Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
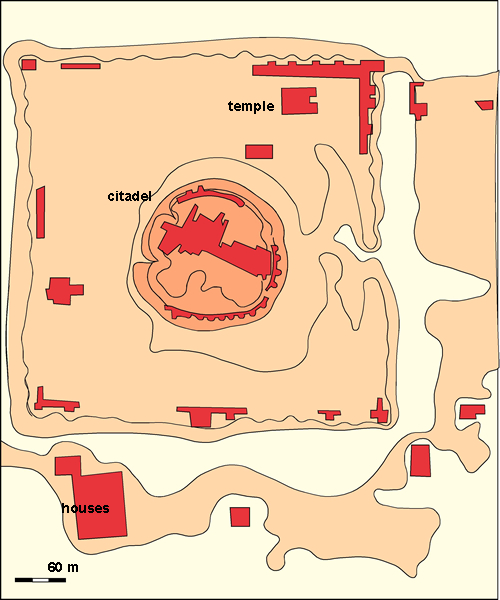
Mundigak is an archaeological site in Kandahar Province, Afghanistan, notable as a key urban center of the Helmand culture during the Bronze Age. Spanning an area of 21 hectares, it was second only to Shahr-i-Sokhta in size. The site reveals a rich cultural sequence from the 5th to the 2nd millennia BCE, displaying architectural and societal complexity with elements such as palaces, temples, and defensive walls. Excavations indicate interactions with regions like Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus Valley. Artifacts include pottery with intricate designs, terracotta figures, and evidence of early metallurgy. Mundigak's significance lies in its demonstration of early urbanization and its role in regional cultural exchanges.