Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
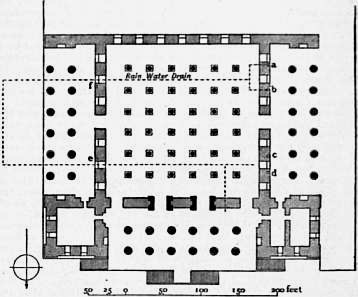
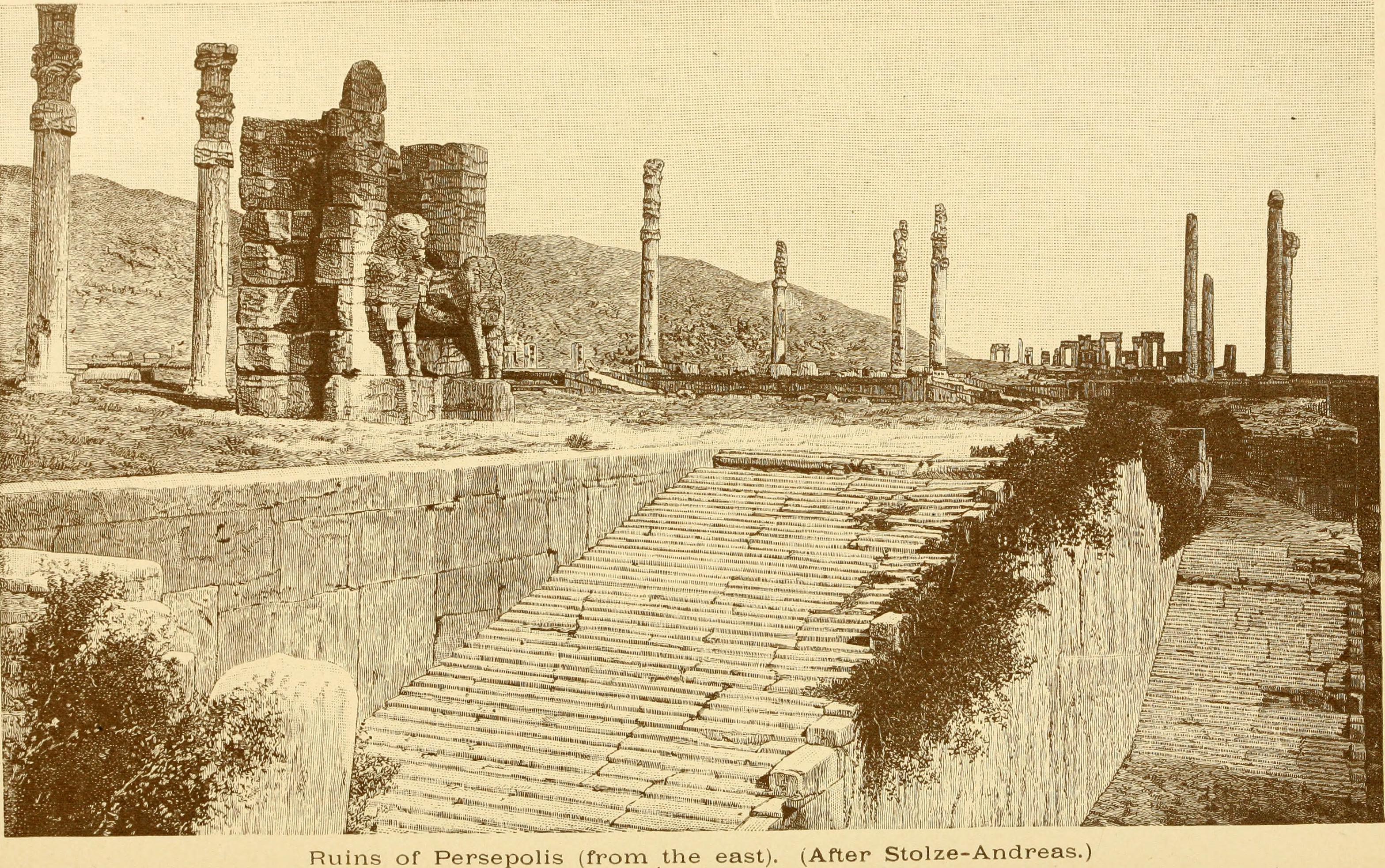
Persepolis, located in modern-day Iran, served as the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire from around 515 BCE, during the reign of Darius I. This archaeological site is renowned for its grandiose palatial complex, featuring intricate reliefs and inscriptions that exemplify Achaemenid architecture. Built on a raised terrace, the site includes significant structures such