Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
The Chemurchek culture is a Bronze Age archaeological culture situated in western Mongolia and neighboring regions, including the Dzungarian Basin of Xinjiang and eastern Kazakhstan. It flourished between approximately 2750 and 1900 BCE, following the Afanasievo culture. Characterized by large rectangular stone fences surrounding collective tombs, the culture featured unique anthropomorphic standing stones with flattened faces, straight noses, and globular eyes. These stelae are indicative of complex burial practices and suggest cultural exchanges or migrations from Western Europe. The Chemurchek people left behind artifacts such as stone bowls, bone tools, ceramics, and bronze items, highlighting a sophisticated material culture. Genetic analysis indicates a blend of Afanasievo and local populations, with European connections suggested by similar stelae found in Southern France.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Chemurchek culture
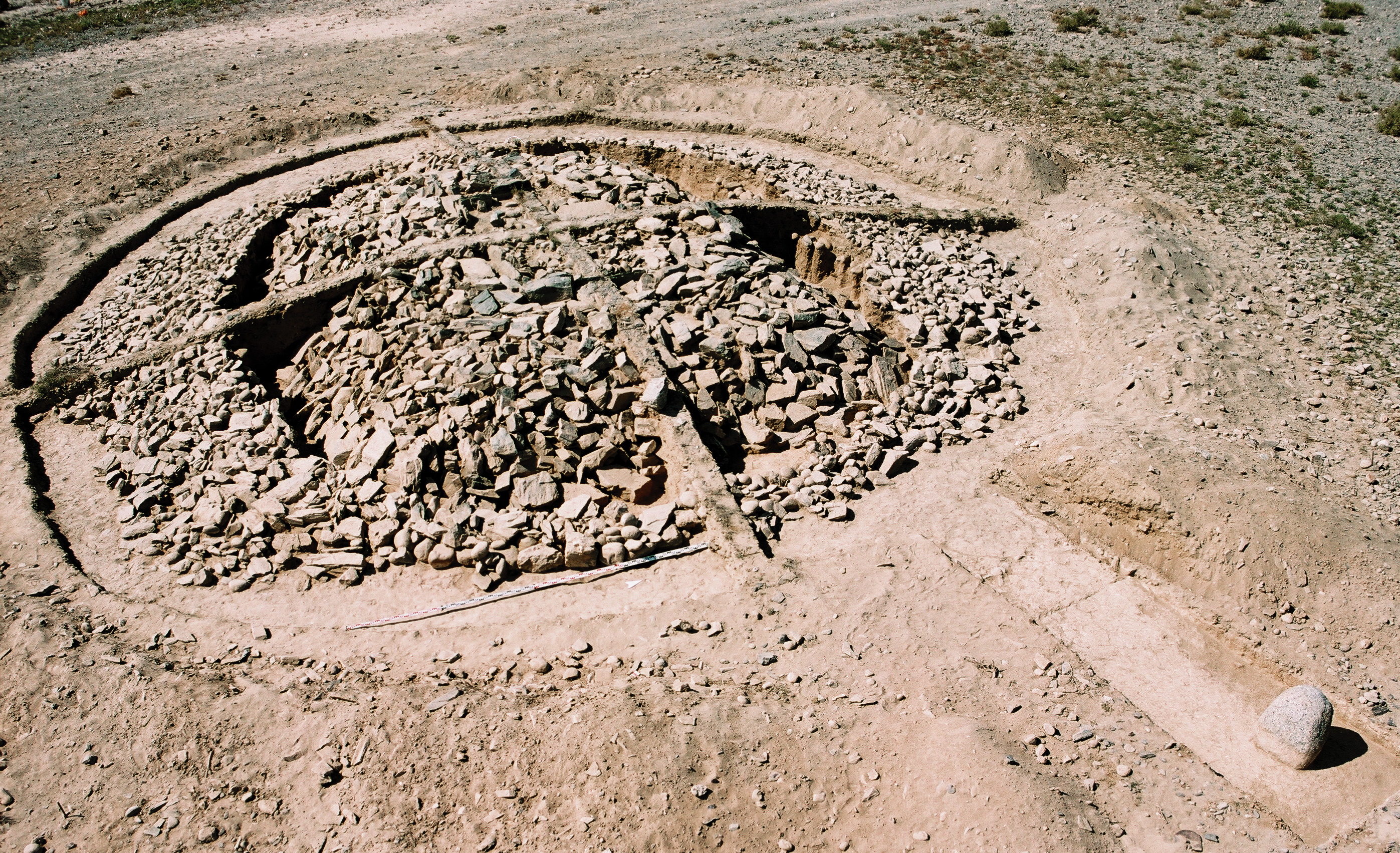
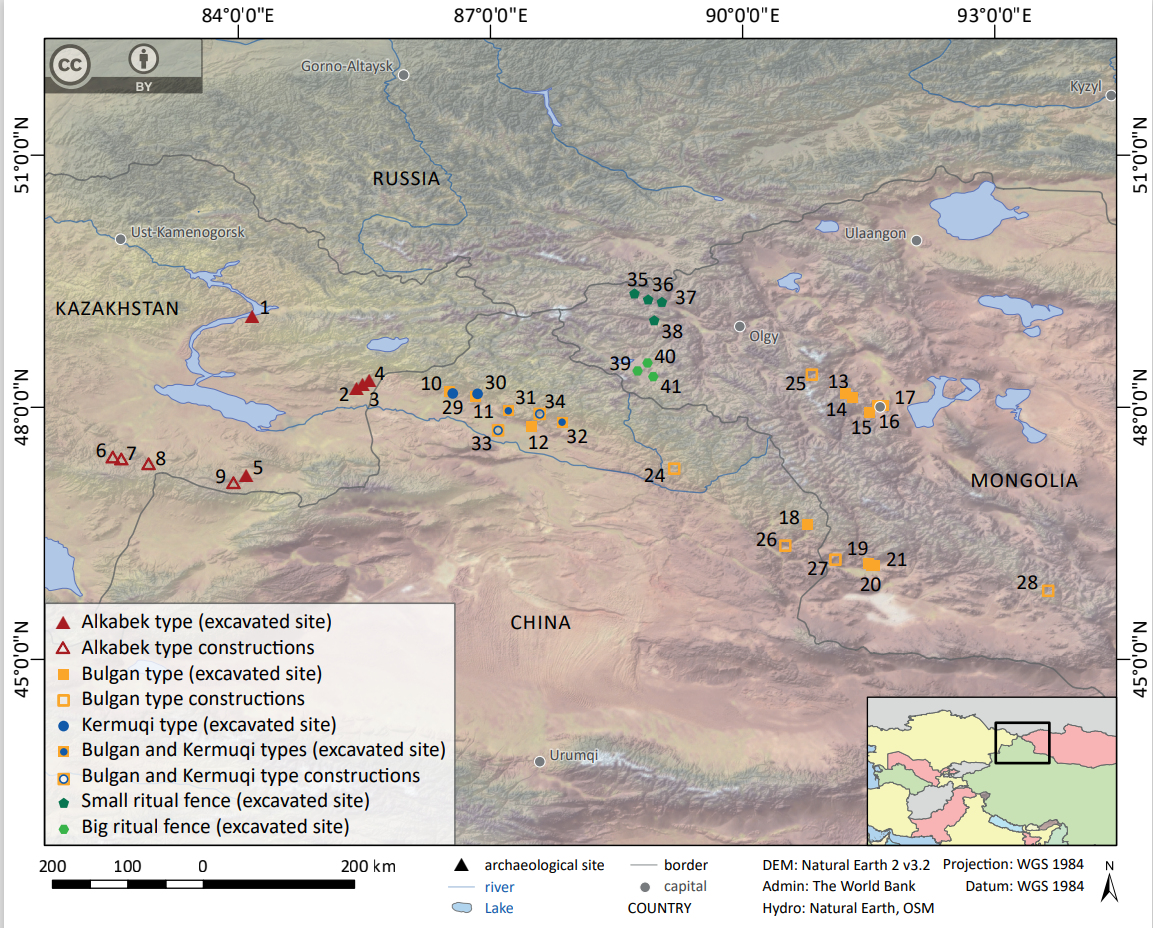

Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Mongolia
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Mongolia

Ordu-Baliq
Ruined Uyghur capital with fortified walls.
