Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Taposiris Magna, established by Ptolemy II Philadelphus in the 3rd century BCE, is a significant archaeological site located in Egypt. Known for its religious importance, the city became a center for the Khoiak festival, dedicated to Osiris. The site features a temple, which may be the final resting place of Cleopatra VII, and a necropolis with Greco-Roman style mummies. The city was strategically positioned on an ancient trade route, facilitated by its harbor. Among its notable structures are a monumental tower and a recently discovered water tunnel, mirroring the Tunnel of Eupalinos in Greece. These attributes highlight Taposiris Magna's role in the cultural and trade exchanges during the Hellenistic period.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Taposiris Magna
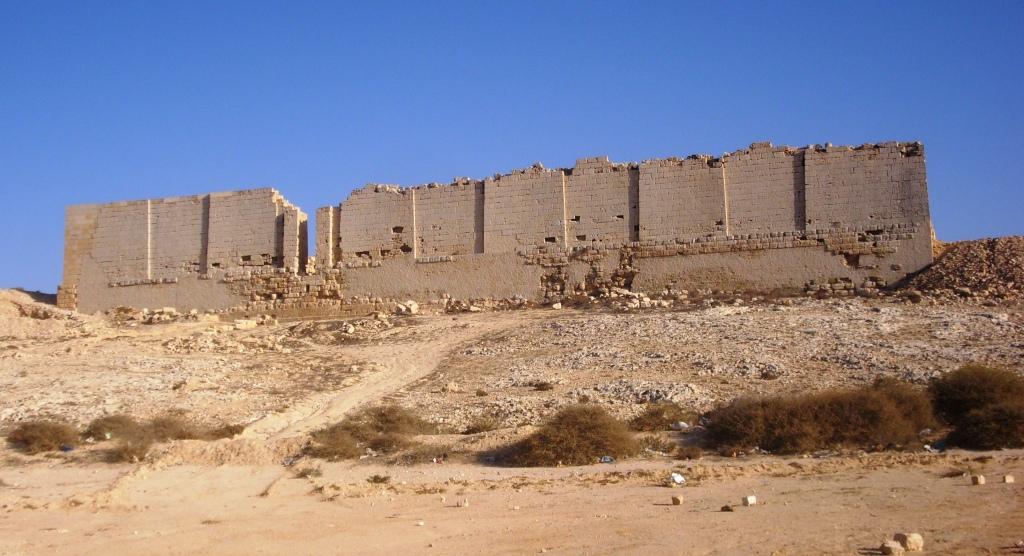
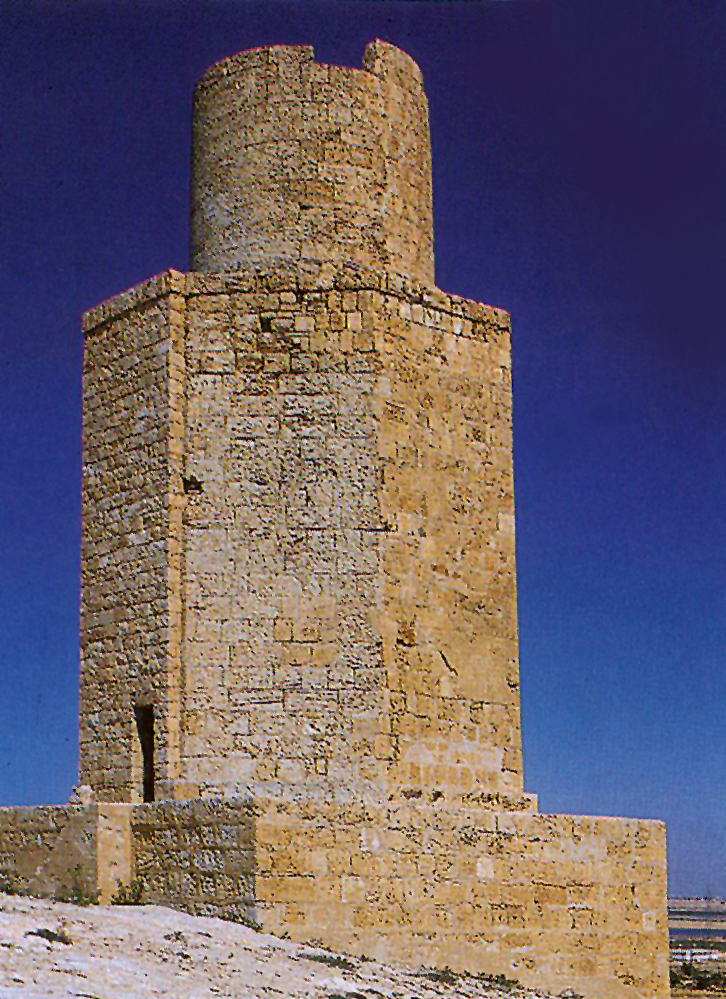
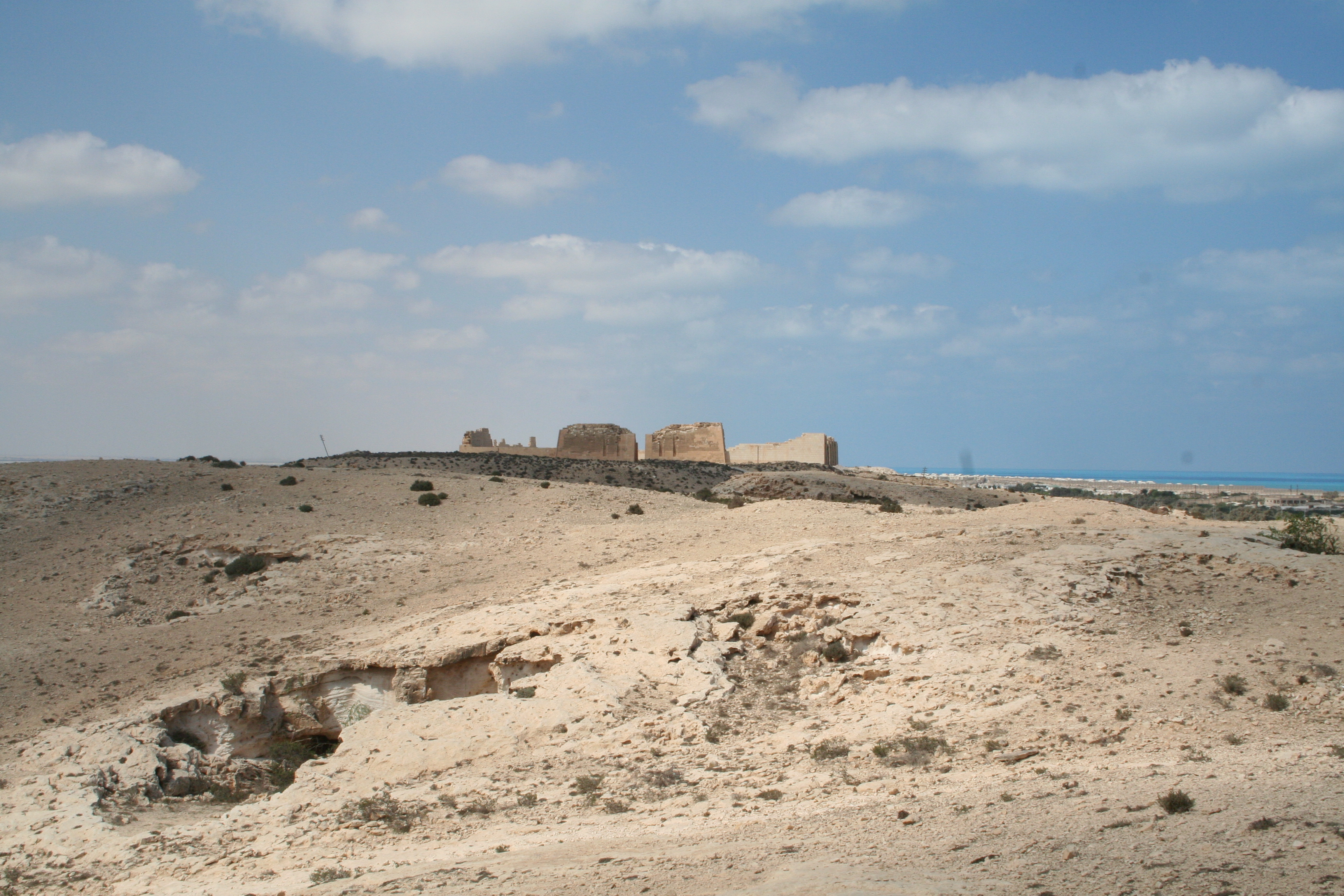



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Water Management Features
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Egypt
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Egypt
Wadi el-Hudi
Ancient Egyptian amethyst mining site.
Elkab
Ancient Egyptian city with temples and tombs.

Akhmim
Ancient city with temples and cemeteries.

Qustul
Lower Nubian cemetery with ancient burials
Marea (ancient city)
Large ancient Egyptian port city remains

Leontopolis
Ancient city with temples and provincial capital