Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
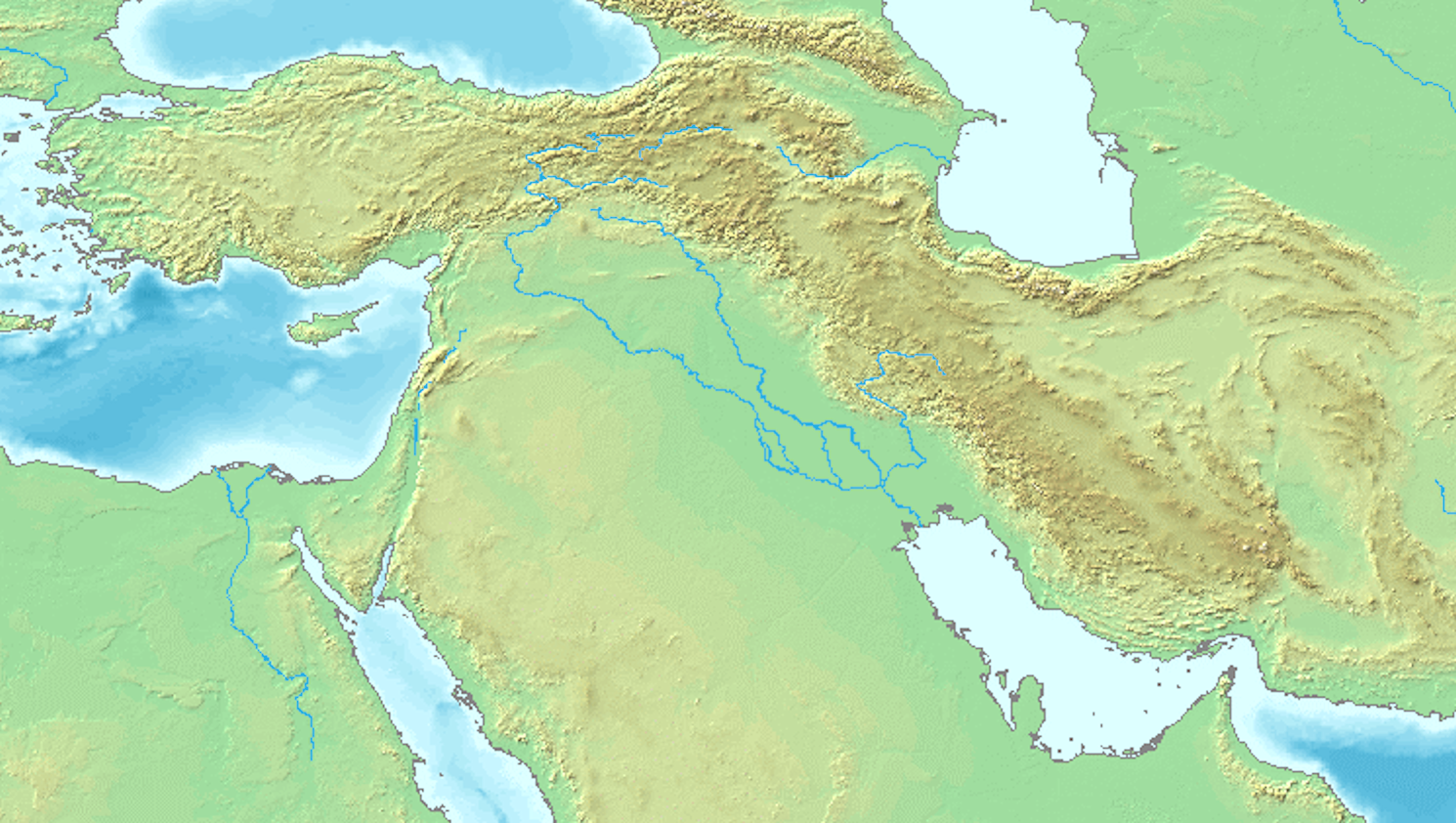
Location
About
Bad-tibira, an ancient Sumerian city, holds a significant place in early Mesopotamian history. Located between Ash Shatrah and Tell as-Senkereh in southern Iraq, it was a notable center during the Early Bronze Age. Known for its association with metallurgy, its name translates to 'Wall of the Copper Worker' or 'Fortress of the Smiths.' The city is mentioned in the Sumerian King List as one of the antediluvian cities and is linked to figures such as Dumuzid the Shepherd. Archaeologically, Bad-tibira is important for its religious and water management structures, including the Iturungal canal built by Ur-Nammu and temples dedicated to deities like Inanna and Kittum. The