Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
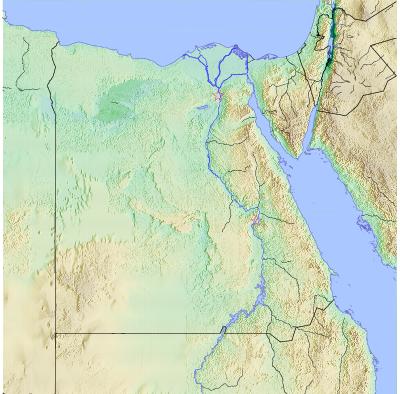
Location
About
El Hiba, also known as Tayu-djayet in antiquity, is an archaeological site of significant historical importance located in the Bani Suwayf governorate of modern Egypt. It was a key frontier town during the late 20th to the 22nd Dynasties, serving as a boundary between the territories of the High Priests of Amun in Thebes and the royal seat in Tanis. The site features massive enclosure walls, with bricks stamped by High Priests Pinedjem I and Menkheperre, indicating its strategic and defensive significance. Additionally, King Shoshenq I constructed a temple dedicated to Amun-Great-of-Roarings, which was further adorned by his son, Osorkon I. Despite its archaeological richness, El Hiba has faced threats from looting, particularly following the 2011 Egyptian Revolution, which has compromised its preservation.
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Egypt
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Egypt

Ballana
Cemetery with tombs and burial mounds
Elkab
Ancient Egyptian city with temples and tombs.
Elephantine
Island with temples and ancient papyri.

Saft el-Hinna
Ancient city with temples and necropolises

Mendes
Ancient city with significant religious structures.

Leontopolis
Ancient city with temples and provincial capital