Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Germa, known as Garama in ancient times, was the capital of the Garamantian Kingdom located in the northeastern Sahara Desert within modern-day Libya. The site was a significant hub during the Late Classical Period, serving as a fortified town with a population of about four thousand inhabitants and additional settlements nearby. The Garamantes, a Berber-speaking people, used this site as their base to conduct raids against the Roman Empire, taking advantage of their strategic location in the desert. The Romans, under Emperor Septimius Severus, briefly captured the city in 203 CE. However, it was eventually conquered by Uqba ibn Nafi during the Arab expansion in 669 CE. The archaeological features, including remnants of towns and villages, reflect its historical importance as a center of power and trade in the region.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Germa
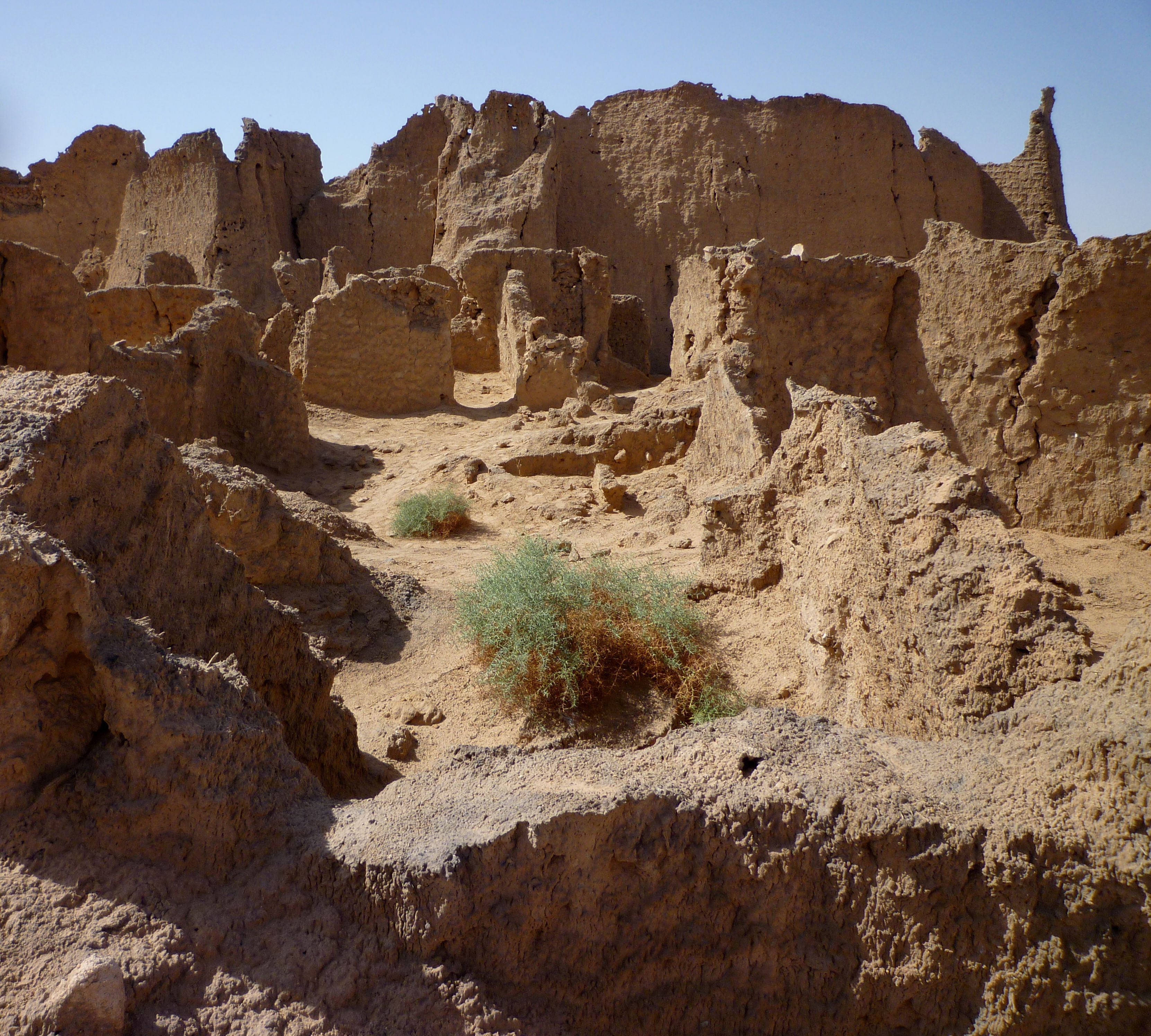

Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Transportation and Communication Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Libya
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Libya

Cyrene, Libya
Ancient Greek and Roman city remains
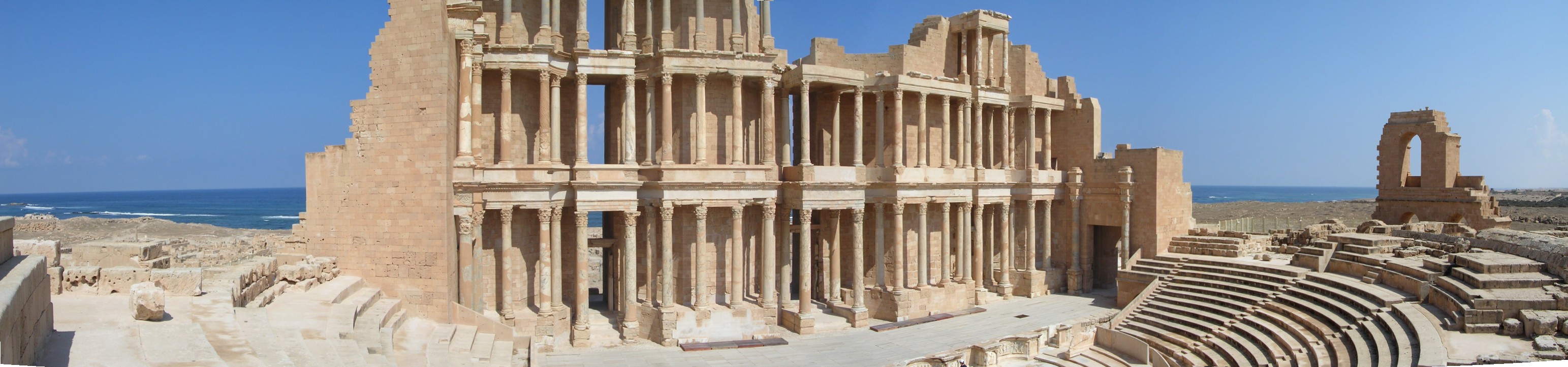

Sabratha
Ancient city with Roman and Byzantine ruins.

Archaeological Site of Sabratha
Excavated Roman and Numidian city in Libya

Gerisa
Ancient Roman city with agricultural structures
Mausoleum of Gasr Doga
Imposing first-century Libyco-Punic mausoleum

Olbia, Libya
Byzantine town with mosaic churches