Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
The Gedi ruins in Kenya represent a significant medieval Swahili coastal settlement, characterized by its stone architecture, including mosques, palaces, and pillar tombs. The site flourished between the 11th and 17th centuries, serving as a crucial trade hub along the Indian Ocean, evidenced by imported materials such as pottery, beads, and coins. Gedi's urban core, defined by an inner and outer wall, reveals insights into the social and economic structures of Swahili culture during this period. The site's archaeological significance lies in its ability to illustrate the development of Swahili urbanism, the spread of Islam, and the impacts of trade networks on East African coastal societies.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Ruins of Gedi
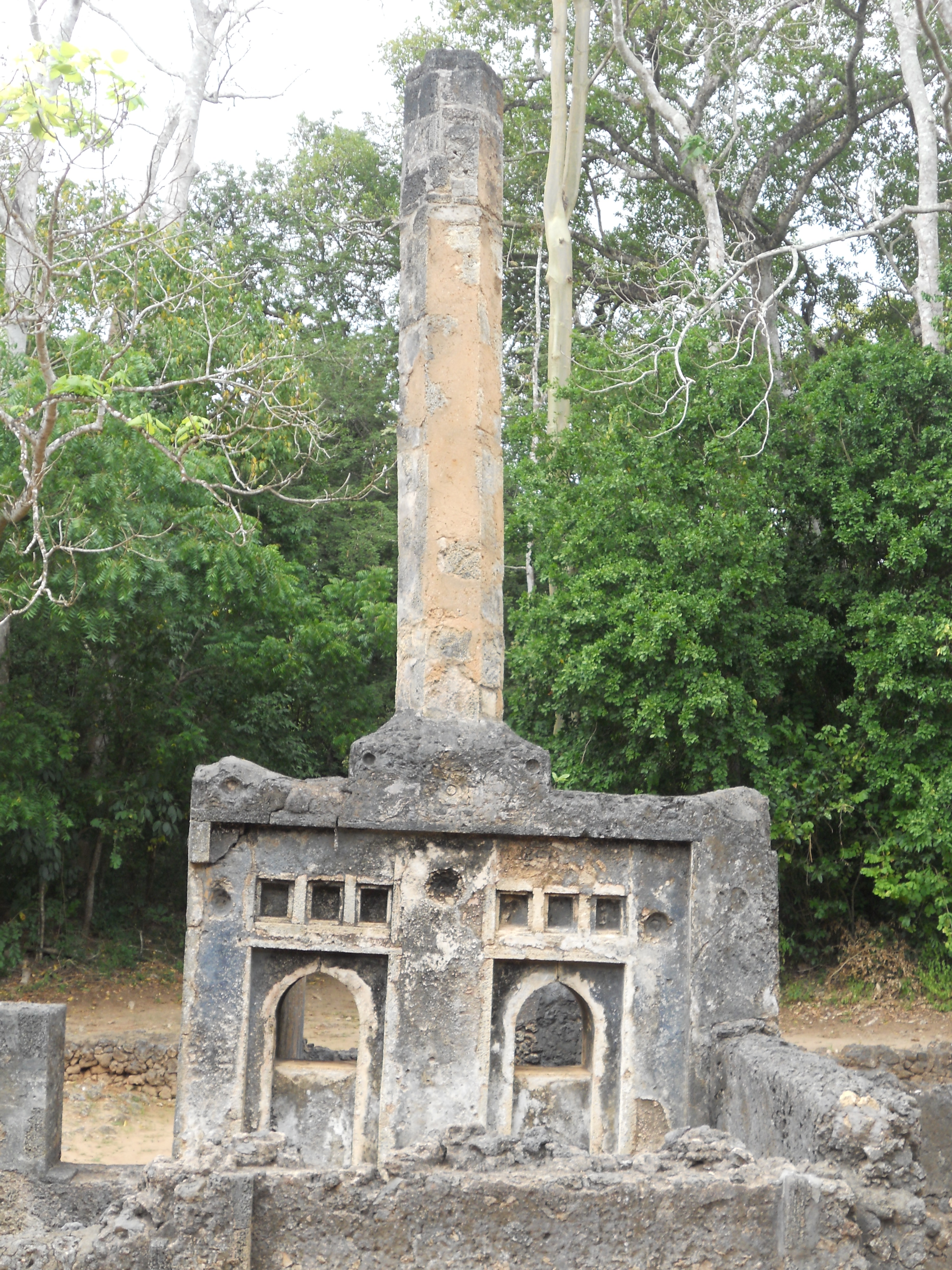
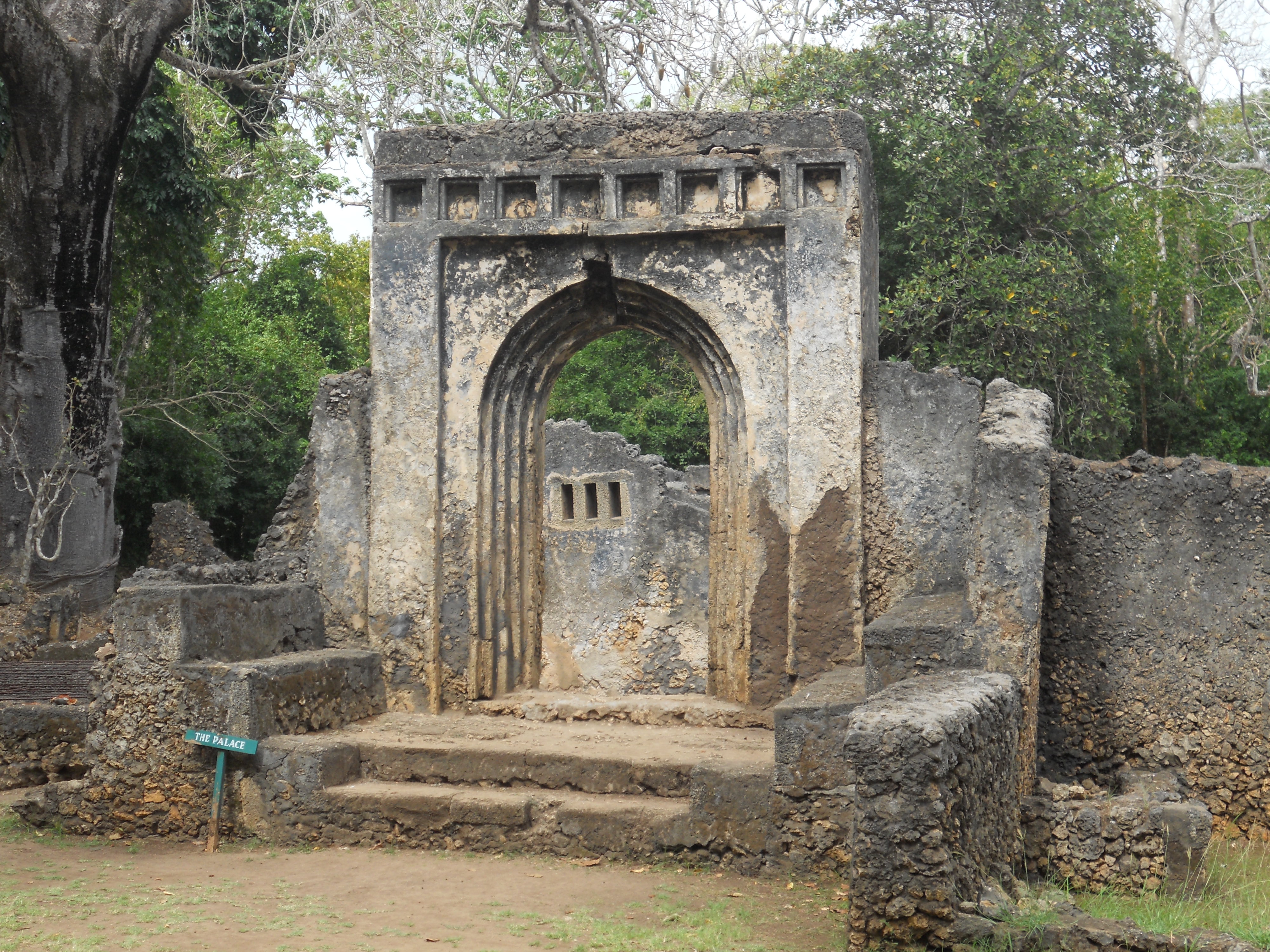
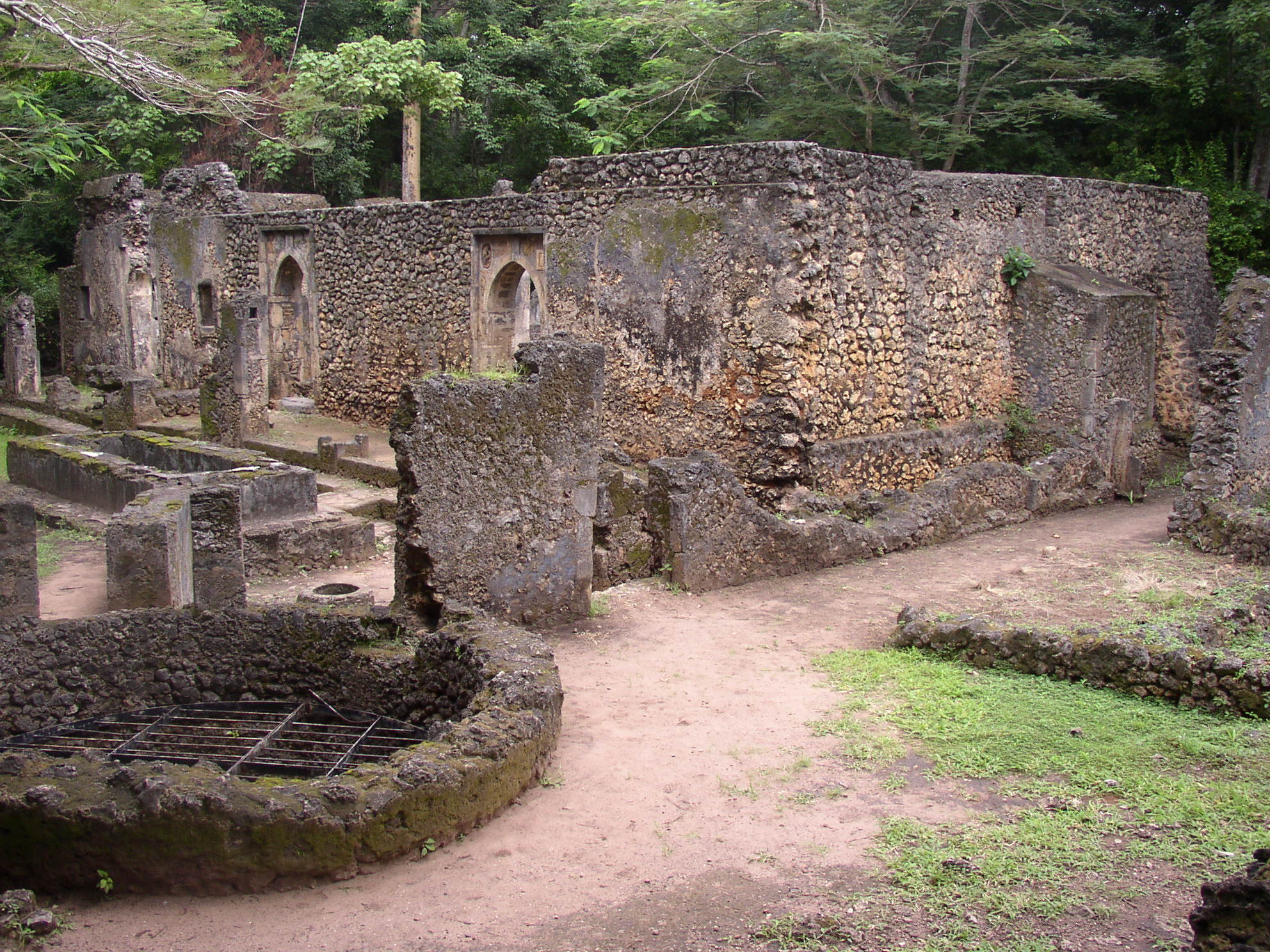



