Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Time Periods
Paleolithic
Mesolithic
Neolithic
Chalcolithic
Bronze Age
Iron Age
Classical Period
Post-Classical Period
Early Modern Period
Industrial Period
Contemporary Period
Location
About
Sanam, located near the Nile River in Sudan, represents a significant archaeological site from the Napatan Period, the zenith of the Kushite Empire between 800 BCE and 300 BCE. The site comprises the remnants of a town widely believed to be Napata, the Kushite capital. Excavations conducted in the early 20th century by Francis Llewellyn Griffith uncovered a poorly preserved temple and a structure termed as a treasury, alongside a vast cemetery. The temple, attributed to King Taharqo, with enhancements by King Aspelta, signifies the religious and cultural developments of the period. The cemetery provides rare insights into the lives of common people during the Napatan Period. Sanam offers a crucial window into the socio-political and religious landscape of ancient Kush, highlighting its significance within the broader context of African archaeology.
Gallery
Explore photographs of ancient structures, artifacts, and archaeological excavations at Sanam, Sudan
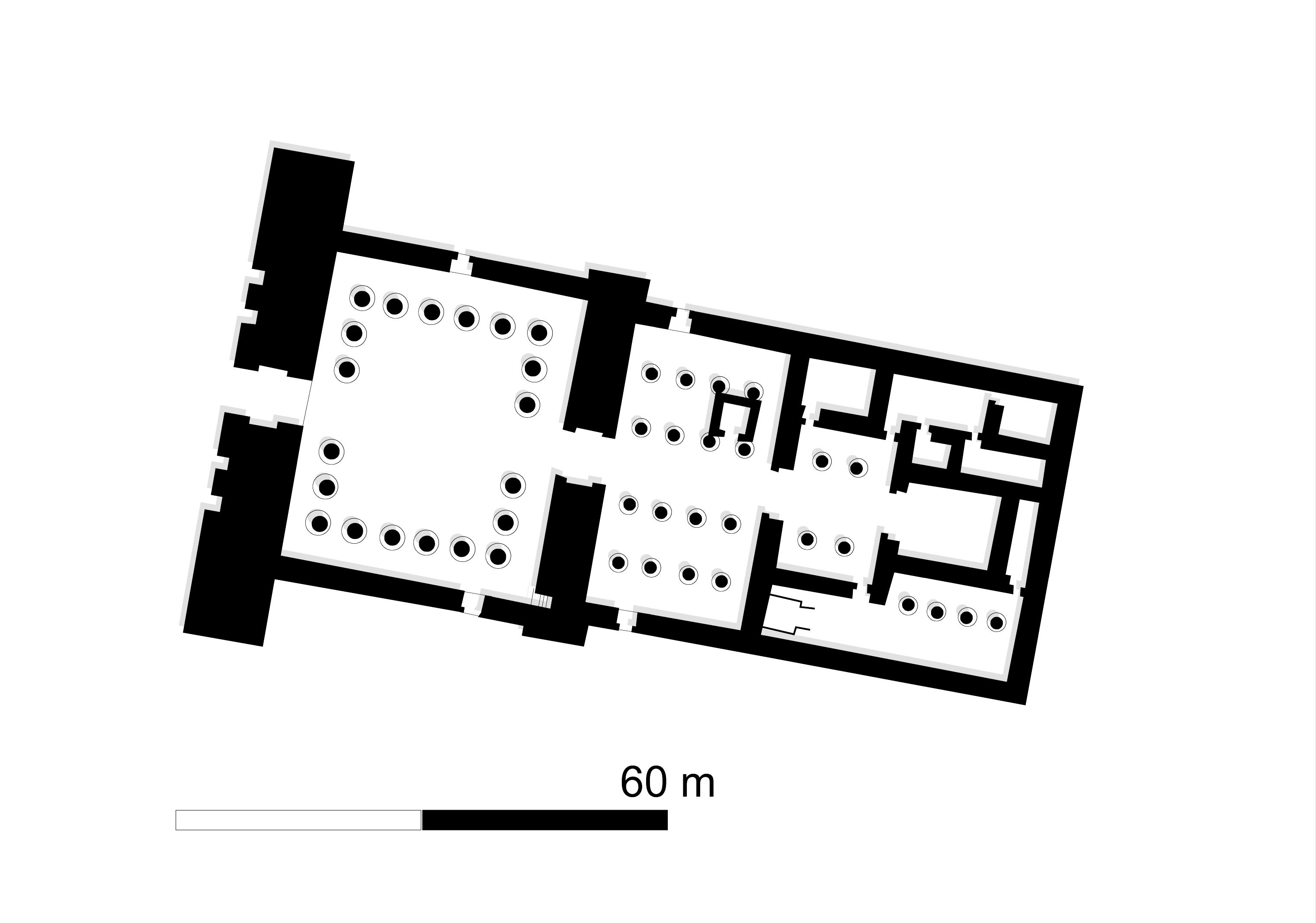
Archaeological Features
Explore the unique architectural and cultural elements found at this historical site
Burial and Funerary Structures
Religious and Ritual Structures
Domestic and Habitation Structures
Historical Timeline
Journey through time and discover key events in this site's archaeological history
Plan Your Visit
Details
- Country
- Sudan
- Source
- Wikipedia
More Sites in Sudan
Soleb
Ancient temple and necropolis in Nubia.
Faras
Underwater city with Christian cathedral art.

