Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
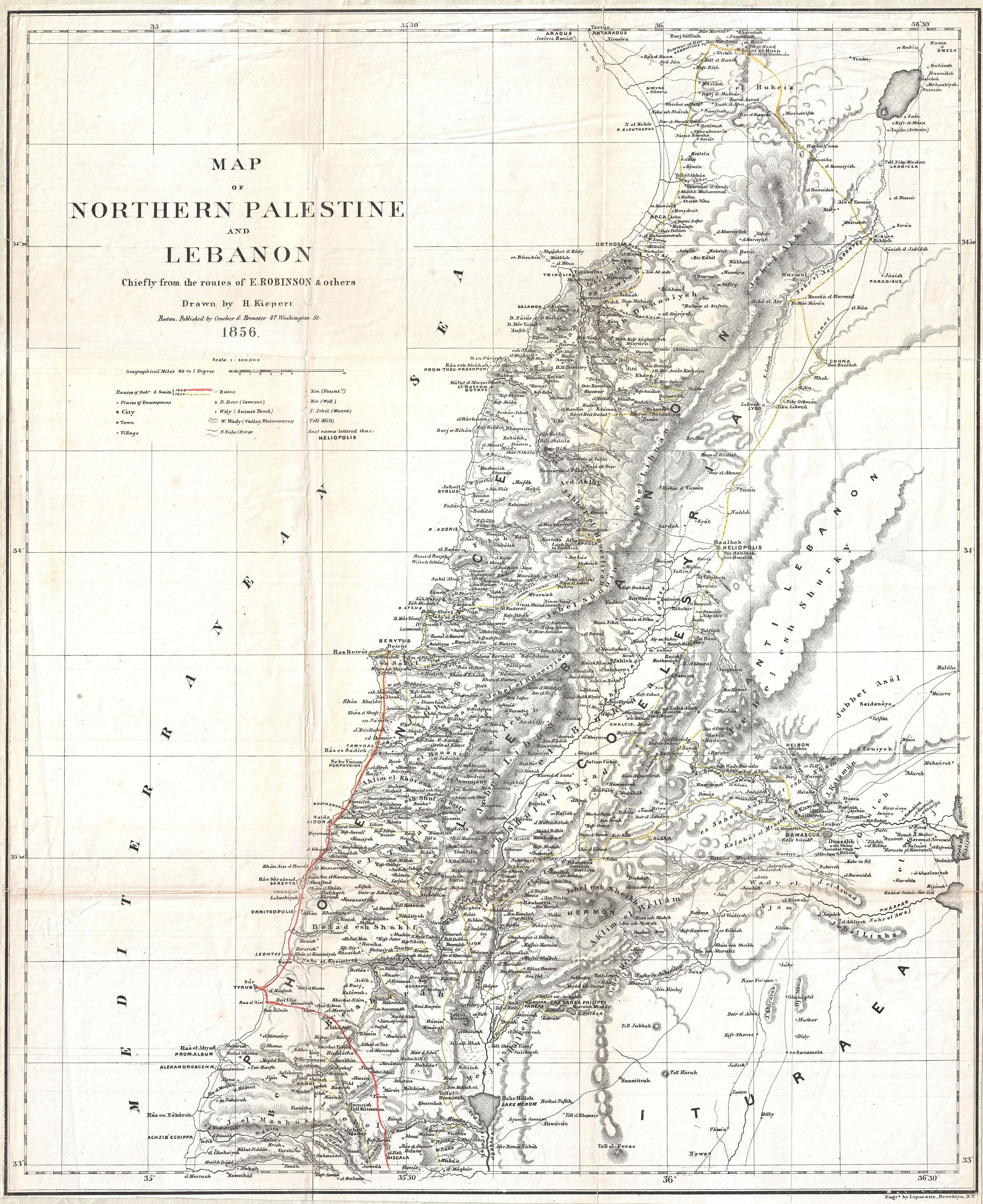
Location
About
Sidon, located on the Mediterranean coast of Lebanon, is an ancient city with a history that spans several millennia, dating back to early prehistory. As a prominent Phoenician city, Sidon was known for its extensive trade, glass production, and purple dye industry, which left a significant archaeological footprint. The city has seen numerous conquerors, from the Egyptians in the Late Bronze Age to the Persians, Greeks, and Romans. Each of these periods has contributed