as the Apadana Palace, the Gate of All Nations, and the Hall of a Hundred Columns. Persepolis was a focal point for ceremonial events, including the Persian New Year, Nowruz. The site was partially destroyed by fire in 330 BCE following its capture by Alexander the Great. Today, Persepolis is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, offering invaluable insights into the art, architecture, and imperial grandeur of the Achaemenid Empire.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Persepolis
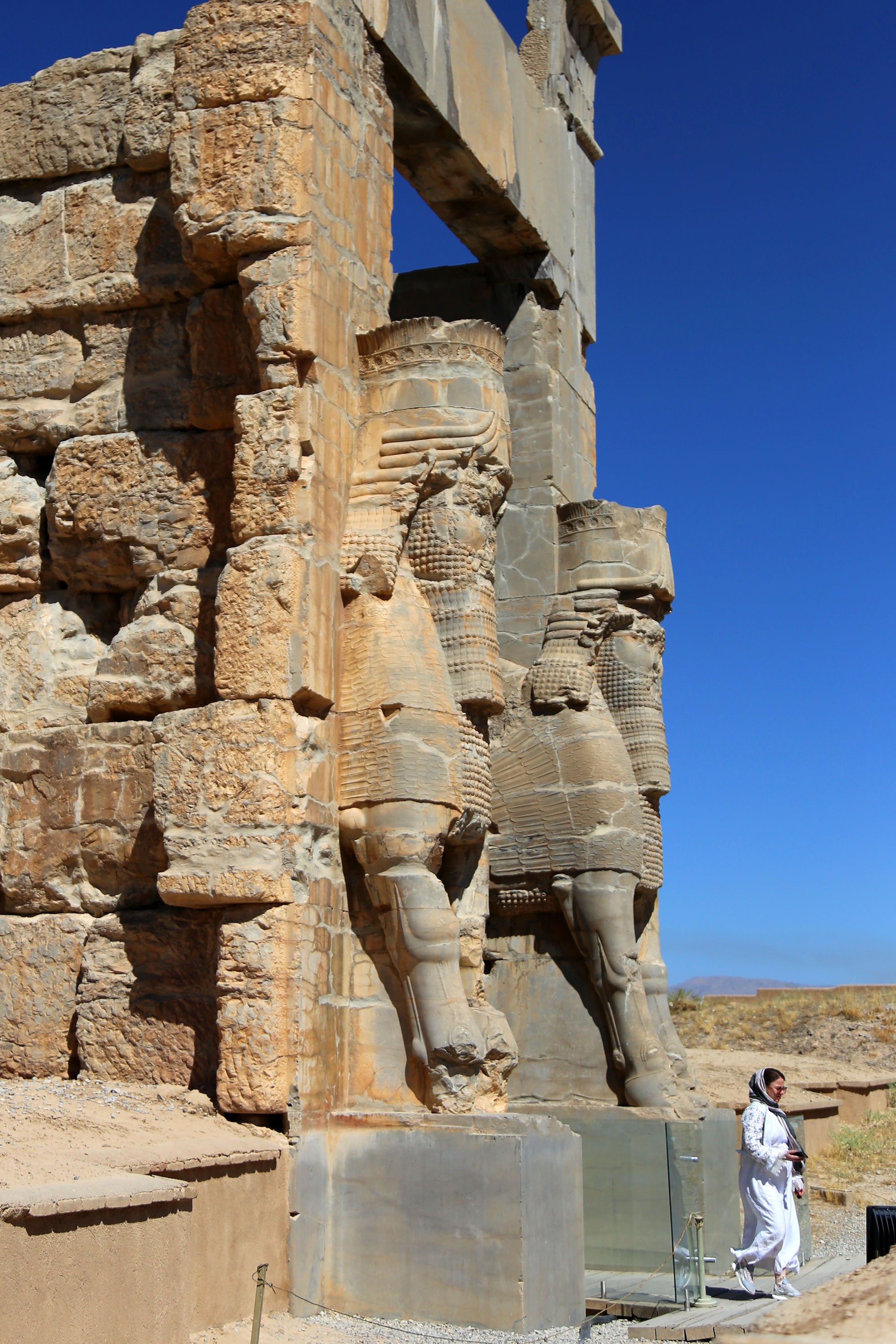

Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Burial and Funerary Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Iran
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Iran

Sari, Iran
Ancient city with rich archaeological history
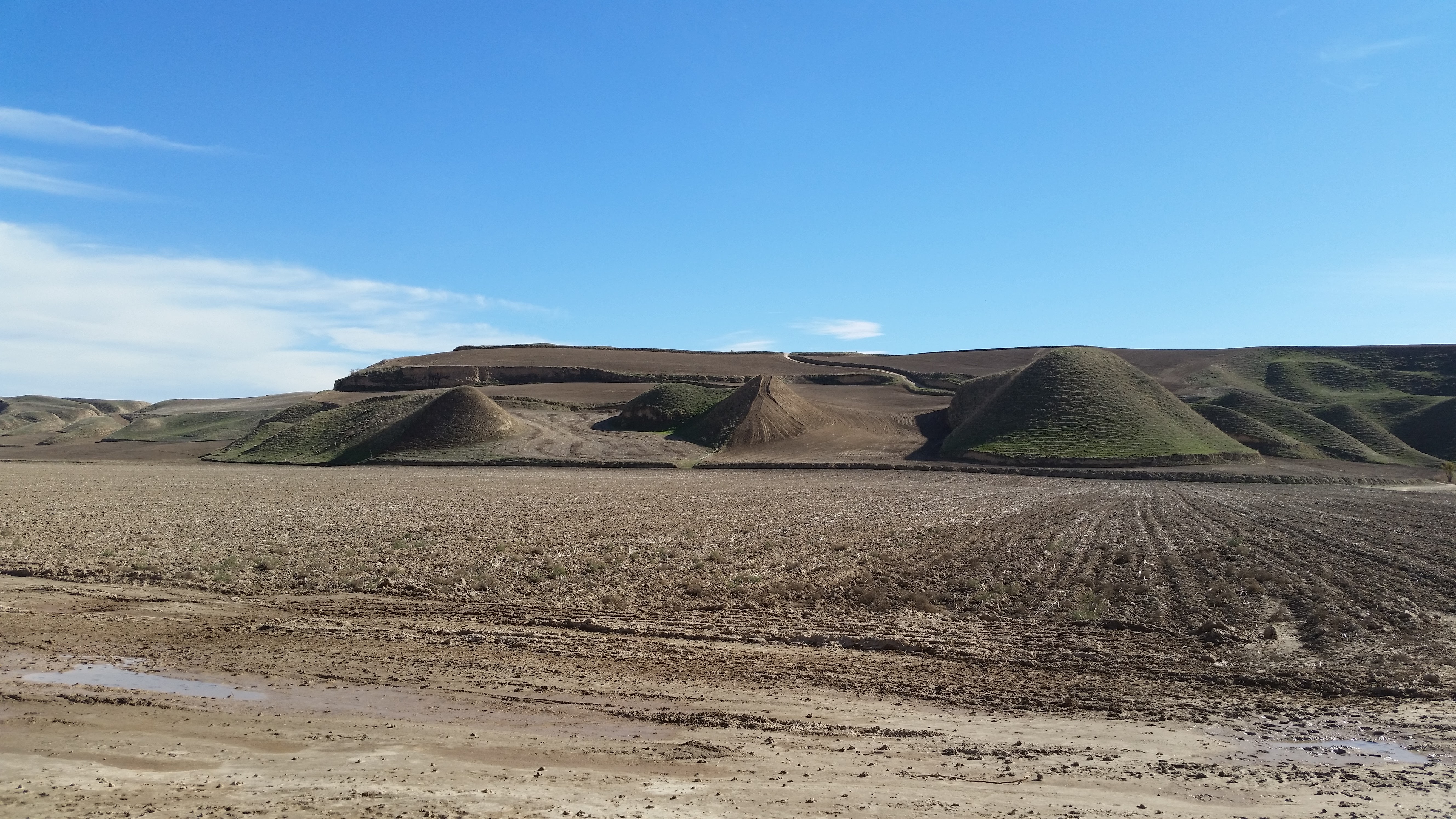

Great Wall of Gorgan
Sasanian-era defensive wall in Iran
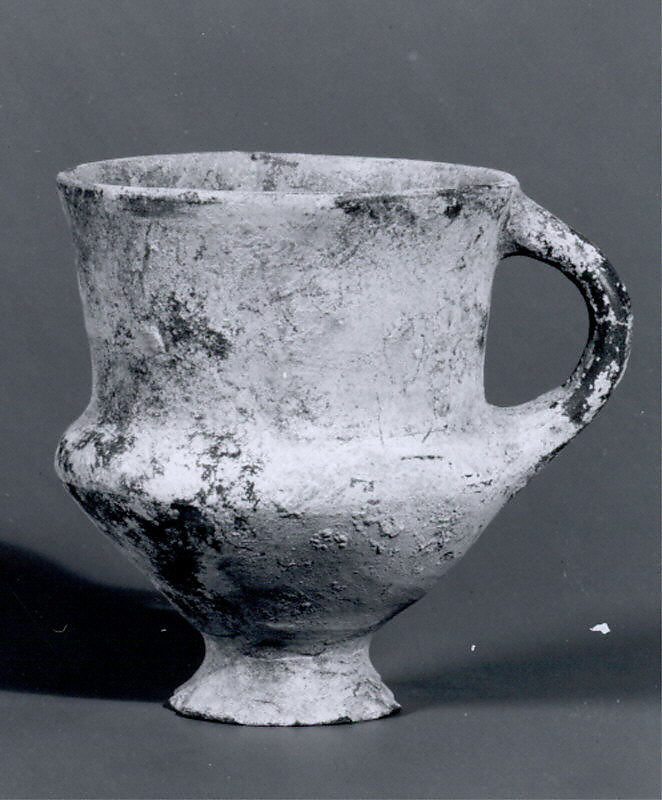

Teppe Hasanlu
Ancient city with well-preserved ruins
Malaverd
Multi-period cave site in Kermanshah, Iran.