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Mundigak
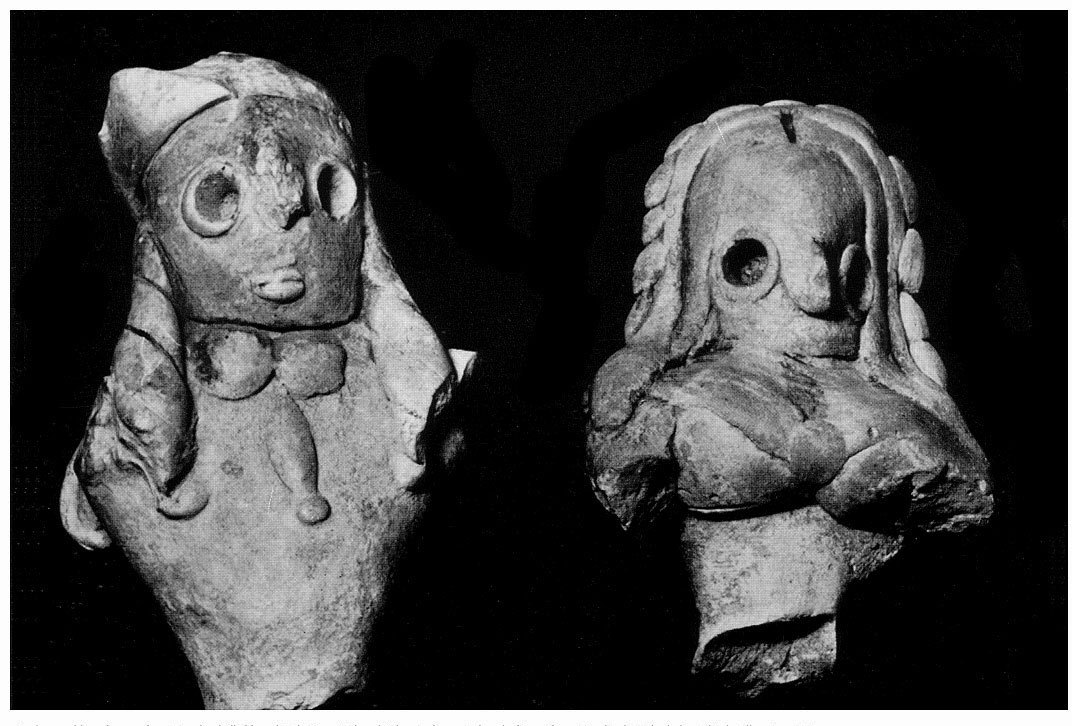
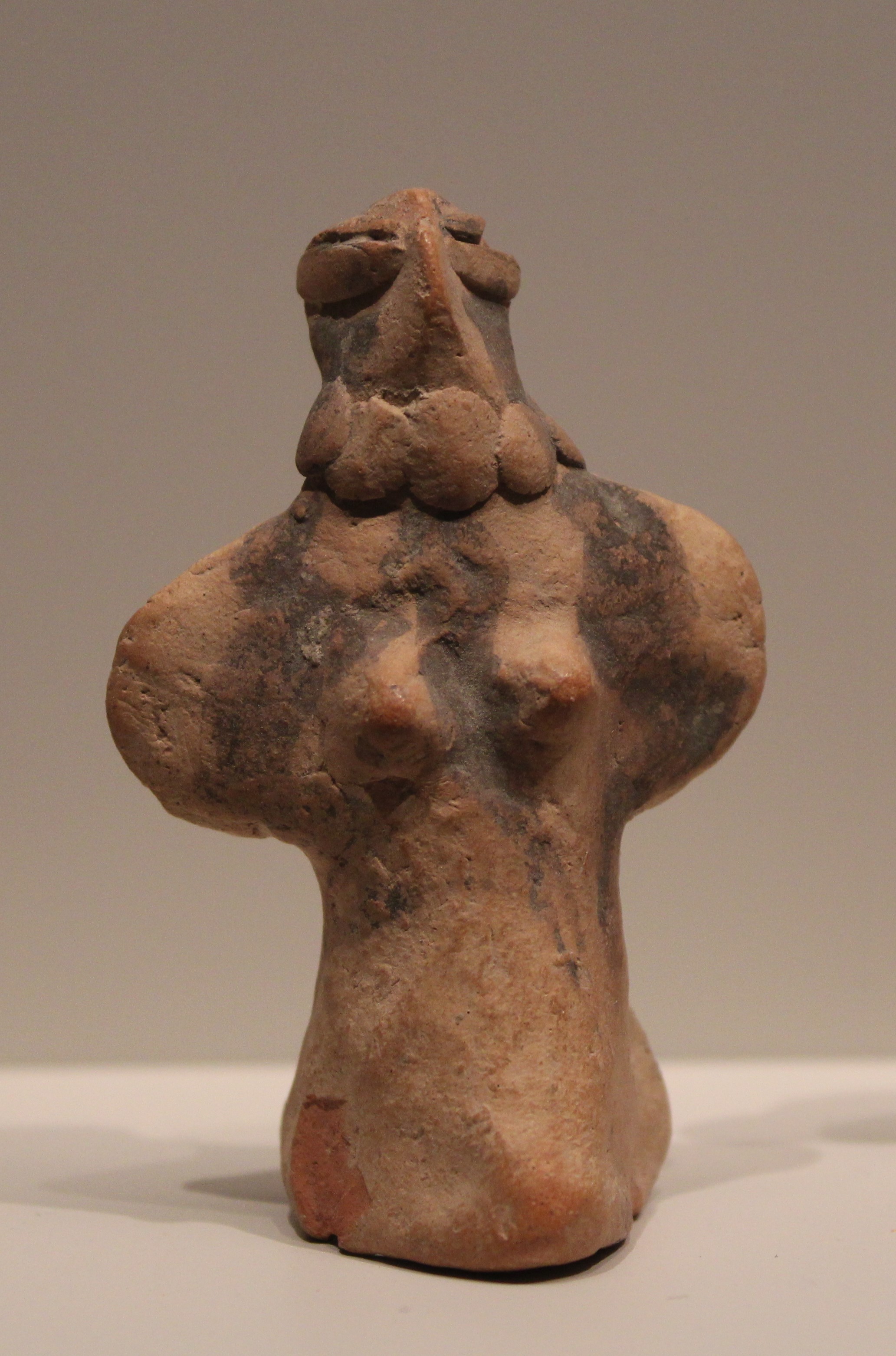



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Water Management Features
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Afghanistan
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Afghanistan
Aq Kupruk
Early stone tools and sculptures discovered.
Yemshi Tepe
Ancient circular fortress with defensive structures
Tepe Fullol
Bronze Age site with treasure cache

Mes Aynak
Buddhist settlement with copper deposits
Dilberjin Tepe
Ancient town with Kushan-era citadel and murals.
Darra-e Kur
Well-stratified rock shelter with artifacts