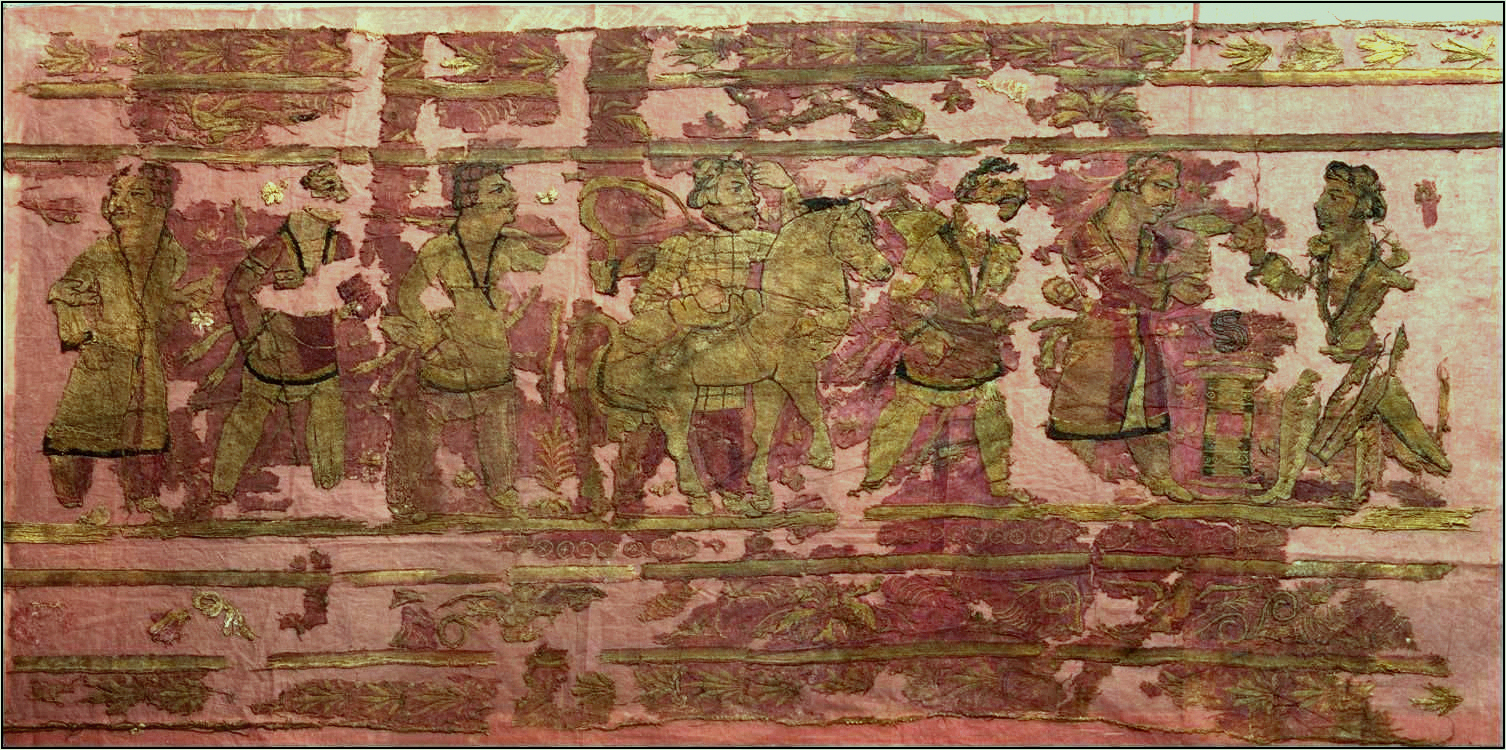

Noin-Ula burial site
Xiongnu burial mounds with preserved artifacts
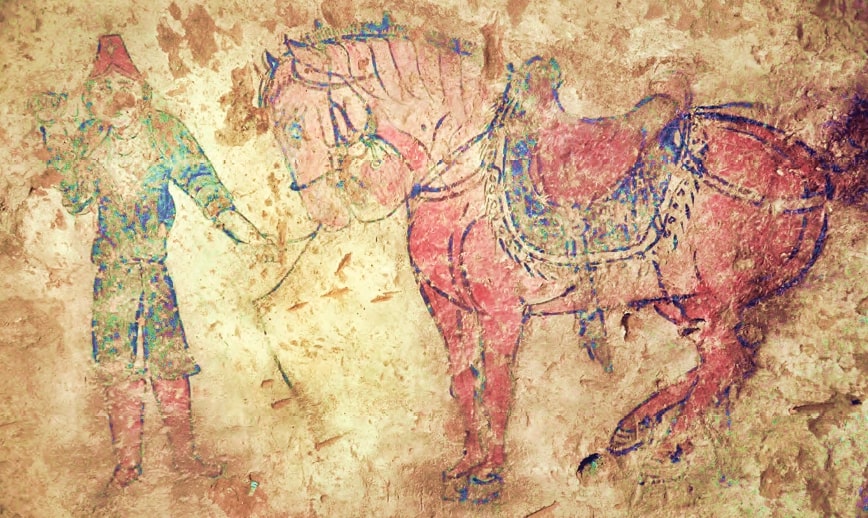

