Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
The Temple of Eshmun, located near Sidon in modern-day Lebanon, is a significant archaeological site that served as a center for the worship of Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. Originally constructed in the 6th century BCE by the Sidonian king Eshmunazar II, the temple complex was expanded over the centuries by subsequent rulers such as Bodashtart and Yatonmilk. The site is noted for its diverse architectural styles, reflecting the various cultural influences from the Achaemenid to the Roman periods. Key features include a monumental podium, Greco-Persian style temple remains, ritual ablution basins, and a network of water channels. The site was occupied from the 7th century BCE until the 8th century CE, witnessing periods of prosperity and decline, especially after the rise of Christianity. Excavations have uncovered valuable Phoenician inscriptions and artifacts, providing insights into the temple's religious significance and the broader history of ancient Sidon.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Temple of Eshmun
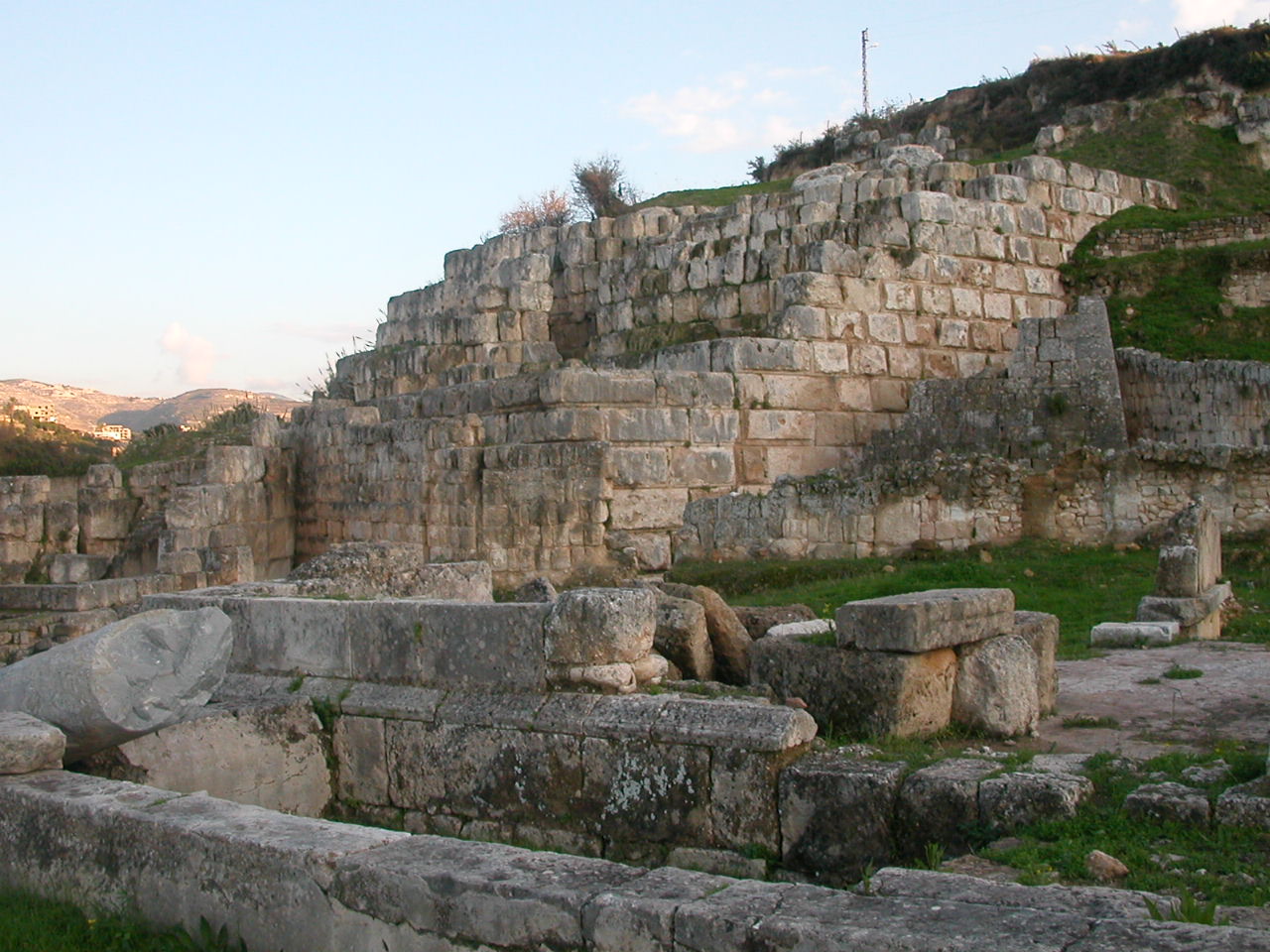
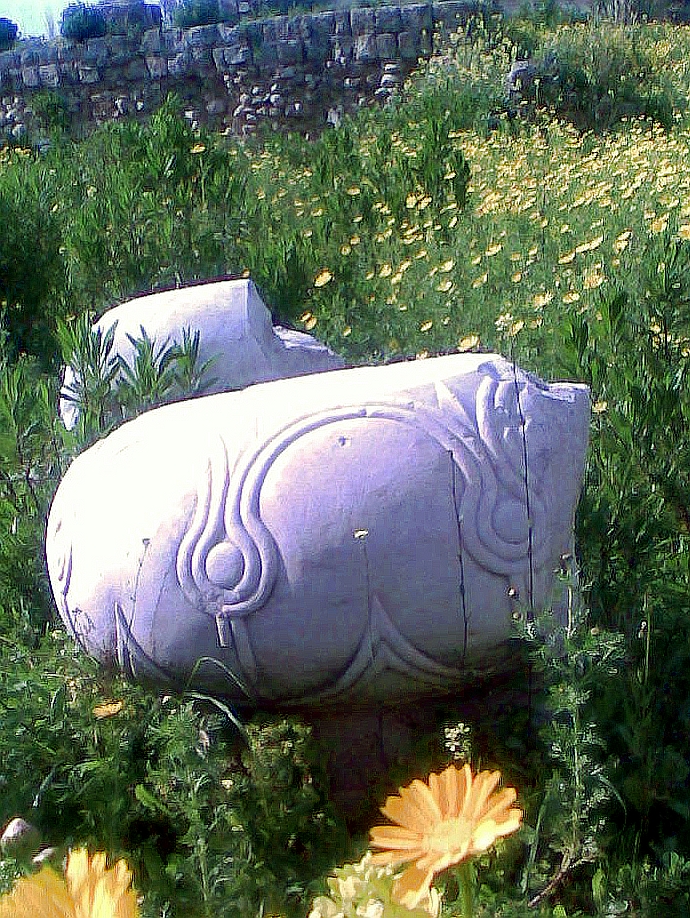



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Water Management Features
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Agricultural and Land Use Features
Transportation and Communication Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Lebanon
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Lebanon

Byblos
Ancient city with layered historical strata

Amioun
Ancient hill town with Roman temples.

Stelae of Nahr el-Kalb
Rock reliefs and inscriptions near Beirut, Lebanon

Arqa
Iron Age city-state with Neolithic origins
Sarepta
Phoenician city with diverse archaeological finds

Sidon
Ancient Phoenician city with rich history