Bardak Siah Palace
Achaemenid Persian palace with sculptures and inscriptions.
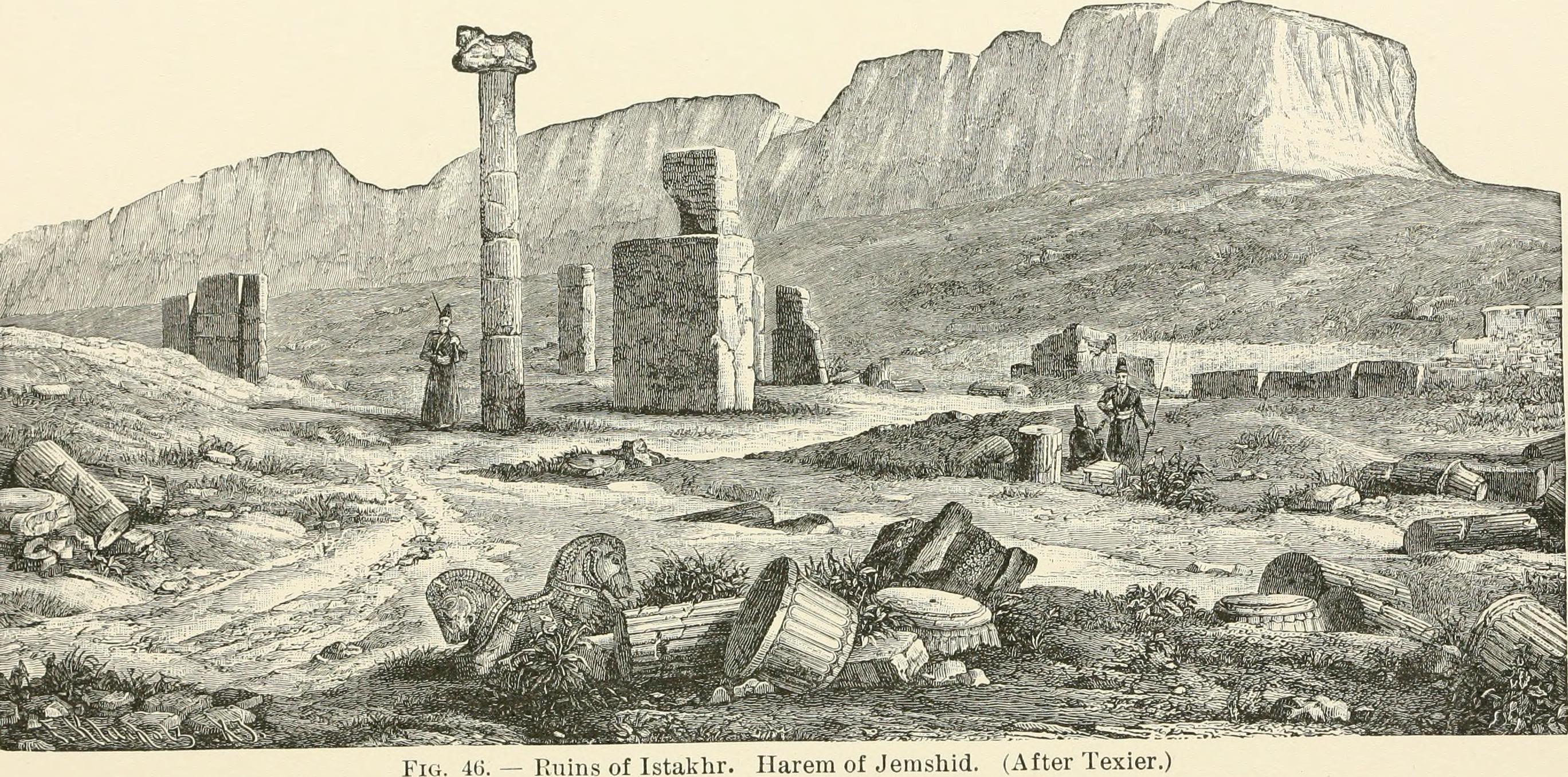
Istakhr
Ancient city with religious and defensive structures.
