Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Tapa Shotor, also known as Tape Shotor, was a significant Sarvastivadin monastery near Hadda, Afghanistan, illustrating a confluence of Greco-Buddhist and Hellenistic artistic traditions. The site, dating back to the 1st century BCE, reflects a unique historical timeline that includes periods under Indo-Scythian, Kushan, and Kidarite influences. The monastery's artistic creations, particularly its clay sculptures and statues, showcase the profound impact of Hellenistic art, possibly a result of Greek migration from the Greco-Bactrian cities. Key features of the site include religious structures like stupas and temples, alongside exquisite decorative elements such as statues and reliefs. Despite its historical significance, Tapa Shotor faced destruction by fire in the 9th century CE, ending centuries of religious and cultural legacy.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Tapa Shotor
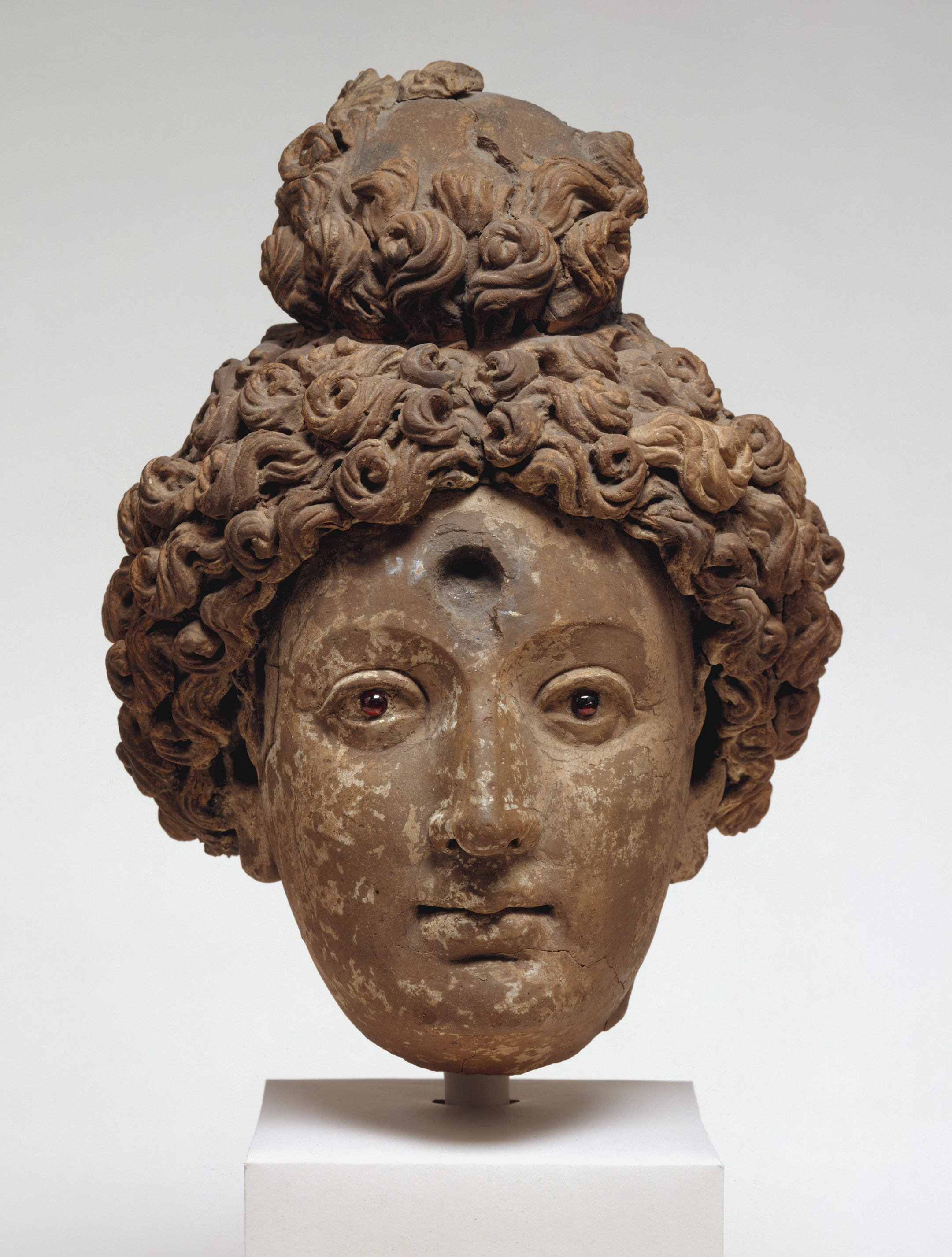