Shoroon Bumbagar tomb
Turkic nobleman tomb with Chinese influence
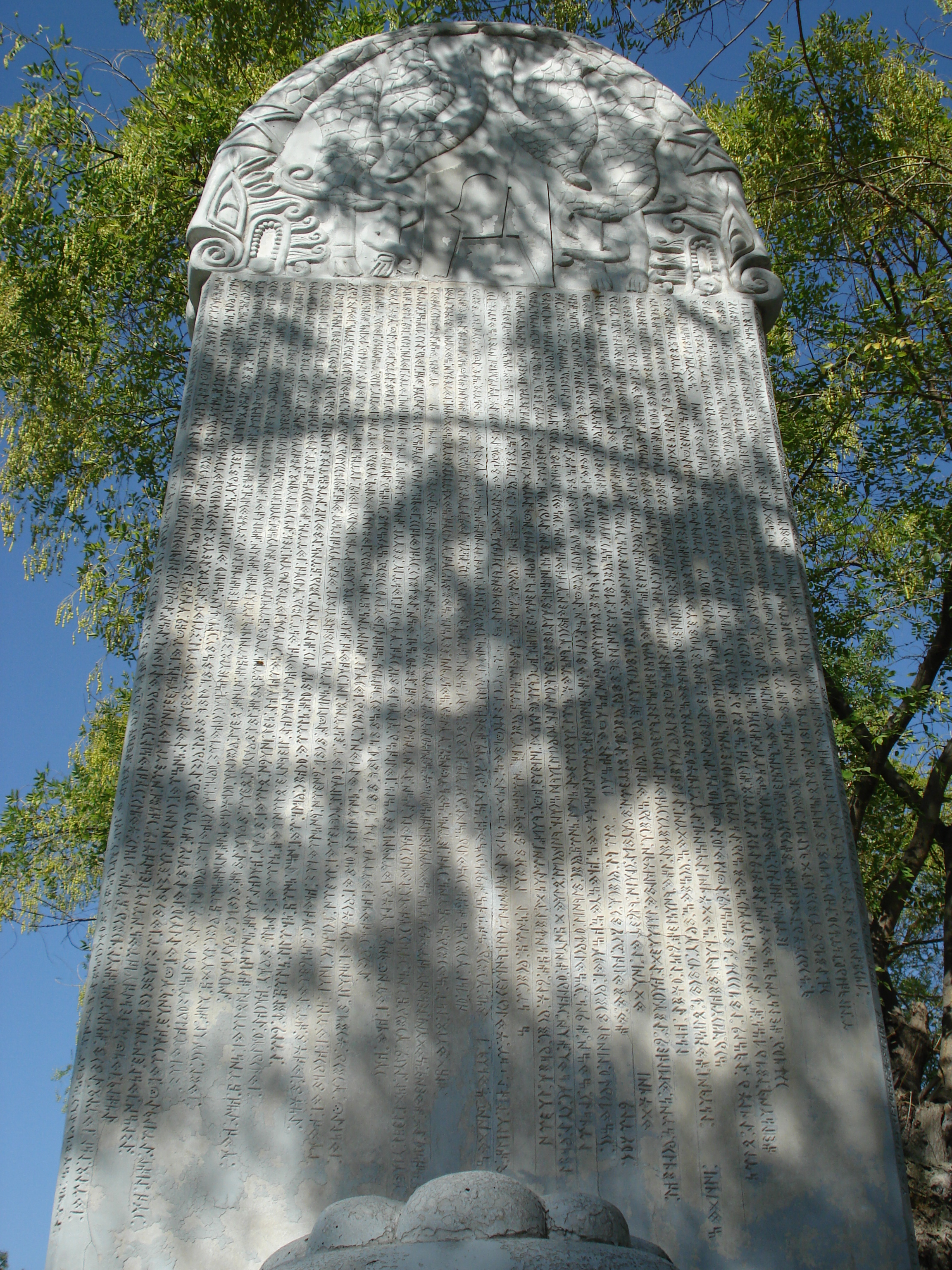

Orkhon inscriptions
Early 8th-century Göktürk memorial steles
