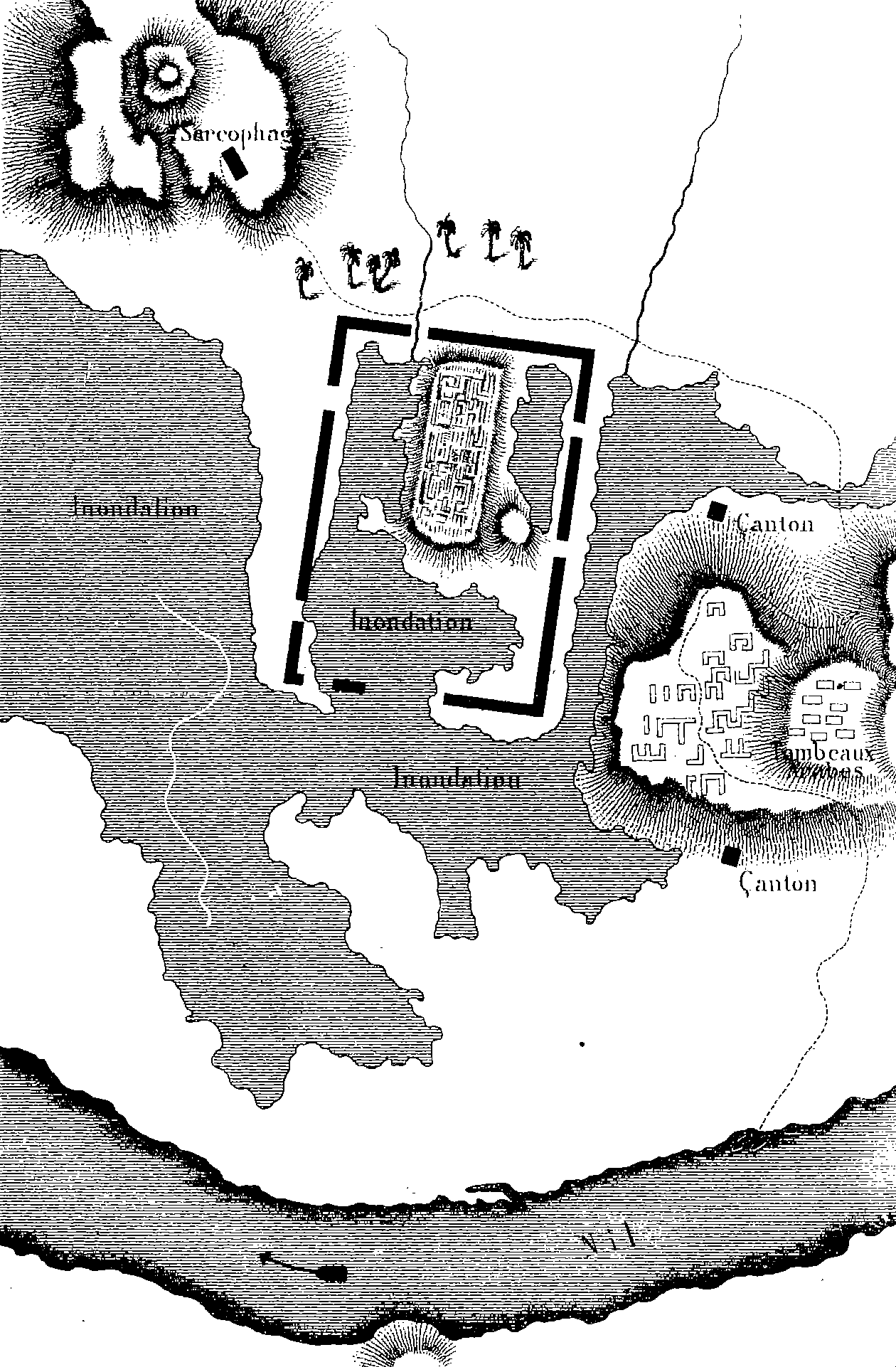
Elkab
Ancient Egyptian city with temples and tombs.
