Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
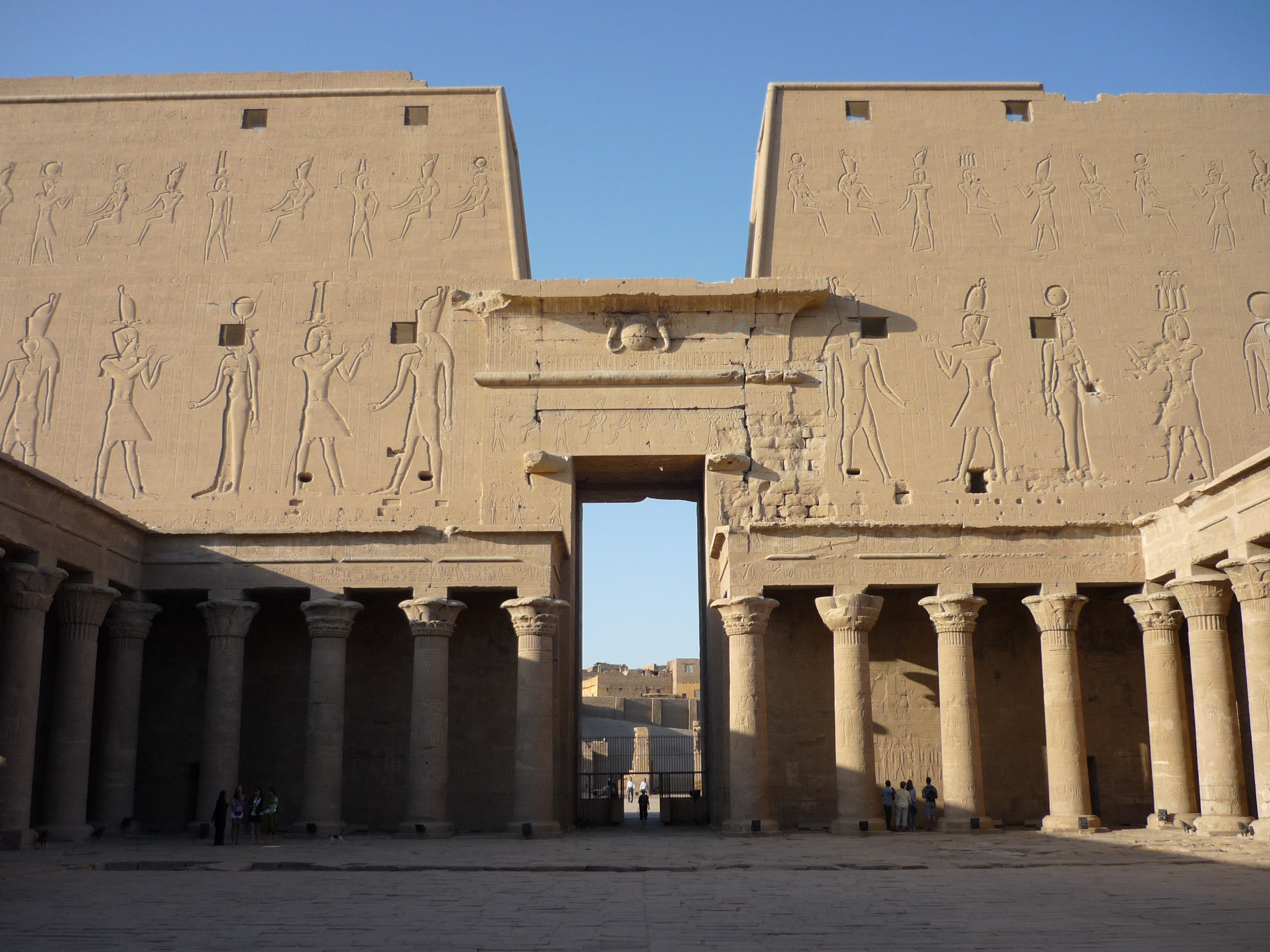
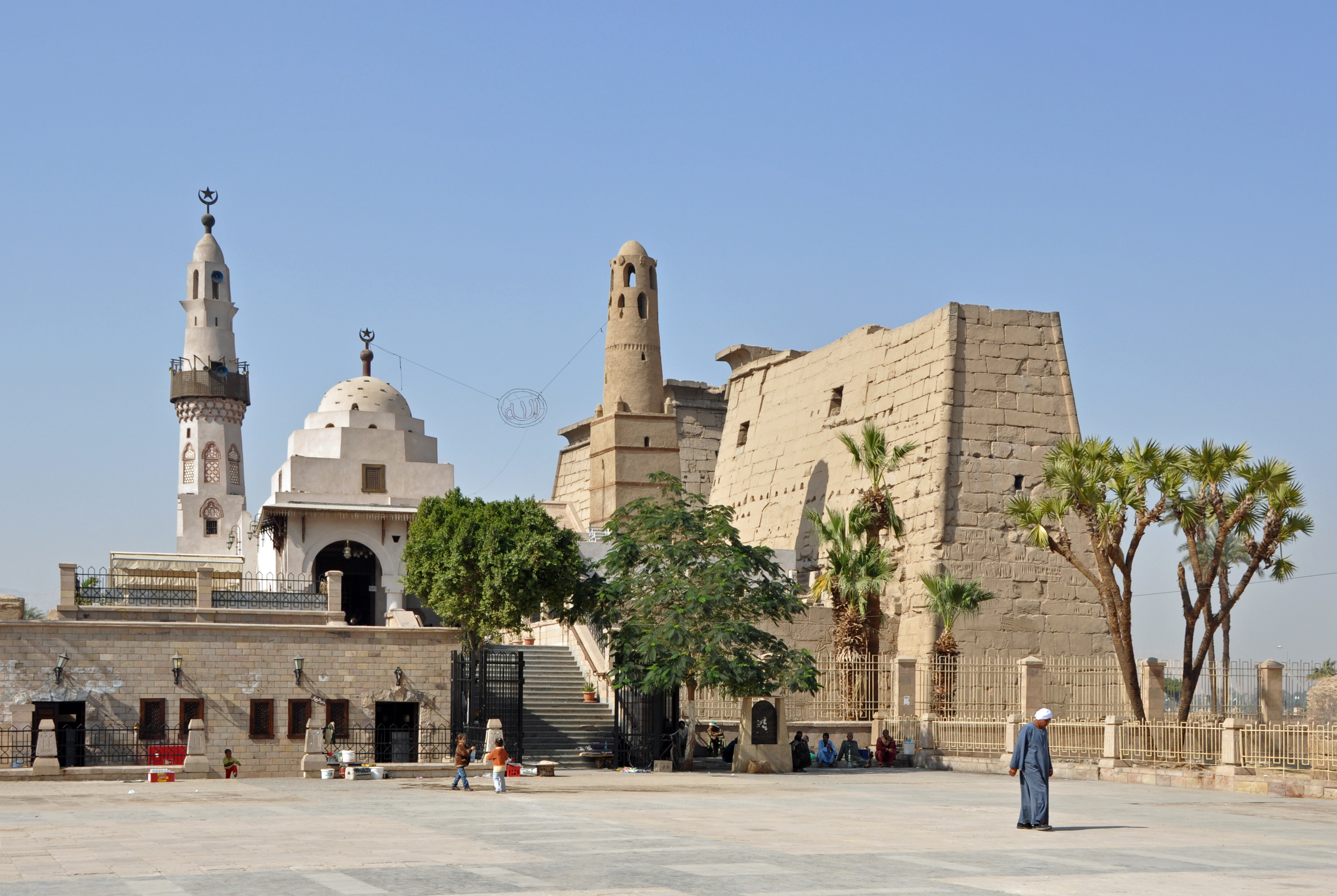
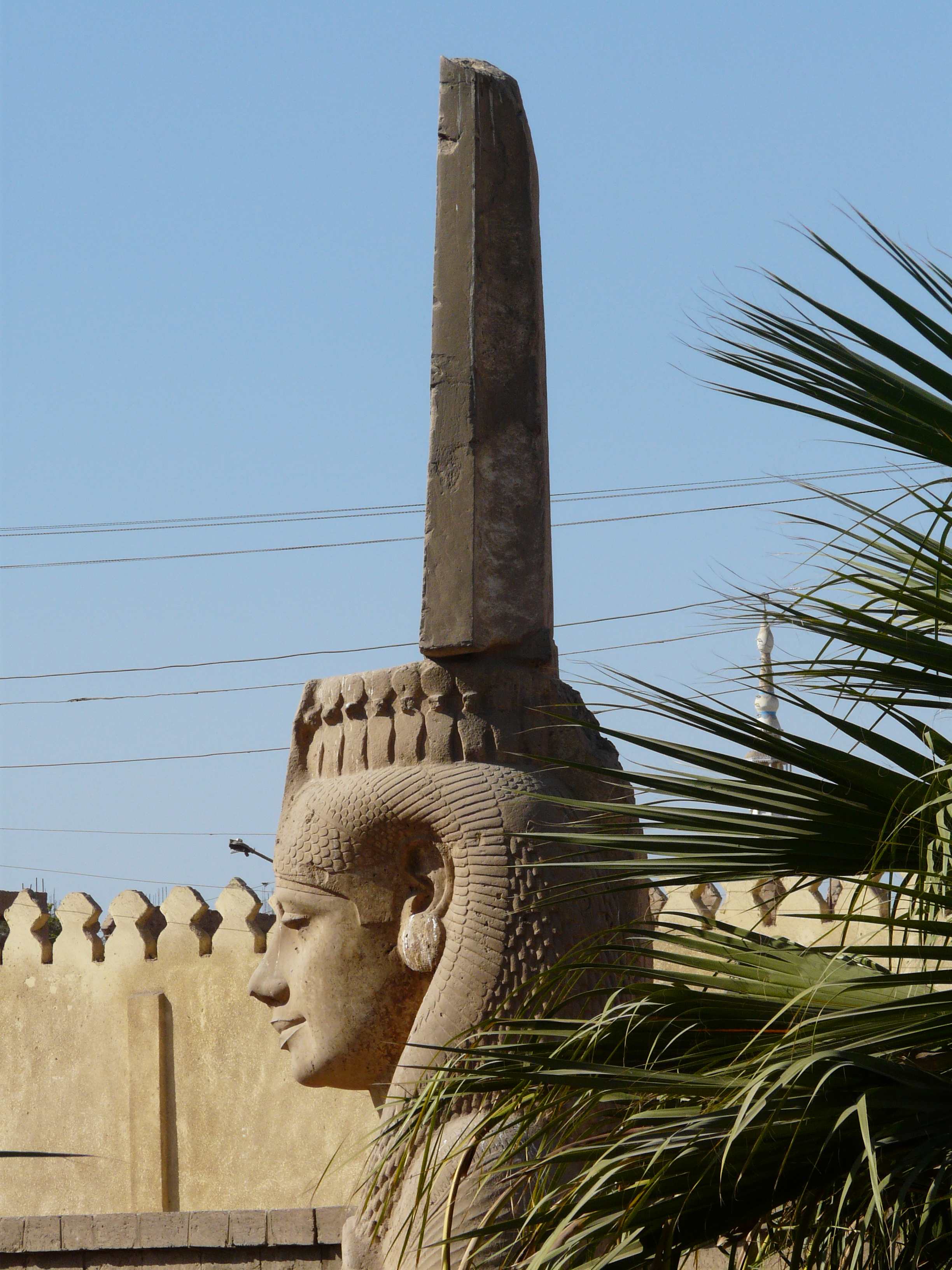
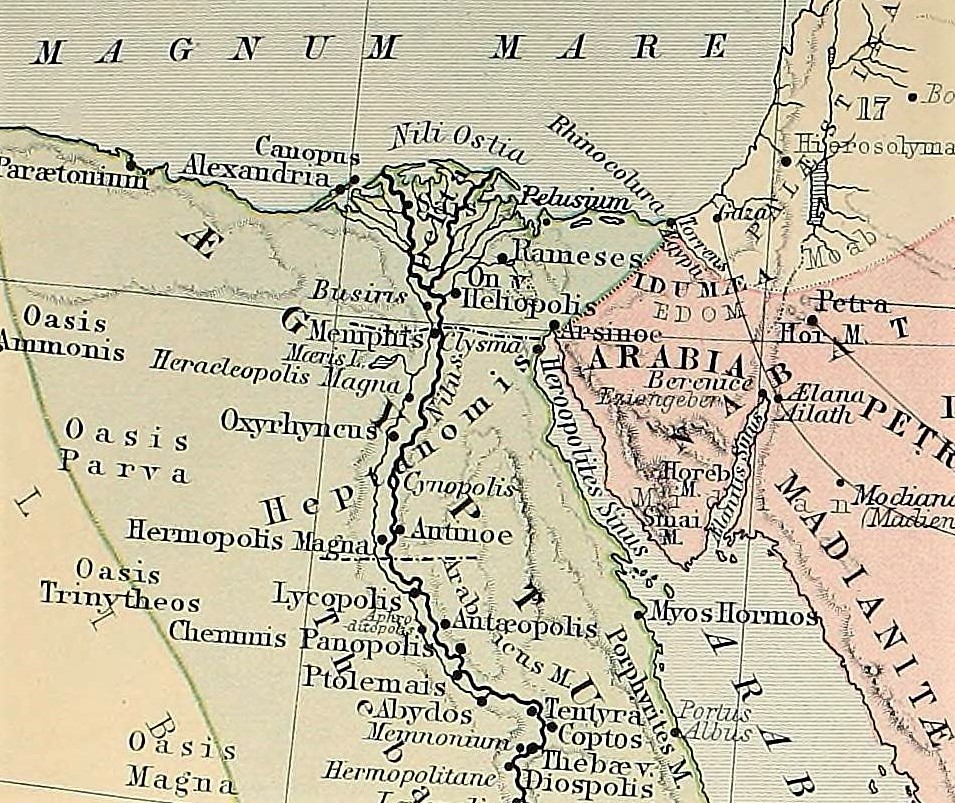
Cynopolis, comprising two ancient Egyptian cities, was significant for its role in the worship of the canine deity Anubis. Situated in Upper Egypt, Cynopolis Superior was known for its temple dedicated to Anubis, while Cynopolis Inferior lay in Lower Egypt's Busirite nome. These cities were notable for their religious importance, with Cynopolis Superior even featuring a burial ground for dogs, highlighting the cultural significance of animals in ancient Egyptian religion. In the 11th century BCE, Cynopolis Superior faced destruction at the hands of Nubia's viceroy, Pinehesy, under Ramses XI's reign. Both cities later evolved into Christian bishoprics, underscoring their continued prominence through the Classical and Post-Classical periods. Today, the remnants of these sites offer valuable insights into the religious and cultural dynamics of ancient Egypt.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Cynopolis
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Egypt
- Source
- Wikipedia