to its rich archaeological record, including temples, tombs, and glassworks. The city's strategic location and harbors played a crucial role in its development as a major trade hub in antiquity. Sidon's historical significance is further underscored by its continuous occupation and adaptation through Byzantine, Crusader, and Ottoman periods, leaving a diverse and layered archaeological legacy.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Sidon
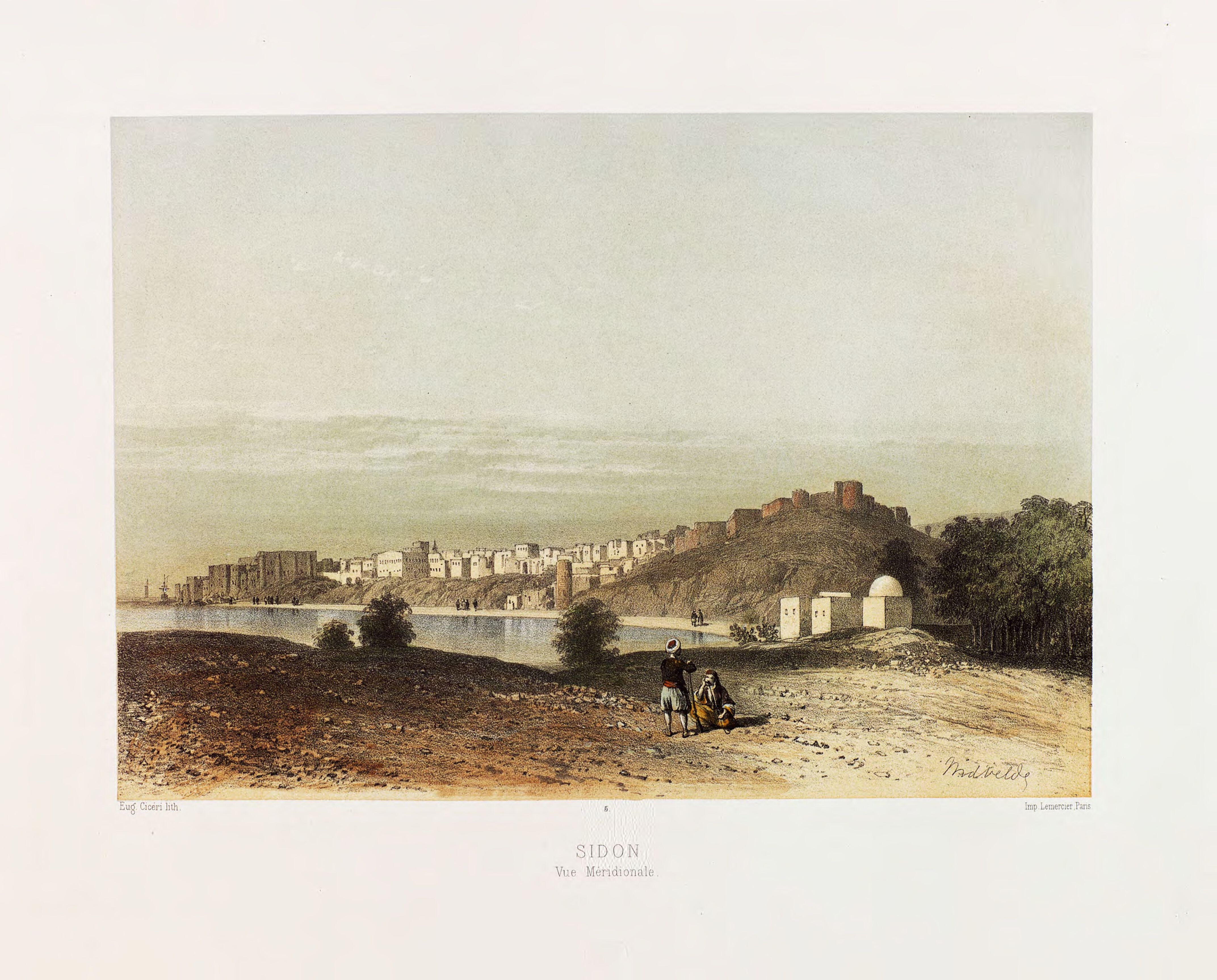
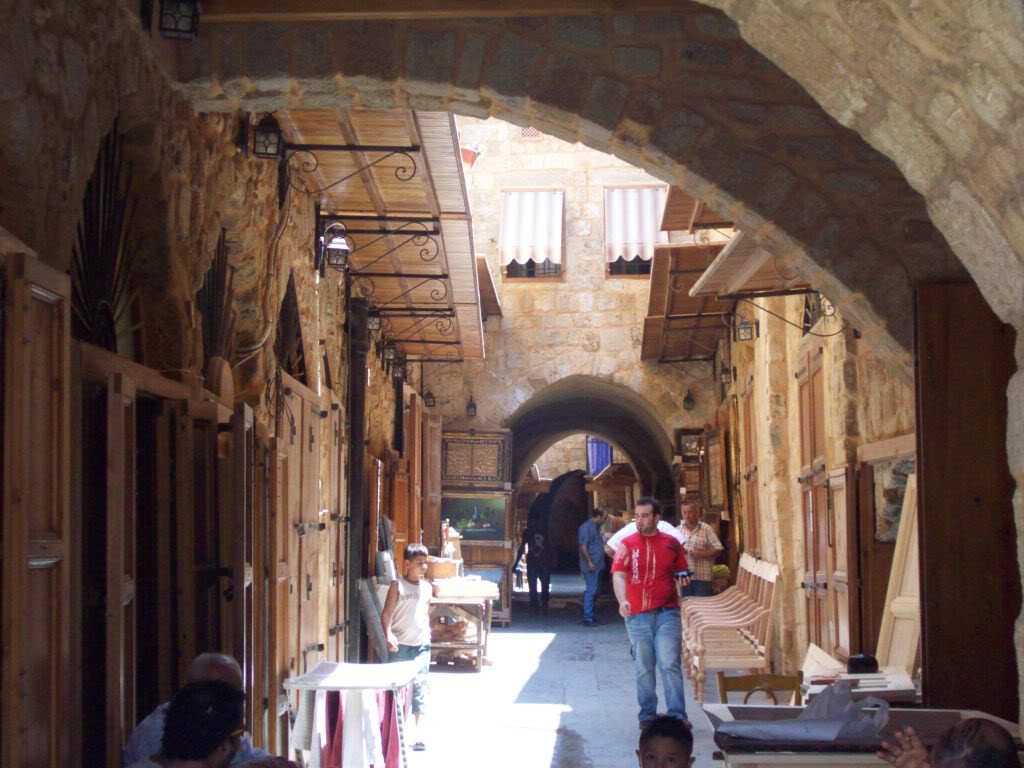



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Water Management Features
Public and Civic Structures
Burial and Funerary Structures
Industrial and Craft Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Lebanon
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Lebanon

Byblos
Ancient city with layered historical strata

Stelae of Nahr el-Kalb
Rock reliefs and inscriptions near Beirut, Lebanon

Jbaa
Neolithic to contemporary Lebanese archaeological site
Baalbek
Ancient city with Roman temples and ruins
Sarepta
Phoenician city with diverse archaeological finds

Chamaa
Historical castle on strategic hill.