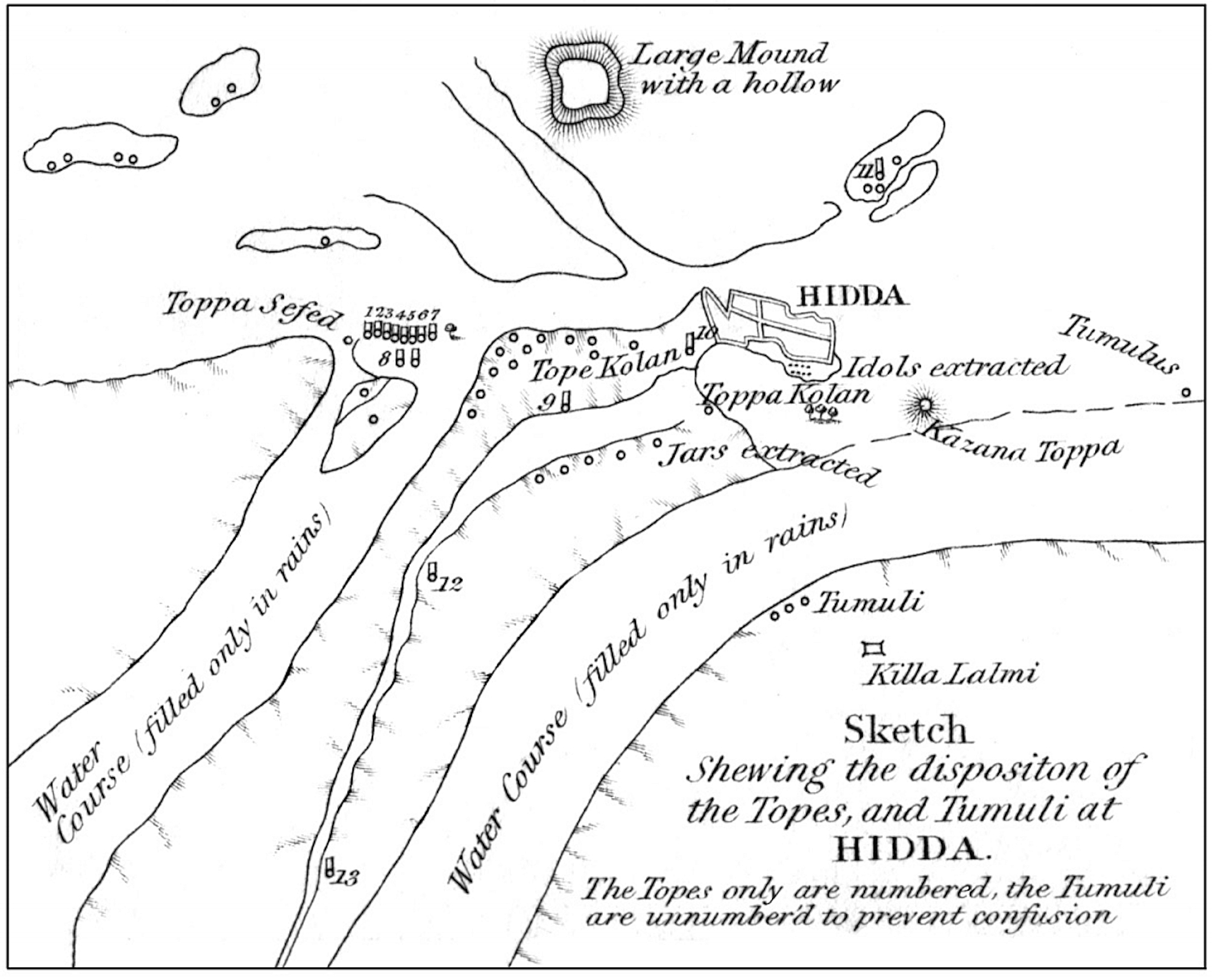
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Religious and Ritual Structures
Artistic and Decorative Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Afghanistan
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Afghanistan

