Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Tillya Tepe is an archaeological site in northern Afghanistan, known for its astonishing hoard of artifacts commonly referred to as the Bactrian gold. Excavated in 1978, the site revealed six burial mounds containing the remains of five women and one man, adorned with approximately 20,600 ornaments made from gold, silver, and ivory. The findings date primarily to the 1st century BCE to the 1st century CE, reflecting a blend of cultural influences, including Scythian, Hellenistic, and local traditions. The presence of coins from Tiberius and other rulers suggests a vibrant interaction of different cultures and economies. Tillya Tepe's significance lies in its rich burial customs and the exquisite craftsmanship of its artifacts, shedding light on the complex socio-political and cultural dynamics of ancient Central Asia.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Tillya Tepe
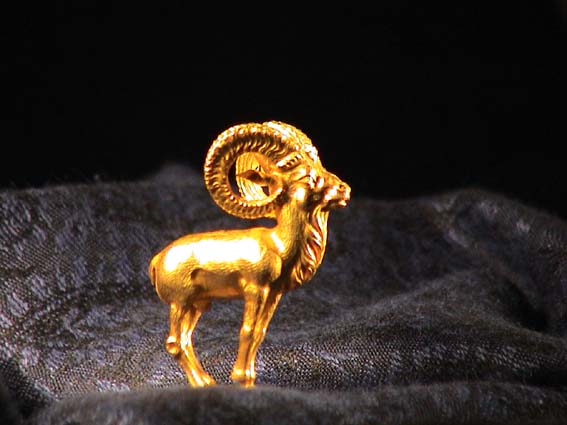
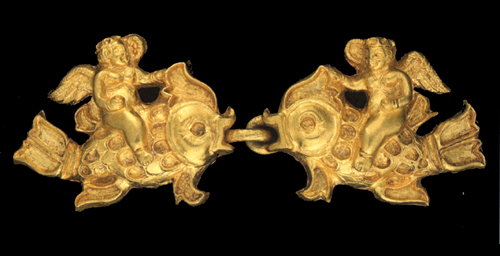


Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Afghanistan
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Afghanistan

Hadda, Afghanistan
Greco-Buddhist archaeological site with monasteries

Takht-e Rostam
Rock-cut Buddhist monastery with stupa.

Bimaran
Ancient stupas from 1st century BCE-CE
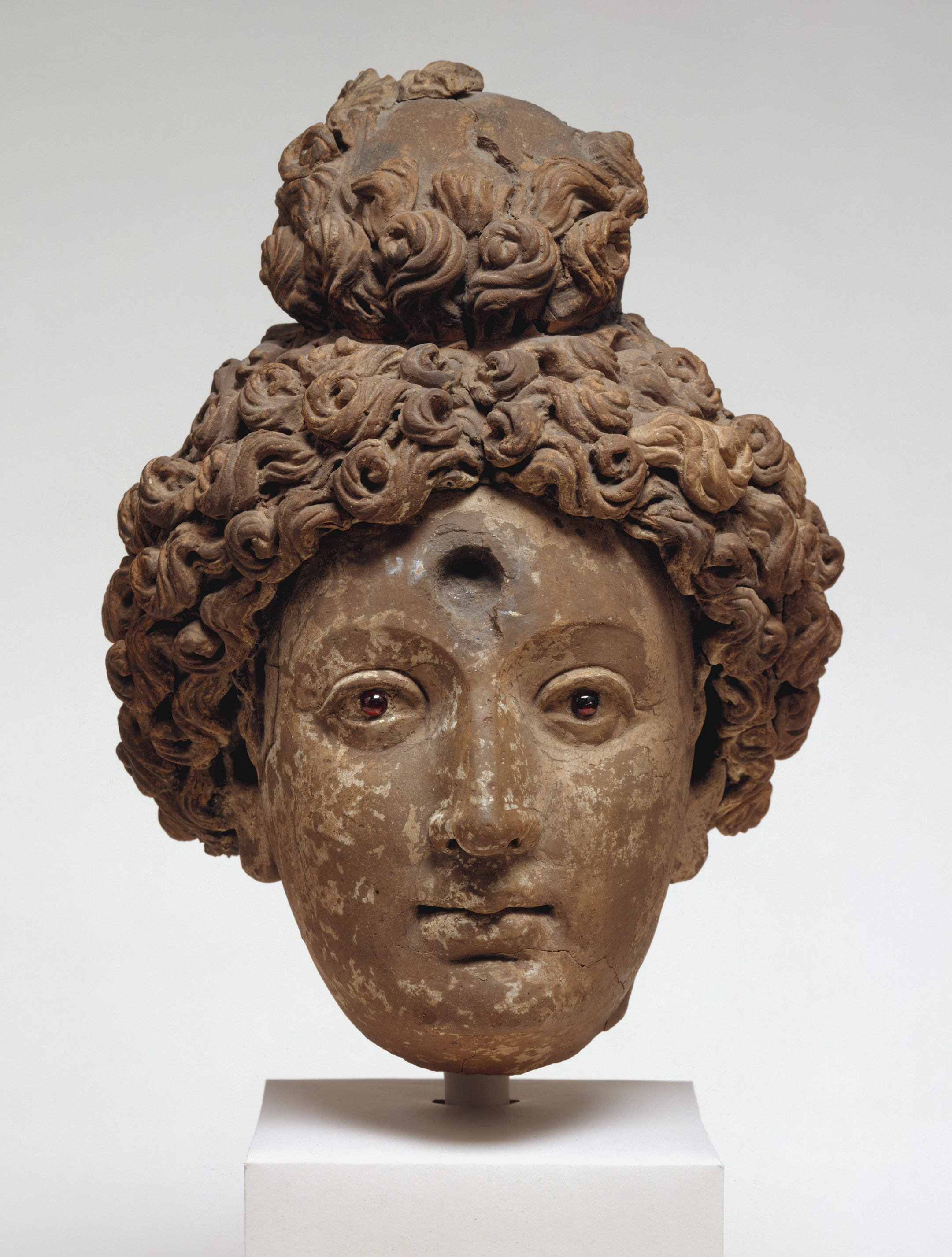

