Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Sabratha, located on the Mediterranean coast west of Tripoli, Libya, is an ancient city with rich archaeological significance. Established around 500 BCE as a Phoenician trading post, it later fell under Carthaginian influence and became part of the Roman Empire following the Punic Wars. The city was significantly romanized during the 2nd and 3rd centuries CE, reaching its architectural peak under the Severan dynasty. Notable structures include Roman temples, public baths, a theatre, and vibrant mosaics, reflecting the city's prominence in Roman North Africa. Sabratha suffered substantial damage from a 4th-century earthquake but experienced a brief revival under Byzantine rule in the 6th century. Following the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, the city declined and trade shifted elsewhere. Despite erosion challenges, Sabratha remains a key site for understanding the region's ancient history.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Sabratha
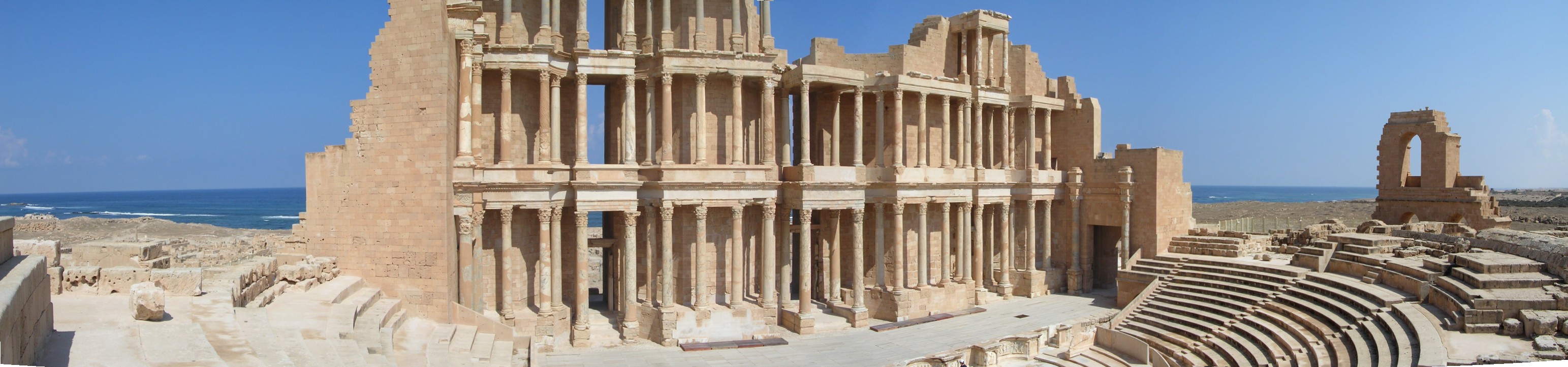
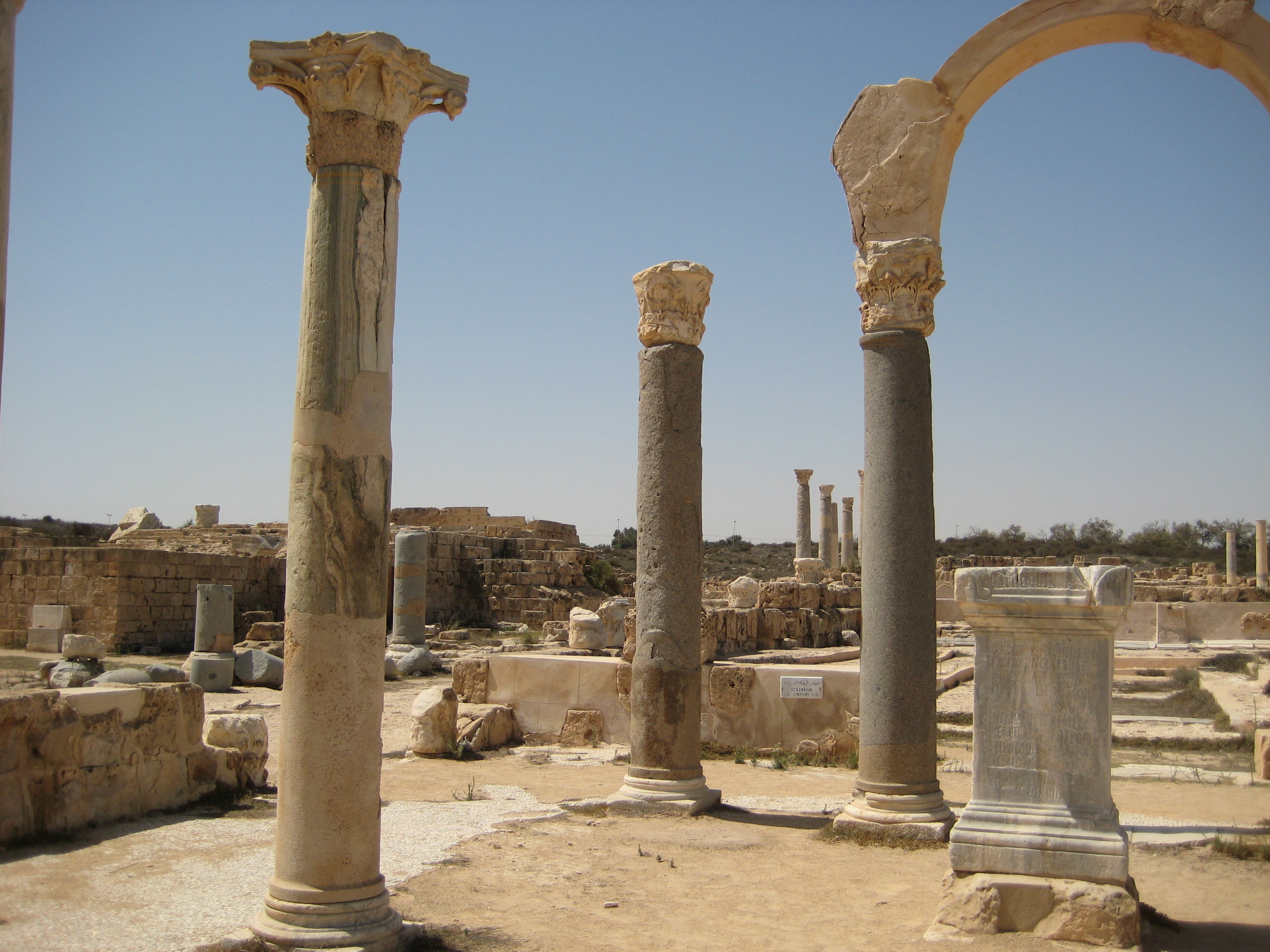
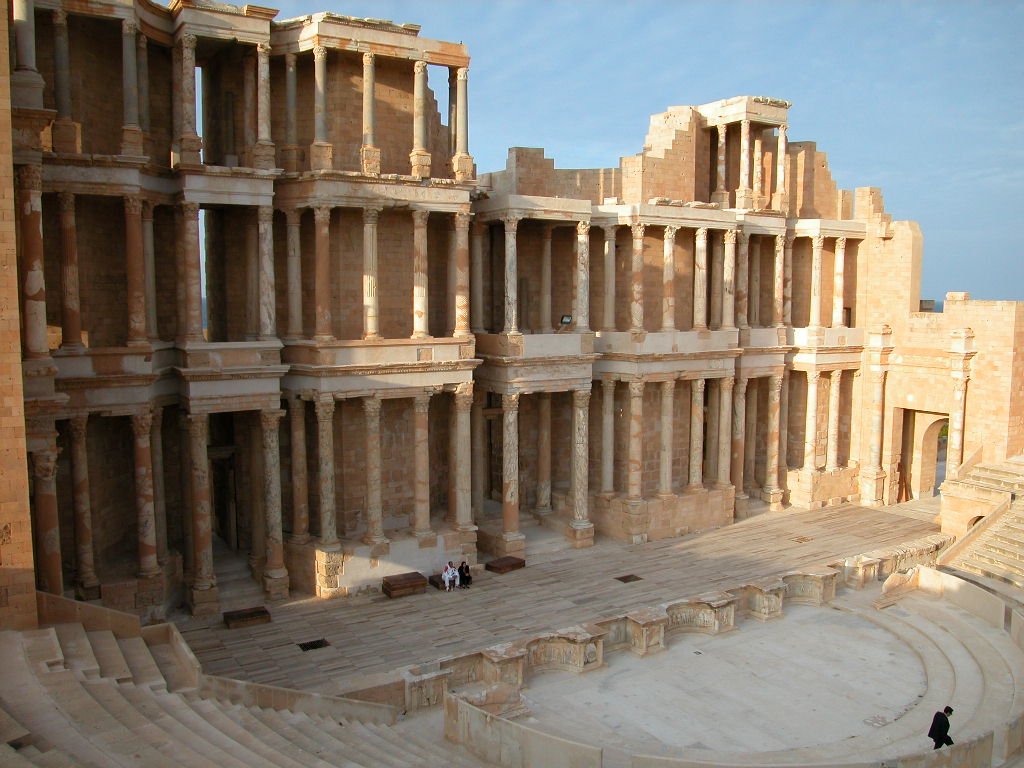



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Public and Civic Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Libya
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Libya

Cyrene, Libya
Ancient Greek and Roman city remains
Ptolemais, Cyrenaica
Ancient city with well-preserved ruins.