Jebel Barkal
Mesa with temples and pyramids in Sudan.

Semna (Nubia)
Middle Kingdom Egyptian fortresses in Nubia
Basa, Sudan
Decayed Meroitic temple with lion sculptures

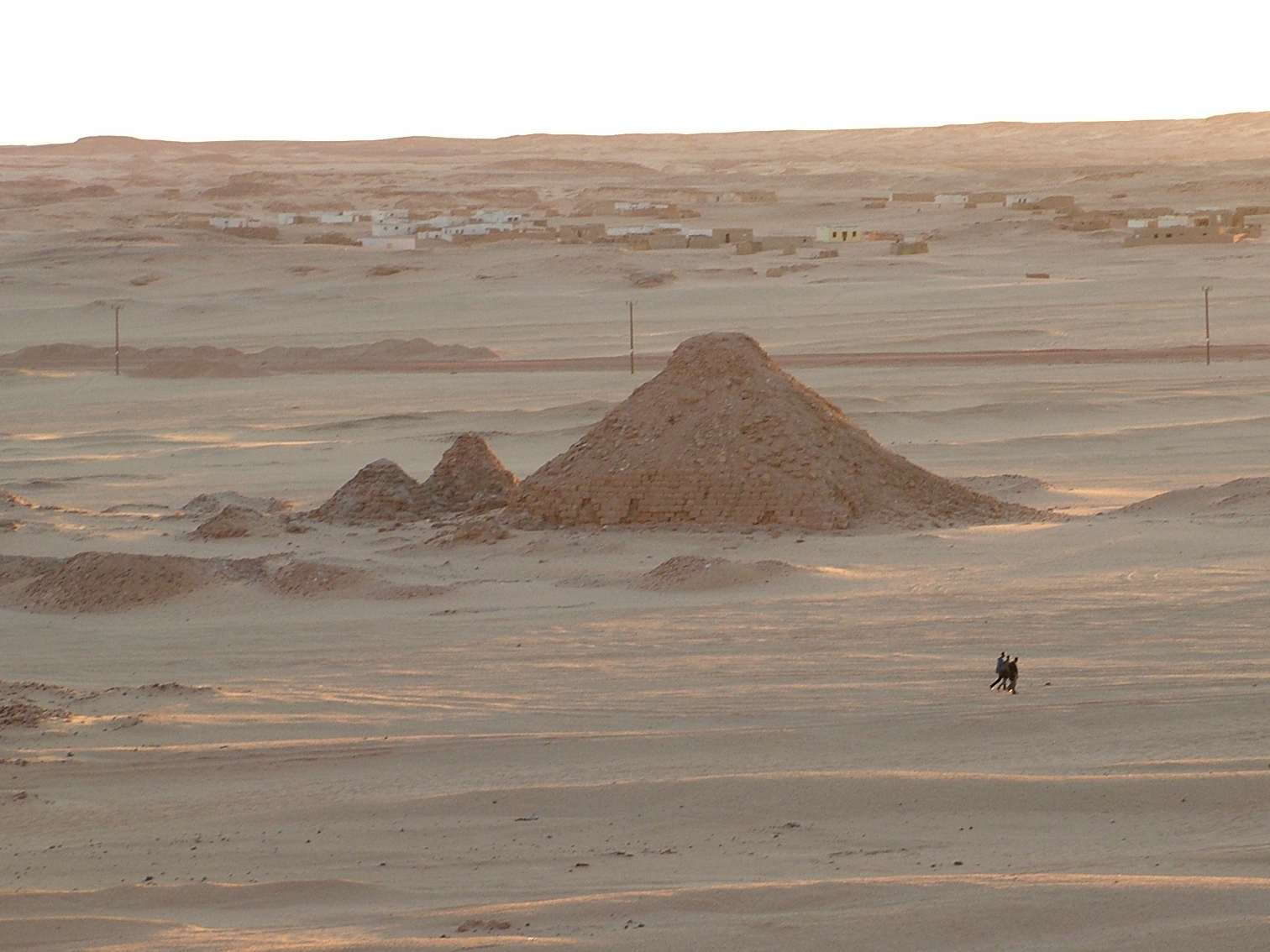
Nuri
Napatan burial site with pyramids in Sudan.