Tapa Shotor
Large Sarvastivadin monastery with Hellenistic influences
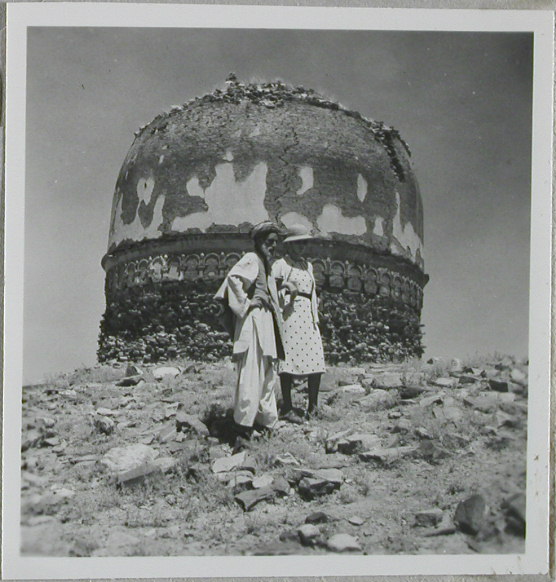

Shewaki
Ancient stupa turned Hindu temple site
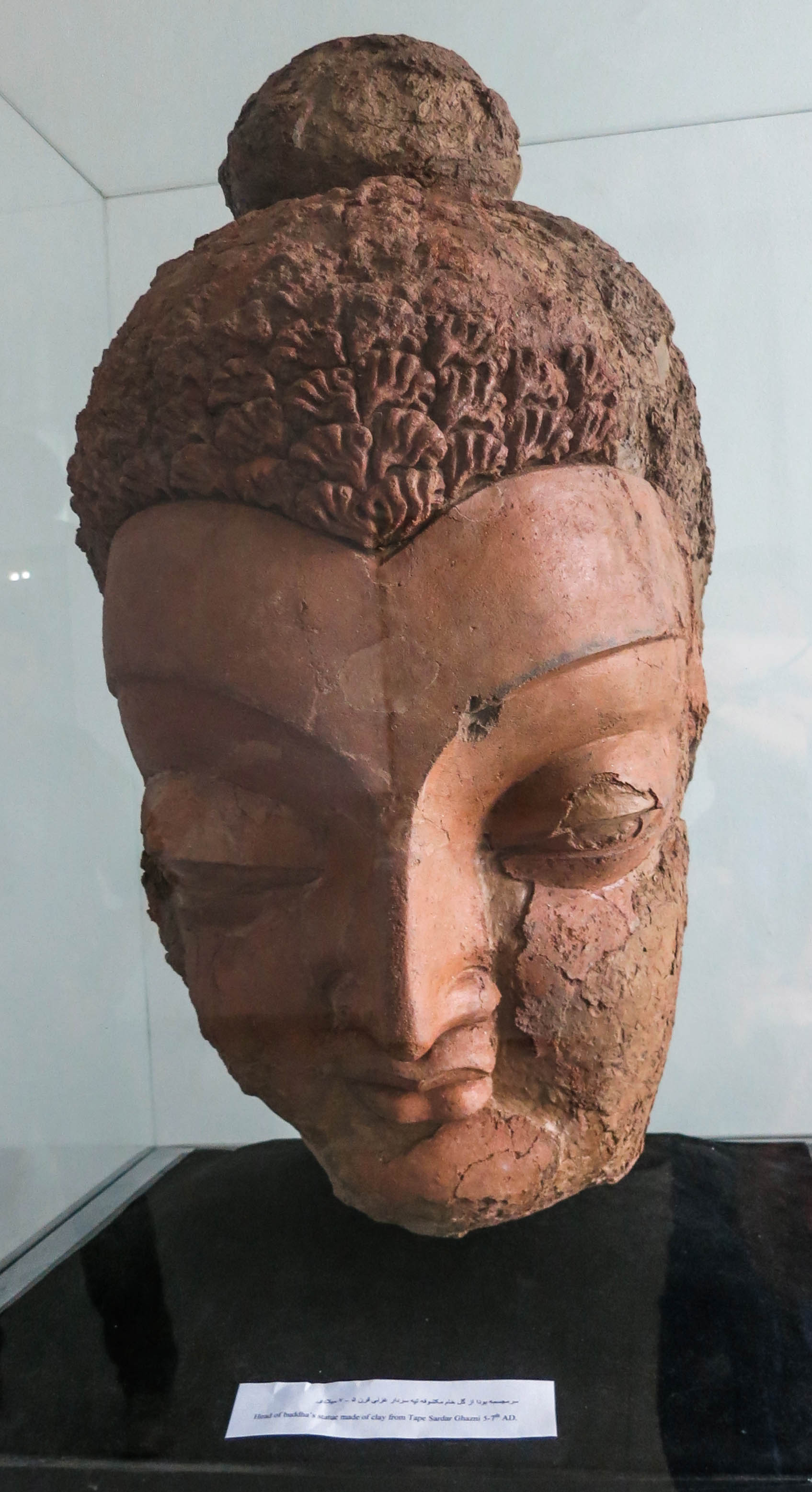

Tepe Sardar
Ancient Buddhist monastery with Hellenistic influence