Shewaki
Ancient stupa turned Hindu temple site
Asqalan, Afghanistan
Ancient tomb site near Kunduz, Afghanistan

Takht-e Rostam
Rock-cut Buddhist monastery with stupa.
Dilberjin Tepe
Ancient town with Kushan-era citadel and murals.
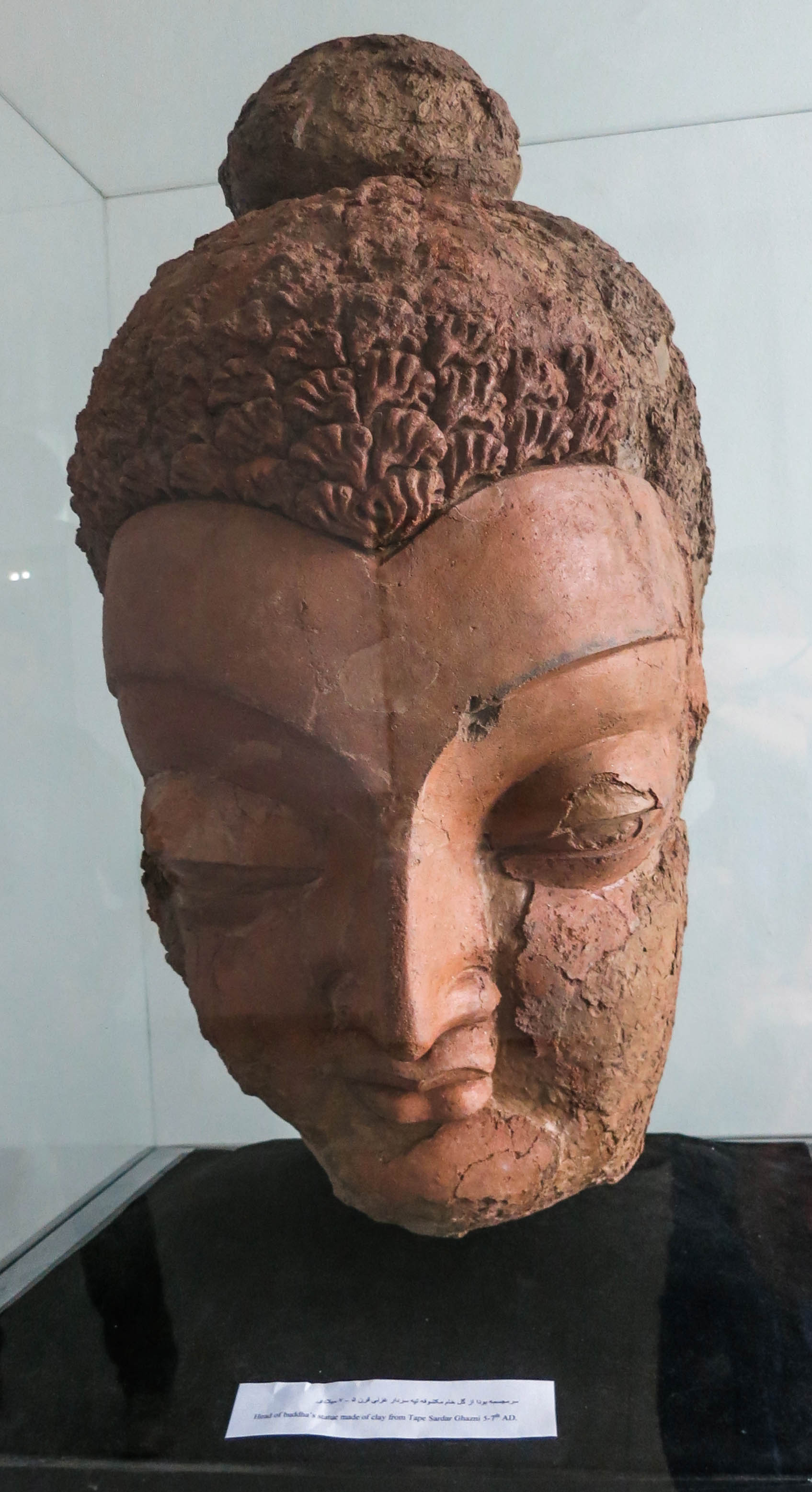

Tepe Sardar
Ancient Buddhist monastery with Hellenistic influence

Ghazni
Ancient city with diverse historical structures