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Water Management Features
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Kenya
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Kenya
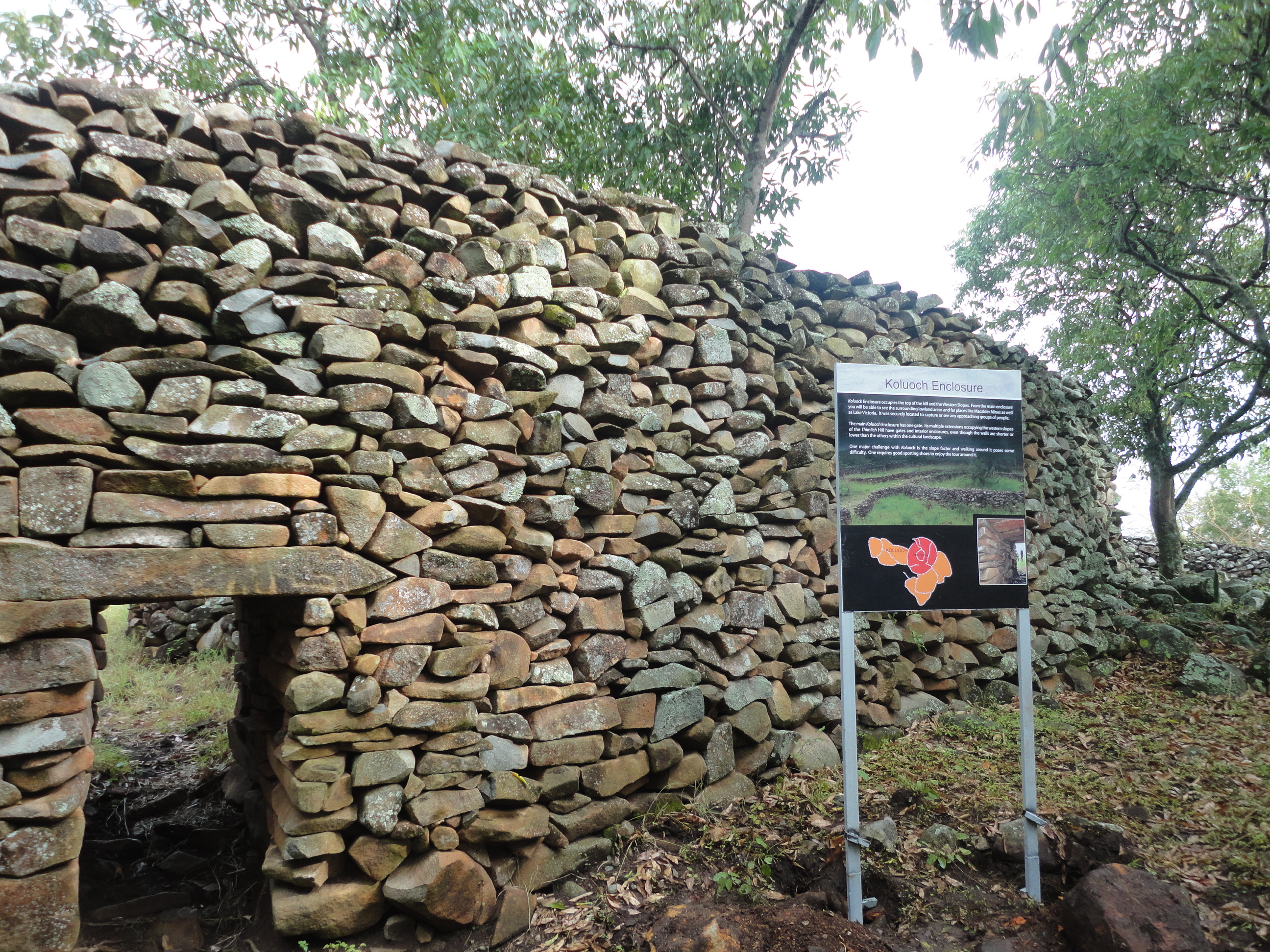

Thimlich Ohinga
Stone-built ruins with interlocking walls
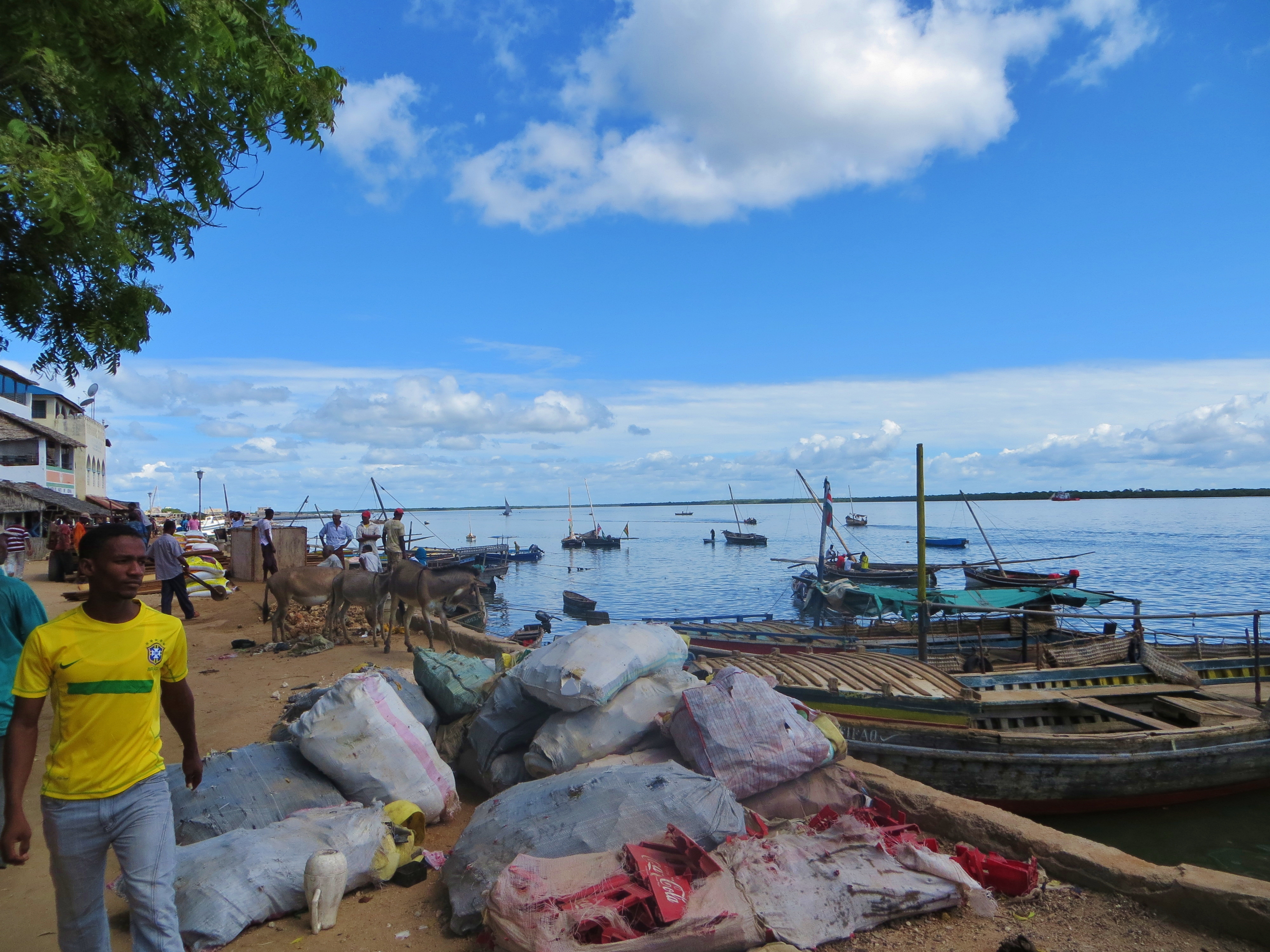

Lamu
