Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Tell es-Sawwan is a significant Neolithic archaeological site in Saladin Province, Iraq, serving as a type site for the Samarran culture. Situated on a high cliff overlooking the Tigris River, the site encompasses a large oval mound with distinct habitation layers. This site contains evidence of irrigation agriculture, indicative of the settlement's adaptation to unreliable rainfall. Notable features include defensive ditches, large mudbrick houses, granaries, and underfloor graves with terracotta and alabaster statuettes. The presence of fine Samarran ware and marble vessels suggests the settlement's prosperity. Radiocarbon dating places the site in the 6th millennium BCE, highlighting its early and significant role in the development of agriculture and Samarran culture in Mesopotamia.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Tell es-Sawwan
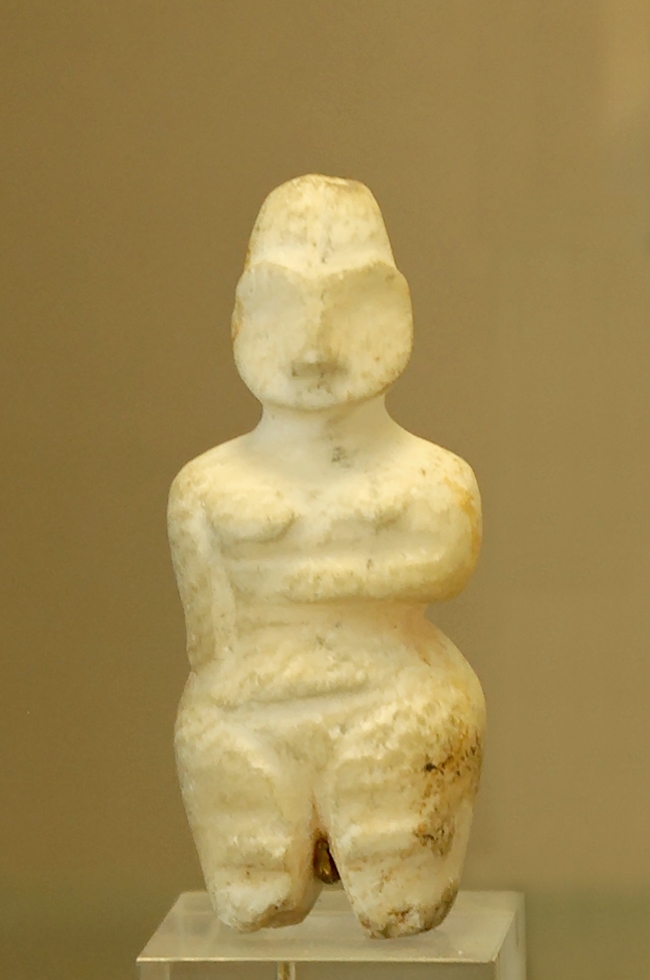



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Storage Structures
Defensive Structures
Burial and Funerary Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Iraq
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Iraq

Tell al-Hawa
Ancient settlement with significant archaeological features
Tell Madhur
Ancient settlement mound with preserved Ubaid house

Nineveh
Ancient Assyrian city with monumental ruins

Isin
Ancient city with temples and walls.

Uruk
Ancient Sumerian city with monumental structures
Hadji Muhammed
Early Ubaid culture painted pottery site.