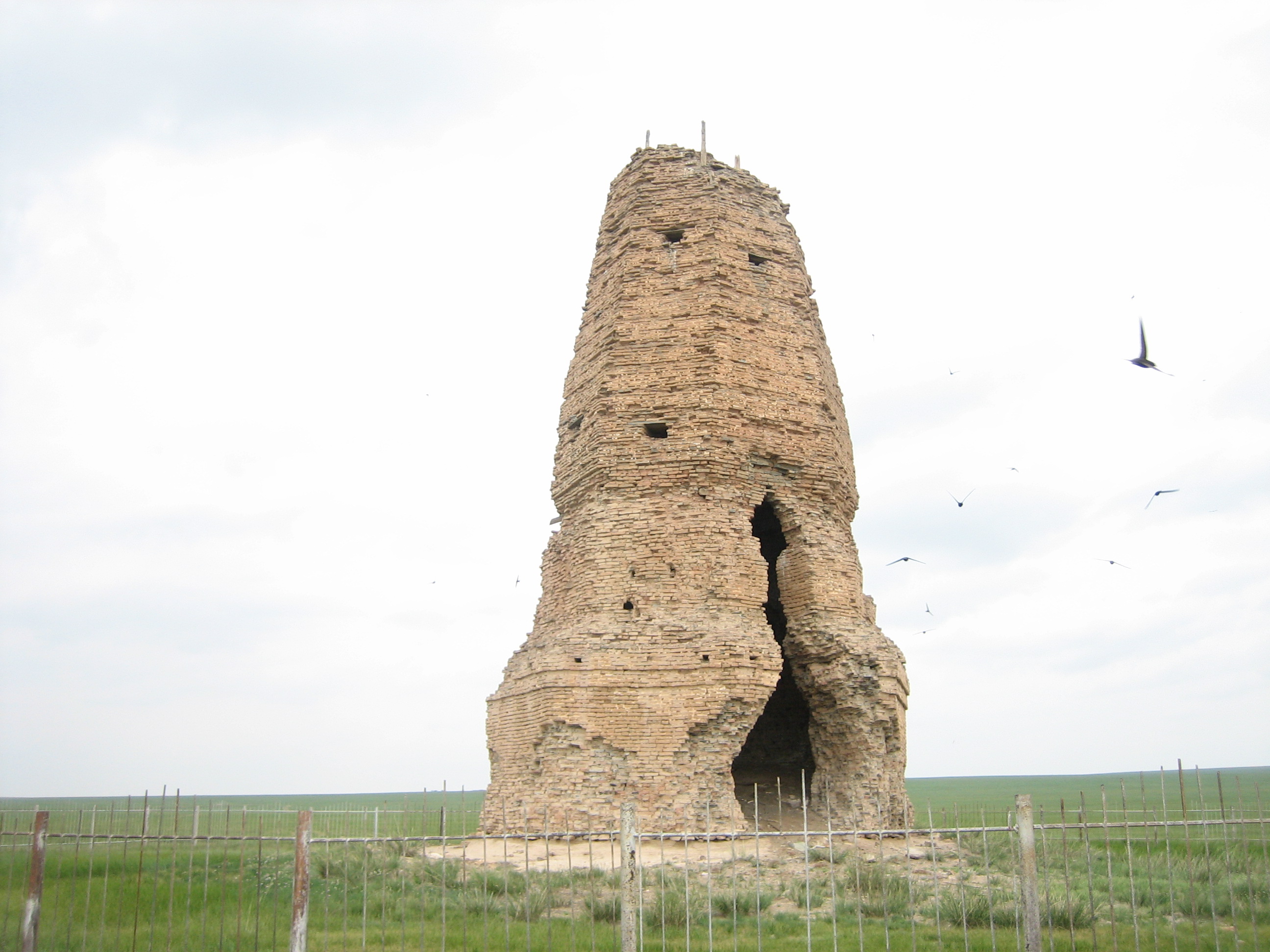

Bars-Hot
Khitan city with mud walls and pagoda.

Khushuu Tsaidam Museum
Museum housing Orkhon inscriptions and monuments