Swahili settlement with forts and mosques
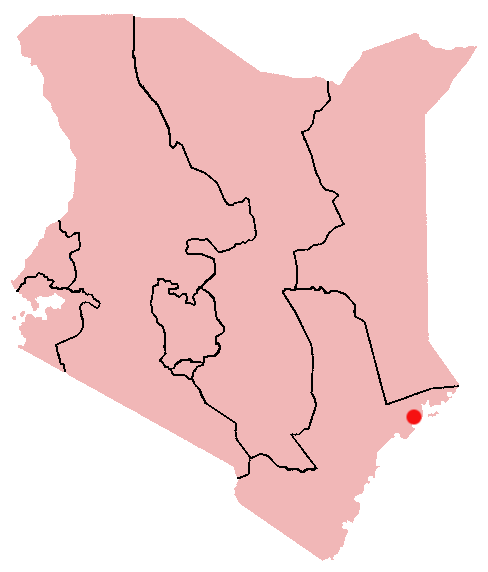
Pate Island
Swahili trading and cultural hub
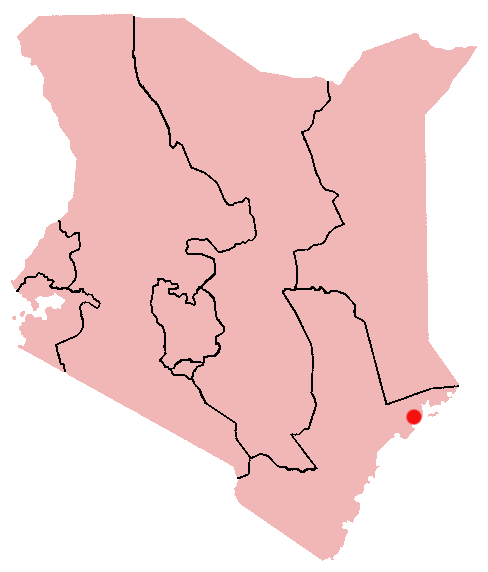
Manda Island
Ruins of ancient trade town on island
Jumba la Mtwana
14th-century coastal structures and relics site.
Mambrui
14th-century Swahili settlement with mosques