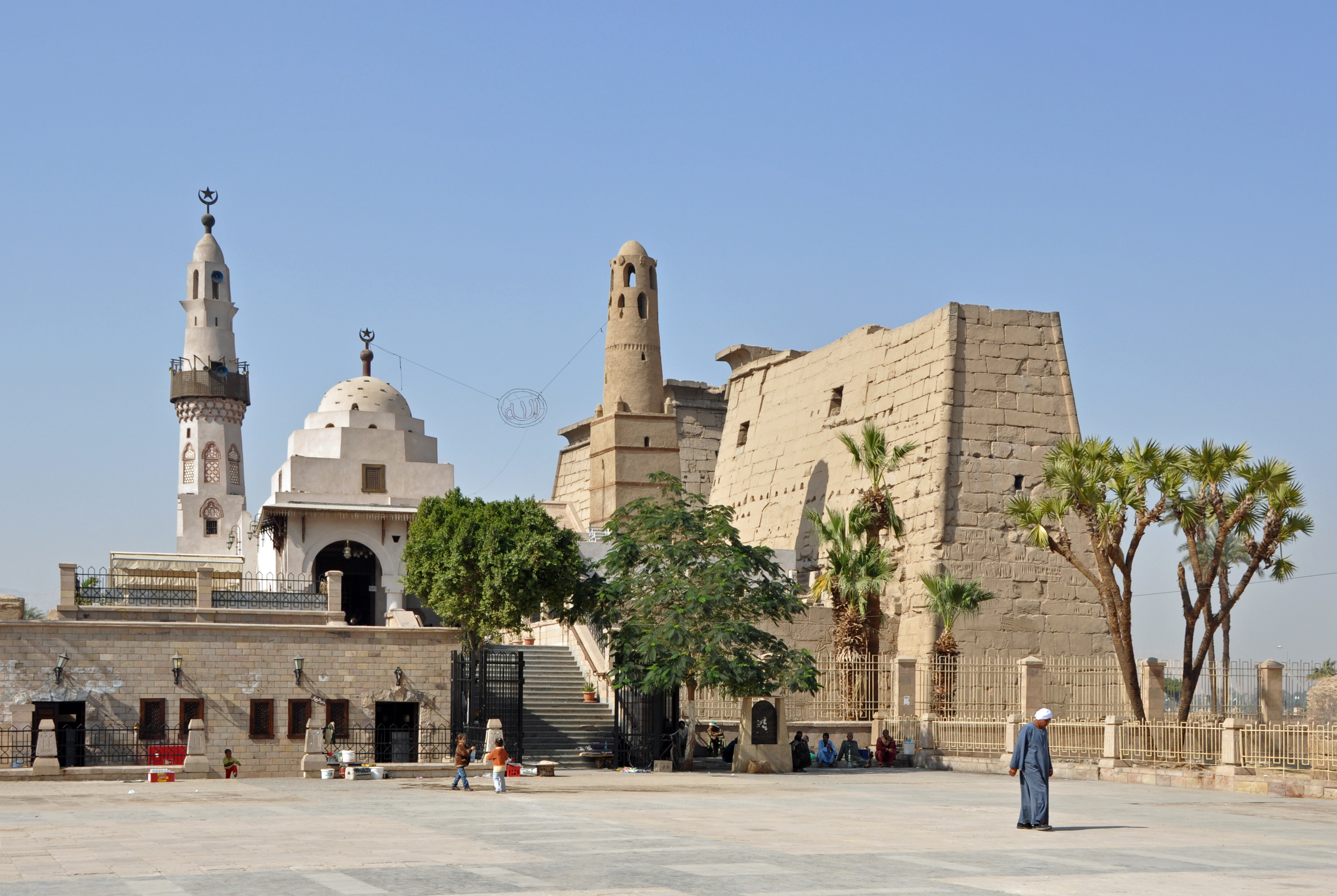

Luxor
Ancient city with temples and tombs