Mausoleum of Gasr Doga
Imposing first-century Libyco-Punic mausoleum
Extramural Sanctuary of Demeter and Persephone, Cyrene
Terraced sanctuary with temples and votive artifacts
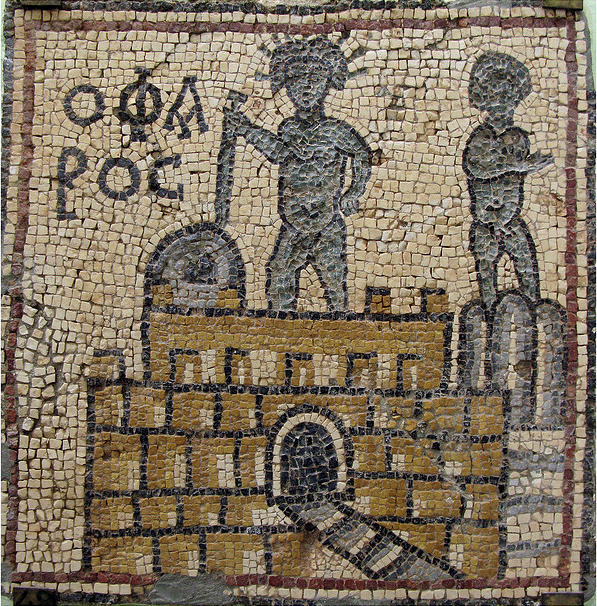

Olbia, Libya
Byzantine town with mosaic churches
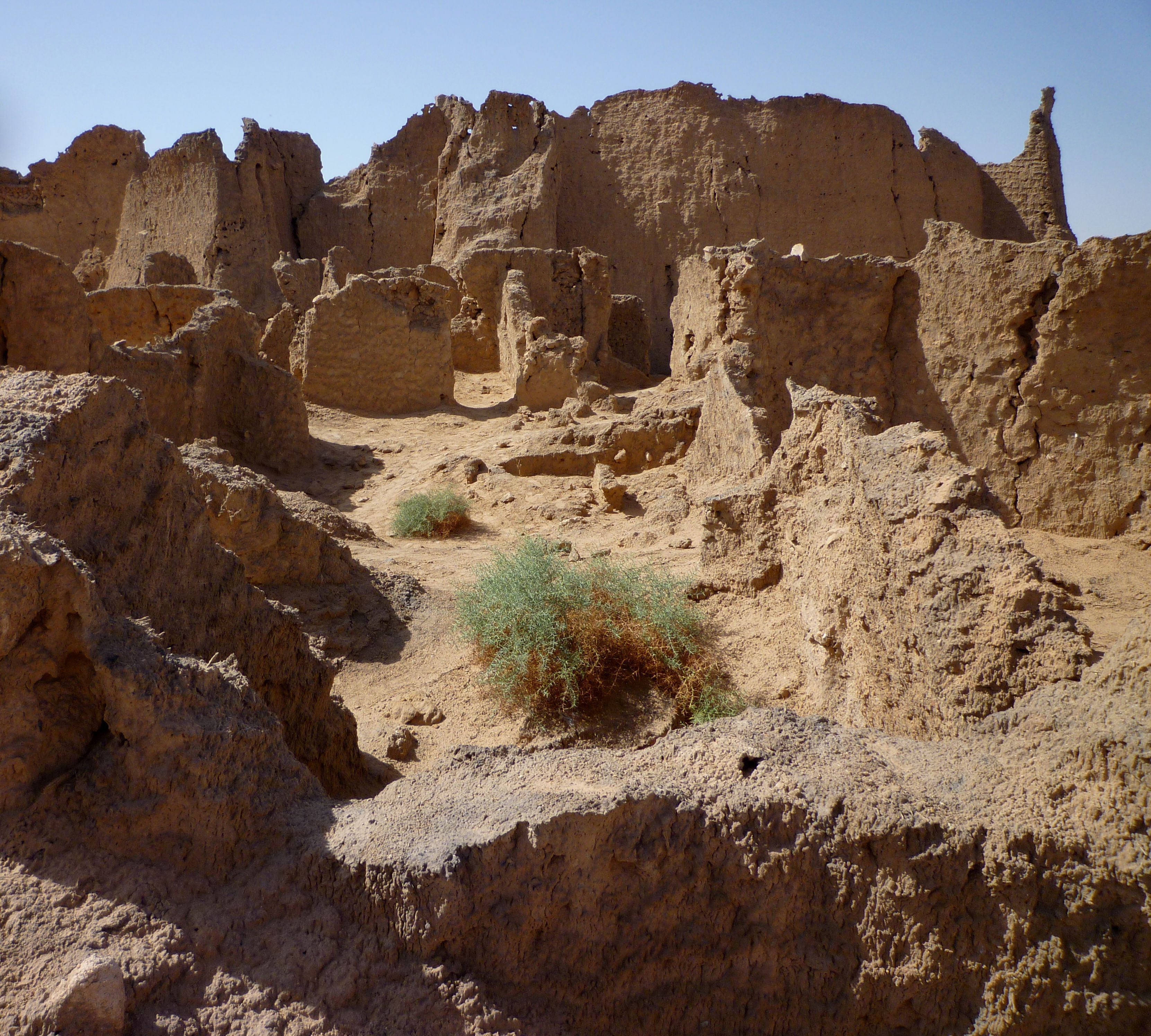

Germa
Ancient Garamantian capital in Sahara Desert
