Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
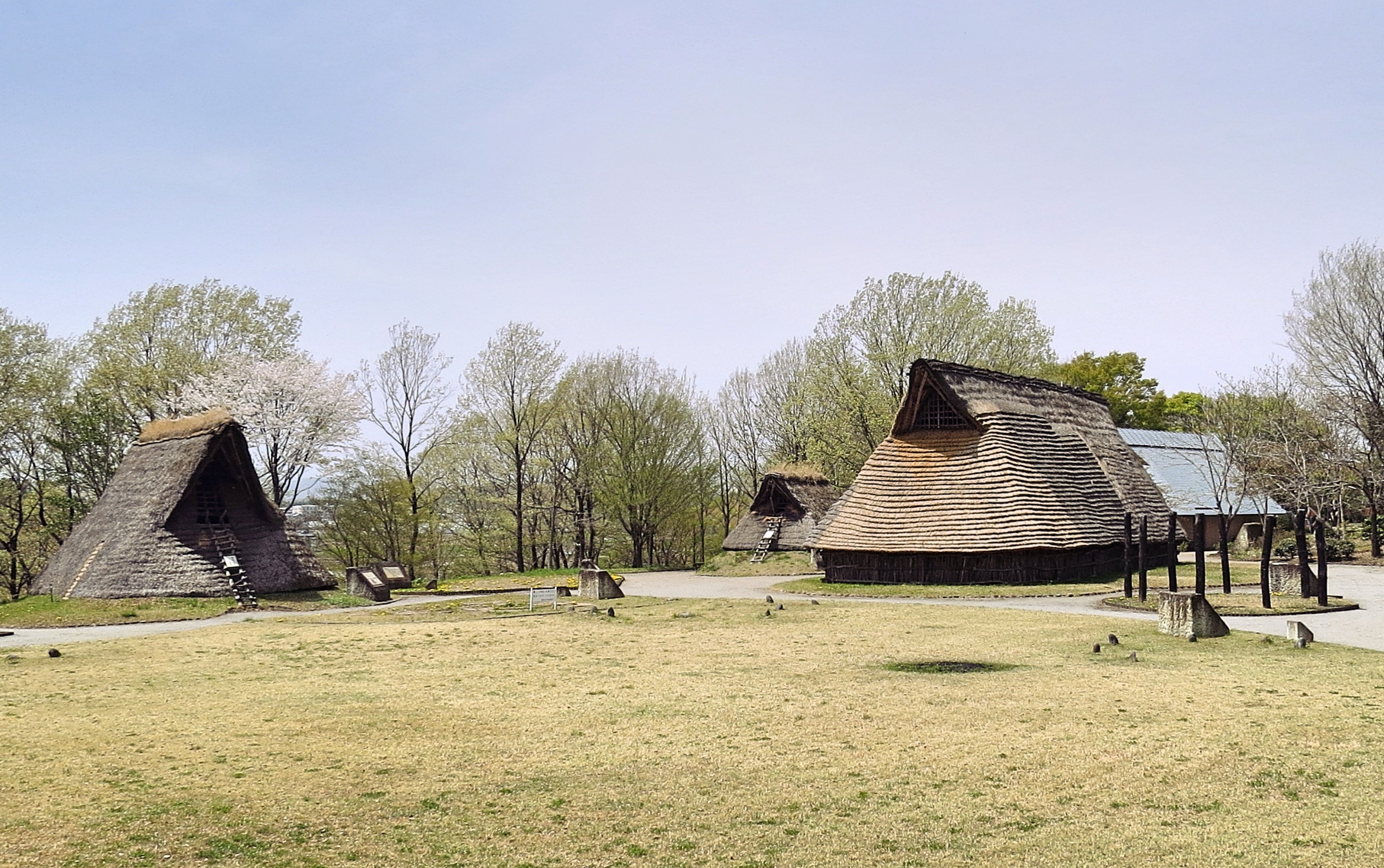
The Sengo ruins, located in Fujinomiya, Shizuoka, Japan, are a significant archaeological site dating back to the early through mid-Jōmon period, around 4000 BCE. Situated at the southeastern foot of Mount Fuji, the site includes the remains of a settlement featuring twenty pit dwellings arranged around a central 50-meter plaza. These dwellings, varying in size from three to 7.3 meters in diameter, suggest a community of considerable size. The presence of overlapping foundations indicates a history of rebuilding over time. The discovery of Jōmon pottery shards and surrounding stone circles further enhances the site's importance in understanding the cultural practices of the Jōmon period. The site's preservation under volcanic ash from Mount Fuji's eruptions provides a unique window into the prehistoric life and environmental conditions of ancient Japan.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Sengo ruins

Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Environmental and Natural Features
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Japan
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Japan

Sannai-Maruyama Site
Large Jōmon period settlement ruins

Mawaki Site
Large Jōmon period settlement site

Tochibaraiwakage ruins
Jōmon period cave dwelling in Nagano, Japan.

Yosekuraiwakage Site
Jōmon period rock shelter with artifacts

Negoyadai Site
Jōmon period settlement with necropolis
Shimofuda Site
Late Jōmon settlement with ritual site