site encapsulates the political and cultural dynamics of Sumer, switching control between city-states like Larsa and Isin in later periods.
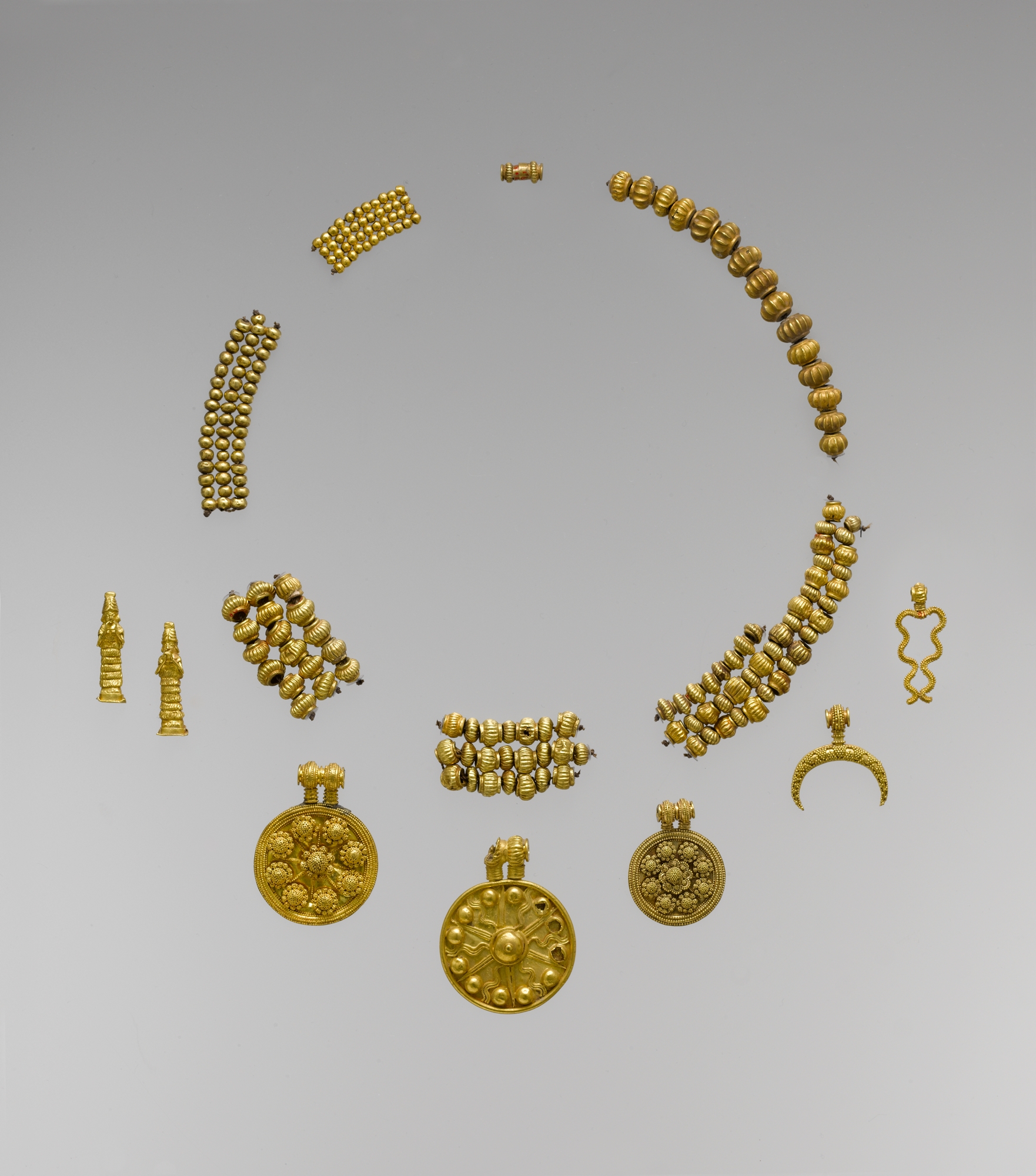
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Bad-tibira



Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Defensive Structures
Water Management Features
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Iraq
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Iraq

Nineveh
Ancient Assyrian city with monumental ruins
Tulul al-Baqarat
Ancient, multiperiod site with temple remains.
Qasr Shemamok
Ancient Near East site with diverse remains
Idu (city)
Ancient town with palace remnants

Dilbat
Ancient city with ziggurat and temple remains
Nippur
Ancient Sumerian city with significant temples