Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
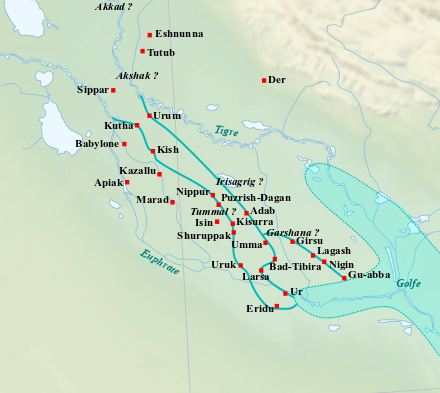
Location
About
Marad, identified as modern Tell Wannat es-Sadum in Iraq, was an influential ancient Near Eastern city established around 2700 BCE during the Sumerian Early Dynastic II period. Notably, Marad featured a significant ziggurat dedicated to its city god Lugal-Marada. The city experienced phases of control under the Akkadian and Ur III empires before a brief period of independence in the Old Babylonian period. The site holds historical significance due to its religious structures and the economic and legal activities recorded in cuneiform tablets. Excavations have uncovered these tablets, as well as graves and residential structures, providing insights into the societal and cultural dynamics of the time. The site's importance is further highlighted by Nebuchadnezzar II's reconstruction of the main temple, emphasizing its enduring significance across centuries.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Marad
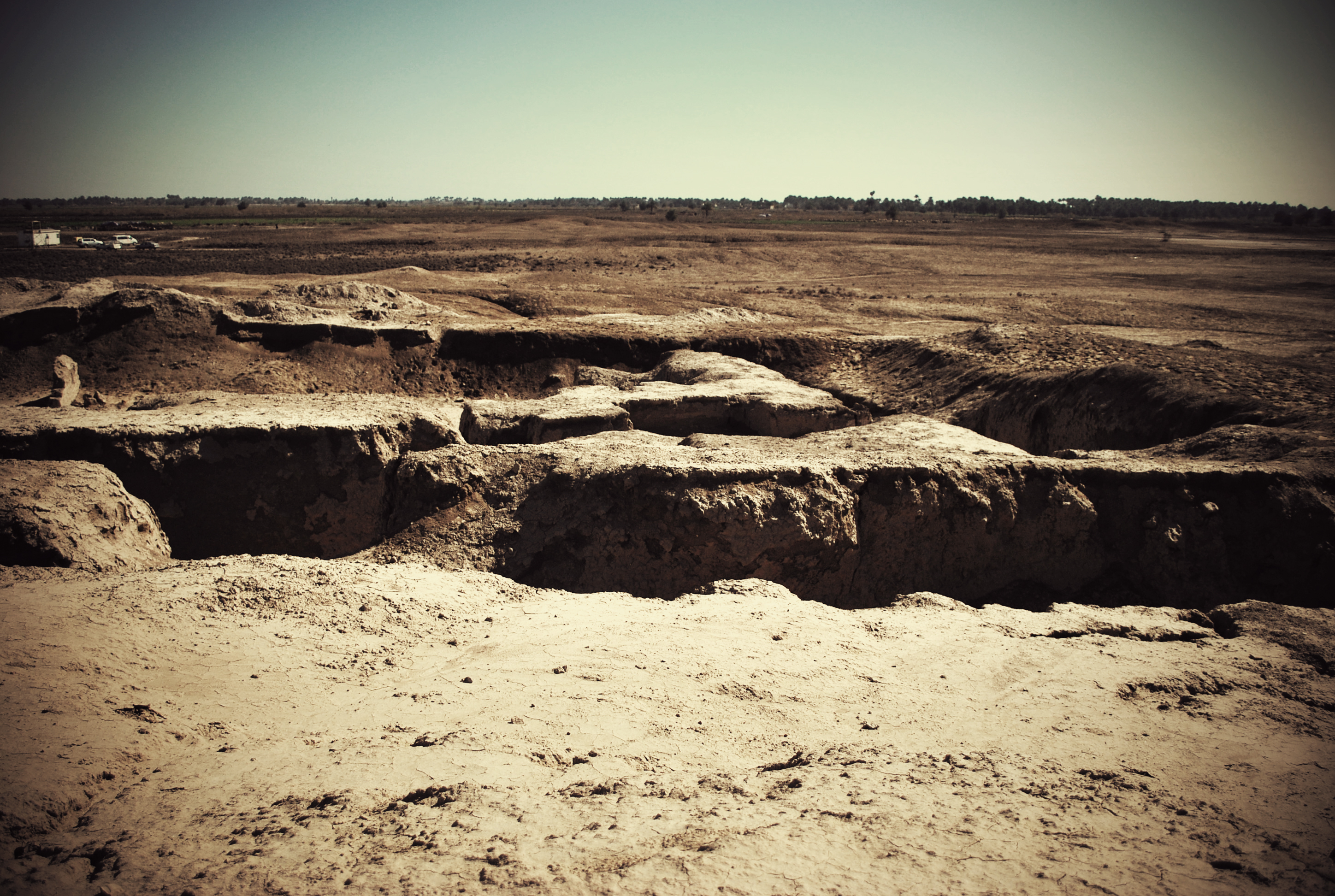
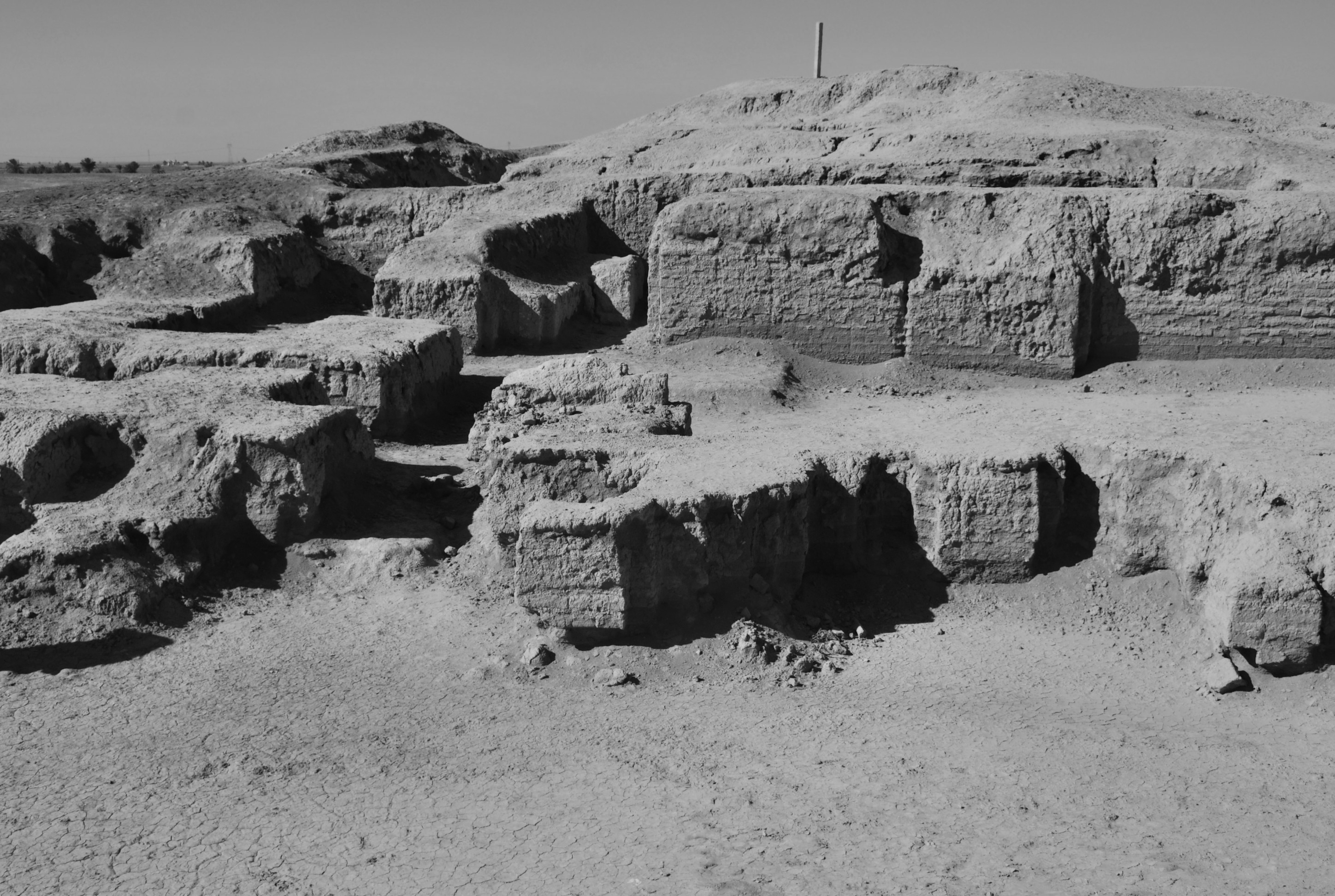



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Miscellaneous Features
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Iraq
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Iraq
Tell al-Lahm
Oblong mound with city wall remnants

Assur
Ancient Assyrian city on the Tigris River

Nineveh
Ancient Assyrian city with monumental ruins

Uruk
Ancient Sumerian city with monumental structures
Kutha
Ancient city with temple and mounds

Tell Taya
Ancient hill city with fortifications and artifacts.