Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
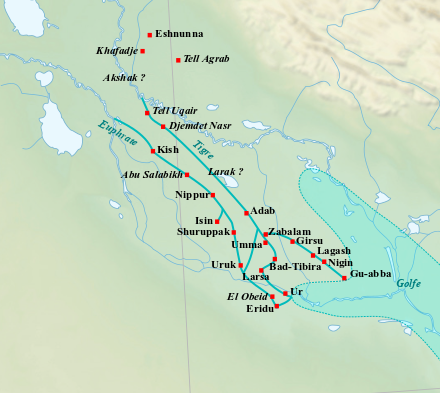
Location
About
The archaeological site of Abu Salabikh in Iraq is a notable Sumerian city that thrived from the Neolithic through the late 3rd millennium BCE. Situated northwest of ancient Nippur, the site consists of three mounds, with the main Early Dynastic mound surrounded by a defensive wall. The city, connected culturally to Kish, Mari, and Ebla, is characterized by its rectilinear urban planning evident from Early Dynastic times. Abu Salabikh is significant for yielding around 500 tablets, including some of the earliest Sumerian literature, such as the Instructions of Shuruppak. The site also features remnants of an Early Dynastic palace and a temple. Notably, the city experienced decline when the Euphrates River shifted its course, leading to abandonment.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Abu Salabikh
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Environmental and Natural Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Iraq
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Iraq

Nineveh
Ancient Assyrian city with monumental ruins
Tulul al-Baqarat
Ancient, multiperiod site with temple remains.

Uruk
Ancient Sumerian city with monumental structures
Tell Madhur
Ancient settlement mound with preserved Ubaid house

Tell Uqair
Ancient settlement with temple and cemetery.

Tell Taya
Ancient hill city with fortifications and artifacts.